多线程入门理解:多线程实际上并不是多个线程同时执行,只是因为CPU处理速度太快了,可以非常快地来回在各个线程之间切换执行,以至于我们人裸眼根本察觉不到它在各个线程之间不停地切换,感觉好像是同时运行一样[1]。线程函数中经常会使用Sleep(t)函数进行CPU使用权的轮换,它表示本线程在未来t毫秒内暂停执行(交出CPU使用权),t毫秒后会重新参与竞争。Sleep(0)的作用是立刻让操作系统重新分配各线程对CPU的使用权[2]。
网上有个流传甚广的多线程示例代码[3]:
/*
编译器设置:项目属性->配置属性->C\C++->代码生成->运行库,选择MT或MTD
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string> // for STL string class
#include <windows.h> // for HANDLE
#include <process.h> // for _beginthread()
using namespace std;
class ThreadX
{
private:
int loopStart;
int loopEnd;
int dispFrequency;
public:
string threadName;
ThreadX( int startValue, int endValue, int frequency )
{
loopStart = startValue;
loopEnd = endValue;
dispFrequency = frequency;
}
static unsigned __stdcall ThreadStaticEntryPoint(void * pThis)
{
ThreadX * pthX = (ThreadX*)pThis; // 参数传入
pthX->ThreadEntryPoint(); // now call the true entry-point-function
return 1; // the thread exit code
}
void ThreadEntryPoint()
{
for (int i = loopStart; i <= loopEnd; ++i)
{
if (i % dispFrequency == 0)
{
printf( "%s: i = %d\n", threadName.c_str(), i );
}
Sleep(0);
}
printf( "%s thread terminating\n", threadName.c_str() );
}
};
int main()
{
ThreadX * o1 = new ThreadX( 0, 1000, 50);
HANDLE hth1;
unsigned uiThread1ID;
hth1 = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex( NULL, // security
0, // stack size
ThreadX::ThreadStaticEntryPoint,
o1, // 参数列表
CREATE_SUSPENDED, // 该线程暂时挂起,指导遇到ResumeThread();如果为NULL,表示立刻执行,无需/ResumeThread语句
&uiThread1ID );
if ( hth1 == 0 )
printf("Failed to create thread 1\n");
DWORD dwExitCode;
GetExitCodeThread( hth1, &dwExitCode ); // should be STILL_ACTIVE = 0x00000103 = 259
printf( "initial thread 1 exit code = %u\n", dwExitCode );
o1->threadName = "t1";
ThreadX * o2 = new ThreadX( 0, 1000, 50 );
HANDLE hth2;
unsigned uiThread2ID;
hth2 = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex( NULL, // security
0, // stack size
ThreadX::ThreadStaticEntryPoint,
o2, // arg list
CREATE_SUSPENDED, // 该线程暂时挂起,直到遇到ResumeThread();如果为NULL,表示立刻执行,无需/ResumeThread语句
&uiThread2ID );
if ( hth2 == 0 )
printf("Failed to create thread 2\n");
GetExitCodeThread( hth2, &dwExitCode ); // should be STILL_ACTIVE = 0x00000103 = 259
printf( "initial thread 2 exit code = %u\n", dwExitCode );
o2->threadName = "t2";
ResumeThread( hth1 ); // 线程开始执行
ResumeThread( hth2 );
//WaitFor语句的作用:等待线程运行结束,INFINITE表示一直等待,直到线程自动结束。
//如果没有WaitFor语句,会导致该线程未执行或未执行完毕就被终止,因为主线程终止了。
WaitForSingleObject( hth1, INFINITE );
WaitForSingleObject( hth2, INFINITE );
GetExitCodeThread( hth1, &dwExitCode );
printf( "thread 1 exited with code %u\n", dwExitCode );
GetExitCodeThread( hth2, &dwExitCode );
printf( "thread 2 exited with code %u\n", dwExitCode );
CloseHandle( hth1 );
CloseHandle( hth2 );
delete o1;
o1 = NULL;
delete o2;
o2 = NULL;
printf("Primary thread terminating.\n");
return 0;
}运行结果:
关于该程序的几点理解:
1主线程(main)创建了两个线程函数,分别用来打印数字。
2线程创建函数_beginthreadx的第四个参数CREATE_SUSPENDED必须与ResumeThread配对使用,如果CREATE_SUSPENDED改为NULL,则不需要ResumeThread语句。
3被创建的两个线程运行结束后才会返回主线执行printf("Primary thread terminating.\n");如果注释WaitForSingleObject语句,会导致两个子线程未执行或未执行完毕就被终止,因为主线程可能提前终止了。
4在创建线程函数时,应该尽量使用_beginthreadx()而不是CreateThread(),至于原因请参考[].
上面一个示例不牵涉线程间同步互斥问题。下面的示例代码利用CS关键段可以有效解决线程间互斥问题[4]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <process.h>
#include <windows.h>
long g_nNum;
unsigned int __stdcall Fun(void *pPM);
const int THREAD_NUM = 10;
//关键段变量声明
CRITICAL_SECTION g_csThreadParameter, g_csThreadCode;
int main()
{
//关键段初始化
InitializeCriticalSection(&g_csThreadParameter);
InitializeCriticalSection(&g_csThreadCode);
HANDLE handle[THREAD_NUM];
g_nNum = 0;
int i = 0;
while (i < THREAD_NUM)
{
EnterCriticalSection(&g_csThreadParameter);//进入子线程序号关键区域
handle[i] = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex(NULL, 0, Fun, &i, 0, NULL);
++i;
}
WaitForMultipleObjects(THREAD_NUM, handle, TRUE, INFINITE);
DeleteCriticalSection(&g_csThreadCode);
DeleteCriticalSection(&g_csThreadParameter);
return 0;
}
unsigned int __stdcall Fun(void *pPM)
{
int nThreadNum = *(int *)pPM;
LeaveCriticalSection(&g_csThreadParameter);//离开子线程序号关键区域
Sleep(50);//some work should to do
EnterCriticalSection(&g_csThreadCode);//进入各子线程互斥区域
g_nNum++;
Sleep(0);//some work should to do
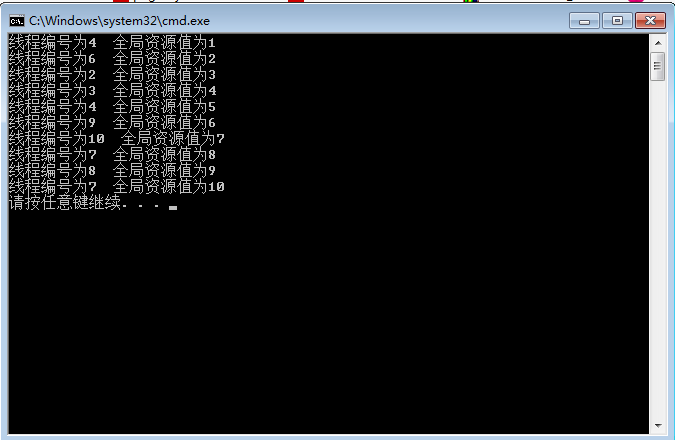
printf("线程编号为%d 全局资源值为%d\n", nThreadNum, g_nNum);
LeaveCriticalSection(&g_csThreadCode);//离开各子线程互斥区域
return 0;
}运行结果:
关于该程序的几点理解:
1主线程创建10个子线程,每个线程输出线程编号及全局变量值,理想输出应该是互不重复的数值。
2CS关键段总共包含始化化、销毁、进入和离开关键区域四个函数。关键段可以解决子线程互斥问题,但无法解决主线程与子线程同步问题,因为主线程可以多次通过EnterCriticalSection(&g_csThreadParameter)进入数据段(因为主线程拥有线程控制权,可以多次Enter)。
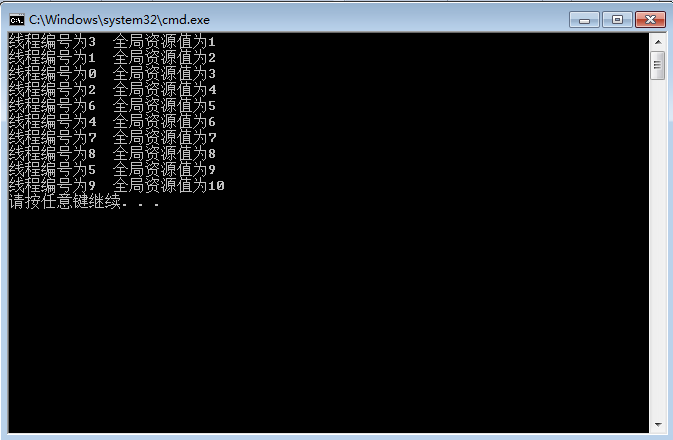
经典多线程问题通常设置一个事件和一个关键段。用事件处理主线程与子线程的同步,用关键段来处理各子线程间的互斥[5]:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <process.h>
#include <windows.h>
long g_nNum;
unsigned int __stdcall Fun(void *pPM);
const int THREAD_NUM = 10;
//事件与关键段
HANDLE g_hThreadEvent;
CRITICAL_SECTION g_csThreadCode;
int main()
{
//初始化事件和关键段 自动置位,初始无触发的匿名事件
g_hThreadEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, FALSE, FALSE, NULL);
InitializeCriticalSection(&g_csThreadCode);
HANDLE handle[THREAD_NUM];
g_nNum = 0;
int i = 0;
while (i < THREAD_NUM)
{
handle[i] = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex(NULL, 0, Fun, &i, 0, NULL);
WaitForSingleObject(g_hThreadEvent, INFINITE); //等待事件被触发
i++;
}
WaitForMultipleObjects(THREAD_NUM, handle, TRUE, INFINITE);
//销毁事件和关键段
CloseHandle(g_hThreadEvent);
DeleteCriticalSection(&g_csThreadCode);
return 0;
}
unsigned int __stdcall Fun(void *pPM)
{
int nThreadNum = *(int *)pPM;
SetEvent(g_hThreadEvent); //触发事件
Sleep(50);//some work should to do
EnterCriticalSection(&g_csThreadCode);
g_nNum++;
Sleep(0);//some work should to do
printf("线程编号为%d 全局资源值为%d\n", nThreadNum, g_nNum);
LeaveCriticalSection(&g_csThreadCode);
return 0;
}运行结果:
有关多线程详细技术可参考MoreWindows的”秒杀多线程”系列博文:http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/category/1115271
另外,Matlab提供Timer对象实现多线程编程,准确的说应该是多个线程按照被分配的时间片轮流执行,如果其中一个线程阻滞或挂掉了,那么其他线程就会受到影响无法继续运行,这种多线程属于应用程序级的多线程,严格说来算作伪多线程。C/C++的多线程属于操作系统级的,各线程虽然轮流获得CPU的使用权,但彼此有很强独立性,一个线程的阻滞不会影响其他线程运行。以上是我个人理解,如有不妥,请不吝指正!
参考:
[1]摘自黑马程序员:http://www.kuqin.com/networkprog/20111225/316672.html
[2] Sleep的详细理解:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_810c86000101aihm.html
[3]_beginthreadx创建多线程:http://blog.csdn.net/laoyang360/article/details/7720656
[4] CS解决多线程互斥:http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/7445233
[5]CS与event联合解决同步互斥:http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/7445233
[6]秒杀多线程系列文章:http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/category/1115271























 1492
1492











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








