前言:最近在看面向对象程序设计时,遇到了几个新鲜的设计模式于是查了查资料,最终把他搞明白了,还是很开心的。。。
桥接模式
桥接模式的定义是这样的:
1、GOF四人帮在《设计模式:可复用面向对象软件的基础》一书中是这样描述的(见下引用),现在听起来感觉云里雾里的,不要在这里纠结,我们接着往下。
将抽象部分和它的实现部分分离,使它们都可以独立的变化。简单粗暴的说,就是抽象对外提供调用的接口;对外隐瞒实现部分,在抽象中引用实现部分,从而实现抽象对实现部分的调用,而抽象中引用的实现部分可以在今后的开发过程中,切换成别的实现部分(《设计模式:可复用面向对象软件的基础》)
2、《大话设计模式》一书中是这样描述的(见下引用)
将抽象部分与他的实现部分分离,使他们都可以独立的变化(《大话设计模式》)
UML类图

实例
1、绘制红色的长方形、白色的圆形(Jelly Young:C++设计模式——桥接模式)
/*
** FileName : BridgePatternDemo
** Author : Jelly Young
** Date : 2013/12/4
** Description : More information (http://www.jellythink.com/)
** Author : Aidan Dai
** Date : 2015/11/20
** Description : 添加注释(http://www.jellythink.com/archives/132)
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
** 实现(颜料)
*/
class Implementor
{
public:
virtual void OperationImpl() = 0;
};
/*
** 具体实现(黄色颜料、绿色颜料、蓝色颜料)
*/
class ConcreteImpementor : public Implementor
{
public:
void OperationImpl()
{
cout << "OperationImpl" << endl;
}
};
/*
** 抽象(平面图形)
** 维护一个指向具体实现的指针(黄色颜料、绿色颜料、蓝色颜料)
*/
class Abstraction
{
public:
Abstraction(Implementor *pImpl) : m_pImpl(pImpl){}
virtual void Operation() = 0;
protected:
Implementor *m_pImpl;
};
/*
** 被提炼的抽象(圆形、正方形、长方形)
*/
class RedfinedAbstraction : public Abstraction
{
public:
RedfinedAbstraction(Implementor *pImpl) : Abstraction(pImpl){}
void Operation()
{
m_pImpl->OperationImpl();
}
};
int main(void)
{
Implementor *pImplObj = new ConcreteImpementor();
Abstraction *pAbsObj = new RedfinedAbstraction(pImplObj);
pAbsObj->Operation();
delete pImplObj;
pImplObj = NULL;
delete pAbsObj;
pAbsObj = NULL;
return 0;
}2、手机软件何时统一(《大话设计模式》)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Implementor{
public:
void virtual Operation() = 0;
};
class ConcreteImplementorA : public Implementor{
public:
void Operation(){
cout << "ConcreteImplementorA" << endl;
}
};
class ConcreteImplementorB : public Implementor{
public:
void Operation(){
cout << "ConcreteImplementorB" << endl;
}
};
class Abstraction{
public:
void SetImplementor(Implementor *implementor){
this->m_implementor = implementor;
}
void virtual Operator() = 0;
protected:
Implementor *m_implementor;
};
class RefinedAbstraction : public Abstraction{
public:
void Operator(){
this->m_implementor->Operation();
}
};
int main(void){
Abstraction *abstraction = new RefinedAbstraction();
Implementor *implementor1 = new ConcreteImplementorA();
abstraction->SetImplementor(implementor1);
abstraction->Operator();
Implementor *implementor2 = new ConcreteImplementorB();
abstraction->SetImplementor(implementor2);
abstraction->Operator();
delete abstraction;
abstraction = NULL;
delete implementor1;
implementor1 = NULL;
delete implementor2;
implementor2 = NULL;
return 0;
}3、自由切换家用电器开关(我给媳妇解释设计模式:第一部分(译文))
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Equipment{
public:
void virtual poweron(string switchName) = 0;
void virtual poweroff(string switchName) = 0;
};
class Fan :public Equipment{
public:
void poweron(string switchName){
cout << "poweron Fan by " << switchName << endl;
}
void poweroff(string switchName){
cout << "poweroff Fan by " << switchName << endl;
}
};
class Light :public Equipment{
public:
void poweron(string switchName){
cout << "poweron Light by " << switchName << endl;
}
void poweroff(string switchName){
cout << "poweroff Light by " << switchName << endl;
}
};
class Switch{
public:
Switch(Equipment *equipment){
this->m_equipment = equipment;
}
void virtual on() = 0;
void virtual off() = 0;
Equipment *m_equipment;
};
class NormalSwitch :public Switch{
public:
NormalSwitch(Equipment *equipment) :Switch(equipment){
this->m_switchName = "NormalSwitch";
}
void on(){
this->m_equipment->poweron(this->m_switchName);
}
void off(){
this->m_equipment->poweroff(this->m_switchName);
}
private:
string m_switchName;
};
class FancySwitch :public Switch{
public:
FancySwitch(Equipment *equipment) :Switch(equipment){
this->m_switchName = "FancySwitch";
}
void on(){
this->m_equipment->poweron(this->m_switchName);
}
void off(){
this->m_equipment->poweroff(this->m_switchName);
}
private:
string m_switchName;
};
int main(void){
Equipment *equipment1 = new Fan();
Equipment *equipment2 = new Light();
Switch *equipmentSwitch1 = new NormalSwitch(equipment1);
Switch *equipmentSwitch2 = new FancySwitch(equipment2);
Switch *equipmentSwitch3 = new NormalSwitch(equipment1);
Switch *equipmentSwitch4 = new FancySwitch(equipment2);
equipmentSwitch1->on();
equipmentSwitch1->off();
equipmentSwitch2->on();
equipmentSwitch2->off();
equipmentSwitch3->on();
equipmentSwitch3->off();
equipmentSwitch4->on();
equipmentSwitch4->off();
delete equipment1;
equipment1 = NULL;
delete equipment2;
equipment2 = NULL;
delete equipmentSwitch1;
delete equipmentSwitch2;
delete equipmentSwitch3;
delete equipmentSwitch4;
equipmentSwitch1 = NULL;
equipmentSwitch2 = NULL;
equipmentSwitch3 = NULL;
equipmentSwitch4 = NULL;
return 0;
}总结
is a 和 has a
1、理解继承:
- 对象的继承关系是在编译时就定义好了,所以无法再无法再运行时改变从父类继承的实现。子类的实现与它的父类有非常紧密的的依赖关系,以至于父类的实现中的任何变化必然会导致子类发生变化。当你需要复用子类时,如果继承下来的实现不适合解决新的问题,则父类必须重写或被其他更适合的类替换。这种依赖关系限制了灵活性并最终限制了复用性。
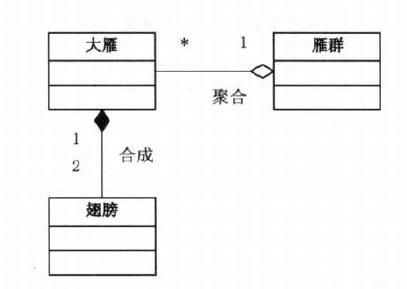
2、理解合成/聚合复用原则
- 合成/聚合复用原则:聚合表示一种弱的“拥有”关系,体现的是A对象可以包含B对象,但B对象不是A对象的一部分;合成则是一种强的“拥有”关系,体现了严格的部分和整体的关系,部分和整体的生命周期是一样的[DRE]。
就像大雁、翅膀和雁群的关系:
3、降低代码耦合度
4、通过实例不断的运用
结束语:
梦想还是要有的,万一实现了了呢!






















 4645
4645

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








