在工作中偶尔会遇到SPI不够用的情况,而我们又要去使用SPI通信协议,此时就需要我们自己去模拟SPI通信协议。我们知道SPI通信协议有四种模式,它们分别如下所示:
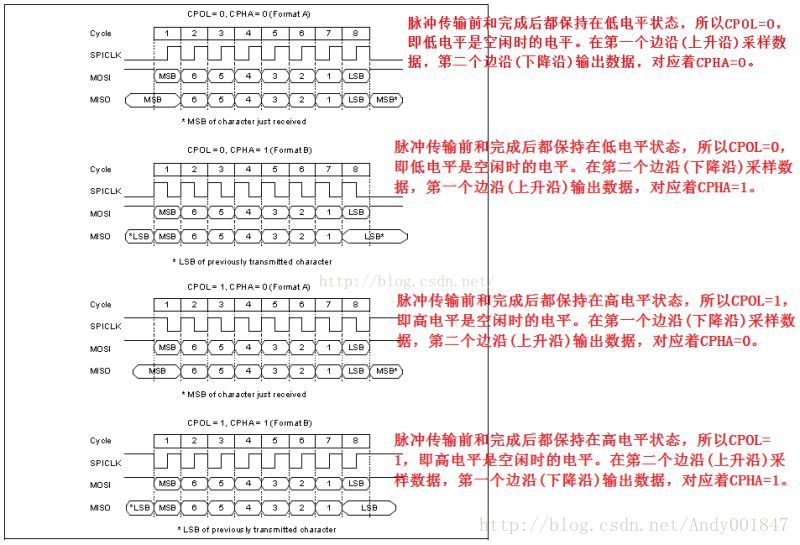
下面是我基于ATSAM4SD16B芯片在Atmel Studio上用普通GPIO模拟的SPI通信协议的代码:
#include "ioport.h"
#include "pio.h"
#include "delay.h"
#include "SAM4S_FSA.h"
#include <assert.h>
// Define 4 SPI pins
#define CS IOPORT_CREATE_PIN(PIOA, 8)
#define SCLK IOPORT_CREATE_PIN(PIOA, 7)
#define MOSI IOPORT_CREATE_PIN(PIOA, 23)
#define MISO IOPORT_CREATE_PIN(PIOA, 20)
#define SPIDelay delay_us(1)
// Define SPI communication mode
typedef enum SPIMode
{
Mode_1, /* Clock Polarity is 0 and Clock Phase is 0 */
Mode_2, /* Clock Polarity is 0 and Clock Phase is 1 */
Mode_3, /* Clock Polarity is 1 and Clock Phase is 0 */
Mode_4, /* Clock Polarity is 1 and Clock Phase is 1 */
}SPIMode;
// Define SPI type
typedef enum SPIType
{
SPIMaster,
SPISlave,
}SPIType;
// Define SPI attribute
typedef struct SpiStruct
{
unsigned int ui_CS;
unsigned int ui_SCLK;
unsigned int ui_MOSI;
unsigned int ui_MISO;
SPIMode spiMode;
SPIType spiType;
}Spi_t;
// Function prototypes
void v_SPIInitSimulate(Spi_t* p_Spi);
void v_CSIsEnableSimulate(Spi_t* p_Spi, int i_IsEnable);
void v_SPIWriteSimulate(Spi_t* p_Spi, unsigned char* puc_Data, int i_DataLength);
void v_SPIReadSimulate(Spi_t* p_Spi, unsigned char* puc_Data, int i_DataLength);
// Define SPI pins
Spi_t Spi_0 =
{
.ui_CS = CS,
.ui_SCLK = SCLK,
.ui_MOSI = MOSI,
.ui_MISO = MISO,
.spiMode = Mode_1,
.spiType = SPIMaster,
};
/*
Brief: SPI protocol initiate
Input: p_Spi, which spi use
Output: None
Return: None
Author: Andy Lai
*/
void v_SPIInitSimulate(Spi_t* p_Spi)
{
assert(p_Spi != NULL);
if(p_Spi->spiMode == SPIMaster)
{
ioport_set_pin_dir(p_Spi->ui_CS, IOPORT_DIR_OUTPUT);
ioport_set_pin_dir(p_Spi->ui_SCLK, IOPORT_DIR_OUTPUT);
ioport_set_pin_dir(p_Spi->ui_MOSI, IOPORT_DIR_OUTPUT);
ioport_set_pin_dir(p_Spi->ui_MISO, IOPORT_DIR_INPUT);
}
else
{
ioport_set_pin_dir(p_Spi->ui_CS, IOPORT_DIR_INPUT);
ioport_set_pin_dir(p_Spi->ui_SCLK, IOPORT_DIR_INPUT);
ioport_set_pin_dir(p_Spi->ui_MOSI, IOPORT_DIR_INPUT);
ioport_set_pin_dir(p_Spi->ui_MISO, IOPORT_DIR_OUTPUT);
}
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_CS);
switch(p_Spi->spiMode)
{
case Mode_1:
case Mode_2:
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
break;
case Mode_3:
case Mode_4:
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
break;
}
}
/*
Brief: CS low level signal enable and high level signal disable
Input: (1)p_Spi, which spi use
(2)i_IsEnable, Chip select(Slave select) enable flag
Output: None
Return: None
Author: Andy Lai
*/
void v_CSIsEnableSimulate(Spi_t* p_Spi, int i_IsEnable)
{
assert(p_Spi != NULL);
if(i_IsEnable)
{
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_CS);
}
else
{
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_CS);
}
}
/*
Brief: Use SPI to write a byte data
Input: (1)p_Spi, which spi use
(2)uc_Bt, write byte data
Output: None
Return: None
Author: Andy Lai
*/
static void v_SPIWriteByte(Spi_t* p_Spi, unsigned char uc_Bt)
{
int i = 0;
assert(p_Spi != NULL);
switch(p_Spi->spiMode)
{
case Mode_1: /* Clock Polarity is 0 and Clock Phase is 0 */
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
for(i = 7; i >= 0; i--)
{
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
SPIDelay;
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
if(uc_Bt & (1 << i))
{
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_MOSI);
}
else
{
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_MOSI);
}
SPIDelay;
}
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
break;
case Mode_2: /* Clock Polarity is 0 and Clock Phase is 1 */
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
for(i = 7; i >= 0; i--)
{
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
if(uc_Bt & (1 << i))
{
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_MOSI);
}
else
{
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_MOSI);
}
SPIDelay;
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
SPIDelay;
}
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
break;
case Mode_3: /* Clock Polarity is 1 and Clock Phase is 0 */
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
for(i = 7; i >= 0; i--)
{
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
if(uc_Bt & (1 << i))
{
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_MOSI);
}
else
{
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_MOSI);
}
SPIDelay;
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
SPIDelay;
}
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
break;
case Mode_4: /* Clock Polarity is 1 and Clock Phase is 1 */
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
for(i = 7; i >= 0; i--)
{
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
if(uc_Bt & (1 << i))
{
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_MOSI);
}
else
{
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_MOSI);
}
SPIDelay;
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
SPIDelay;
}
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
/*
Brief: Use SPI protocol to write data
Input: (1)p_Spi, which spi use
(2)puc_Data, write data string
(3)i_DataLength, write data length
Output: None
Return: None
Author: Andy Lai
*/
void v_SPIWriteSimulate(Spi_t* p_Spi, unsigned char* puc_Data, int i_DataLength)
{
int i = 0;
assert(p_Spi != NULL);
assert(puc_Data != NULL);
assert(i_DataLength > 0);
v_CSIsEnableSimulate(p_Spi, 1);
delay_us(8);
// Write data
for(i = 0; i < i_DataLength; i++)
{
v_SPIWriteByte(p_Spi, puc_Data[i]);
}
delay_us(8);
v_CSIsEnableSimulate(p_Spi, 0);
}
/*
Brief: Read a byte data from SPI
Input: p_Spi, which spi use
Output: None
Return: Read data
Author: Andy Lai
*/
static unsigned char uc_SPIReadByte(Spi_t* p_Spi)
{
int i = 0;
unsigned char uc_ReadData = 0;
assert(p_Spi != NULL);
switch(p_Spi->spiMode)
{
case Mode_1: /* Clock Polarity is 0 and Clock Phase is 0 */
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
SPIDelay;
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
uc_ReadData = uc_ReadData << 1;
uc_ReadData |= pio_get_pin_value(p_Spi->ui_MISO);
SPIDelay;
}
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
break;
case Mode_2: /* Clock Polarity is 0 and Clock Phase is 1 */
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
SPIDelay;
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
uc_ReadData = uc_ReadData << 1;
uc_ReadData |= pio_get_pin_value(p_Spi->ui_MISO);
SPIDelay;
}
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
break;
case Mode_3: /* Clock Polarity is 1 and Clock Phase is 0 */
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
SPIDelay;
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
uc_ReadData = uc_ReadData << 1;
uc_ReadData |= pio_get_pin_value(p_Spi->ui_MISO);
SPIDelay;
}
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
break;
case Mode_4: /* Clock Polarity is 1 and Clock Phase is 1 */
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
pio_set_pin_low(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
SPIDelay;
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
uc_ReadData = uc_ReadData << 1;
uc_ReadData |= pio_get_pin_value(p_Spi->ui_MISO);
SPIDelay;
}
pio_set_pin_high(p_Spi->ui_SCLK);
break;
default:
break;
}
return uc_ReadData;
}
/*
Brief: Use SPI to read data
Input: (1)p_Spi, which SPI use;
(2)i_DataLength, the length of data that need to read
Output: puc_Data, need to get data
Return: None
Author: Andy Lai
*/
void v_SPIReadSimulate(Spi_t* p_Spi, unsigned char* puc_Data, int i_DataLength)
{
int i = 0;
assert(p_Spi != NULL);
assert(i_DataLength > 0);
v_CSIsEnableSimulate(p_Spi, 1);
delay_us(8);
// Read data
for(i = 0; i < i_DataLength; i++)
{
puc_Data[i] = uc_SPIReadByte(p_Spi);
}
delay_us(8);
v_CSIsEnableSimulate(p_Spi, 0);
}参考博客:http://blog.csdn.net/yangzheng_yz/article/details/50470577
























 968
968

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








