一、整体操作
①打开目录文件:opendir
②读取目录项:readdir
③关闭目录文件:closedir
注意:所需要用到的头文件
#ifndef __HEAD_H__ //防止头文件被重复定义
#define __HEAD_H__//防止头文件被重复定义
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <time.h>
#endif//防止头文件被重复定义
二、opendir/closedir
opendir
①函数原型:DIR *opendir(const char *name);
②功能:打开目录获得一个目录流指针
③函数参数:name:目录文件的路径
④返回值:成功返回目录流指针,失败返回NULL
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
DIR *dp = NULL;
dp = opendir(".");//打开'.'
if (NULL == dp)
{
perror("fail to opendir");
return -1;
}
}2.closedir
①函数原型:int closedir(DIR *dirp);
②功能:关闭目录流
③函数参数:dirp:目录流指针
④返回值:成功返回0 ,失败返回-1
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
DIR *dp = NULL;
struct dirent *pp = NULL;
dp = opendir(".");
if (NULL == dp)
{
perror("fail to opendir");
return -1;
}
while (1)
{
pp = readdir(dp);
if (NULL == pp)
{
break;
}
if ('.' == pp->d_name[0])
{
continue;
}
printf("%s\n", pp->d_name);
}
closedir(dp); //关闭目录流
return 0;
}三、readdir
①函数原型:struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp);
②功能:读取目录中下一个目录项的信息
③函数参数:dirp:目录流指针
④返回值:成功返回目录项结构体信息,失败返回NULL
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
DIR *dp = NULL;
struct dirent *pp = NULL;
dp = opendir(".");
if (NULL == dp)
{
perror("fail to opendir");
return -1;
}
while (1)
{
pp = readdir(dp); //读取目录中下一个目录项的信息
if (NULL == pp)
{
break;
}
if ('.' == pp->d_name[0]) //不输出隐藏文件
{
continue;
}
printf("%s\n", pp->d_name);
}
closedir(dp);
return 0;
}输出结果:
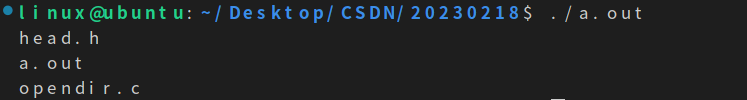
四、mkdir
①函数原型:int mkdir(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
②功能:创建一个目录文件
③函数参数:pathname:目录的路径 mode:目录的权限
④返回值:成功返回0 失败返回-1
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
mkdir("aaa",0664);//创建一个aaa的文件,基于权限为0664
return 0;
}创建结果:

五、rmdir
①函数原型:int rmdir(const char *pathname);
②功能:删除空目录
③函数参数:pathname:删除目录路径
④返回值:成功返回0 ,失败返回-1
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
rmdir("aaa"); //将上一步mkdir所创建的aaa文件删除
return 0;
}六、getcwd
①函数原型:char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size);
②功能:获得当前工作目录的绝对路径
③函数参数:buf:存放路径字符串空间首地址 size:最多存放字符串的个数
④返回值:成功返回字符串空间首地址,失败返回NULL
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
char tmp[4096] = {0};
getcwd(tmp, sizeof(tmp));//获得当前工作目录的绝对路径,存放到tmp当中
printf("%s\n",tmp);
return 0;
}输出结果:

七、chdir
①函数原型:int chdir(const char *path);
②功能:切换当前的工作路径
③函数参数:path:要切换到的路径
④返回值:成功返回0 ,失败返回-1
#include "head.h"
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
char tmp[4096] = {0};
getcwd(tmp, sizeof(tmp));//获得当前工作目录的绝对路径,存放到tmp当中
printf("%s\n",tmp);//输出当前绝对路径
printf("================================\n");
chdir("..");//返回上一级目录
getcwd(tmp, sizeof(tmp));//获得上一级工作目录的绝对路径,存放到tmp当中
printf("%s\n",tmp);//输出上一级工作目录的绝对路径
return 0;
}输出结果:






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








