接口Executor仅仅是一种规范,是一种声明,是一种定义,并没有实现任何的功能,所以大多数的情况下,需要使用接口的实现类来完成指定的功能,比如ThreadPoolExecutor类就是Executor的实现类,但ThreadPoolExecutor在使用上并不是那么方便,在实例化时需要传入很多歌参数,还要考虑线程的并发数等与线程池运行效率有关的参数,所以官方建议使用Executors工程类来创建线程池对象。
Executors工厂类的结构如下图所示:
类Executors中的方法如下图所示:
TP_1:使用newCachedThreadPool()方法创建无界线程池
使用Executors类的newCachedThreadPool()方法创建的是无界线程池,可以进行线程自动回收。所谓的“无界线程池”就是池中存放线程个数是理论上的Integer.MAX_VALUE最大值。
创建实验用的项目Executors_1,类ThreadPool2NewCachedThreadPoolTest.java如下:
package com.yc.semephore_7;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadPool2NewCachedThreadPoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
executorService.execute(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("ThreadA begin:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println( "A");
System.out.println("ThreadA end:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
executorService.execute(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println( "ThreadB begin:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("B");
System.out.println( "ThreadB end:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
运行的某一次结果如下:
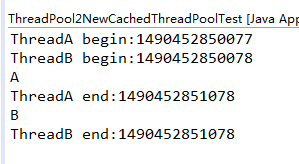 从打印的时间来看,A和B几乎是在相同的时间开始begin的,也就是创建了2个线程,2个线程之间是异步运行的。继续
实验,创建新类ThreadPool2NewCachedThreadPoolForTest.java如下:
从打印的时间来看,A和B几乎是在相同的时间开始begin的,也就是创建了2个线程,2个线程之间是异步运行的。继续
实验,创建新类ThreadPool2NewCachedThreadPoolForTest.java如下:
package com.yc.semephore_7;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadPool2NewCachedThreadPoolForTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++){
executorService.execute(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println( "run ->");
}
});
}
}
}
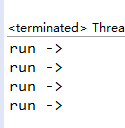
运行结果如下:
TP_2:验证newCachedThreadPool()创建为Thread池
前面的实验都没有验证newCachedThreadPool()方法创建的是线程池。在本测试中将得到验证。
创建项目Executors_2,类MyThread.java代码如下:
package com.yc.executors;
public class MyThread implements Runnable{
private String userName;
public MyThread(String userName){
this.userName = userName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "userName=" + userName + " begin-> " + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "userName=" + userName + " end-> " + System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
类ThreadPool2NewCachedThreadPoolIsTest.java代码如下:
package com.yc.executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadPool2NewCachedThreadPoolIsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i ++){
executorService.execute(new MyThread( ""+(i+1) ) );
}
}
}
测试结果如下:
pool-1-thread-1userName=1 begin-> 1490516211122
pool-1-thread-3userName=3 begin-> 1490516211122
pool-1-thread-4userName=4 begin-> 1490516211122
pool-1-thread-7userName=7 begin-> 1490516211122
pool-1-thread-8userName=8 begin-> 1490516211123
pool-1-thread-2userName=2 begin-> 1490516211123
pool-1-thread-5userName=5 begin-> 1490516211123
pool-1-thread-6userName=6 begin-> 1490516211123
pool-1-thread-1userName=1 end-> 1490516212122
pool-1-thread-7userName=7 end-> 1490516212122
pool-1-thread-4userName=4 end-> 1490516212122
pool-1-thread-3userName=3 end-> 1490516212122
pool-1-thread-8userName=8 end-> 1490516212123
pool-1-thread-2userName=2 end-> 1490516212123
pool-1-thread-5userName=5 end-> 1490516212123
pool-1-thread-6userName=6 end-> 1490516212123说明线程池对象创建是完全成功的,但还没有达到池中线程对象可以服用的效果哟,下面要实现这样的效果。
将ThreadPool2NewCachedThreadPoolIsTest.java代码改成如下所示:
测试结果如下所示:
此方法的使用和前面的newFixedThreadPool(int , ThreadFactory)相似。
package com.yc.executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ThreadPool2NewCachedThreadPoolIsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++){
executorService.execute(new MyThread( ""+(i+1) ) );
}
Thread.sleep(2 * 1000);
System.out.println("\n\n");
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++){
executorService.execute(new MyThread( ""+(i+1) ) );
}
}
}
测试结果如下所示:
pool-1-thread-1userName=1 begin-> 1490516619860
pool-1-thread-4userName=4 begin-> 1490516619861
pool-1-thread-2userName=2 begin-> 1490516619861
pool-1-thread-3userName=3 begin-> 1490516619860
pool-1-thread-3userName=3 end-> 1490516620861
pool-1-thread-2userName=2 end-> 1490516620861
pool-1-thread-4userName=4 end-> 1490516620861
pool-1-thread-1userName=1 end-> 1490516620861
pool-1-thread-3userName=1 begin-> 1490516621861
pool-1-thread-4userName=2 begin-> 1490516621861
pool-1-thread-2userName=4 begin-> 1490516621861
pool-1-thread-1userName=3 begin-> 1490516621861
pool-1-thread-3userName=1 end-> 1490516622861
pool-1-thread-1userName=3 end-> 1490516622861
pool-1-thread-4userName=2 end-> 1490516622861
pool-1-thread-2userName=4 end-> 1490516622861
TP_3:使用newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory)定制线程工厂
无界线程池中的Thread类还可以有程序员自己定制,方法newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory)就是解决这个问题。
创建项目Executors_3,创建MyThreadFactory,java线程工厂类代码如下:
类MyThreadFactoryTest.java代码如下:
有界线程池中的Thread类还可以有程序员自己定制,方法newFixedThreadPool(int nThread, ThreadFactory threadFactory)就是解决这个问题的。
package com.yc.executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
public class MyThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory{
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread rThread = new Thread(r);
rThread.setName("定制池中的线程->" + Math.random());
return rThread;
}
}
类MyThreadFactoryTest.java代码如下:
package com.yc.executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class MyThreadFactoryTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThreadFactory myThreadFactory = new MyThreadFactory();
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(myThreadFactory);
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i ++){
executorService.execute(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我在使用 - " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}
}
我在使用 - 定制池中的线程->0.7251183137194371
我在使用 - 定制池中的线程->0.7895540239349206
我在使用 - 定制池中的线程->0.055382936386370485
我在使用 - 定制池中的线程->0.7251183137194371
我在使用 - 定制池中的线程->0.4625204924896881
我在使用 - 定制池中的线程->0.5101540668259192
我在使用 - 定制池中的线程->0.7895540239349206
我在使用 - 定制池中的线程->0.8130499478281913
通过使用自定义的ThreadFactory接口实现类,实现了线程对象的定制型。
TP_4:使用newFixedThreadPool(int)方法创建有界线程池
方法newFixedThreadPool(int)创建的是有界线程池,也就是池中的线程个数可以指定最大数量。
创建项目Executors_3。类MyRunnable.java代码如下:
package com.yc.executors_1;
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
private String userName;
public MyRunnable(String userName){
this.userName = userName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - userName=" + userName + " - begin:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(2 * 1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " - userName=" + userName + " - end:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
类TPNewFixedThreadPooIntTest.java代码如下:
测试结果如下:
可以看到池中最多可允许有三个线程同时在线,当thread-2和thread-3 end后立马接着运行。
package com.yc.executors_1;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class TPNewFixedThreadPoolIntTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i ++){
executorService.execute(new MyRunnable( (i+1) + ""));
}
}
}
测试结果如下:
pool-1-thread-1 - userName=1 - begin:1490520507288
pool-1-thread-3 - userName=3 - begin:1490520507288
pool-1-thread-2 - userName=2 - begin:1490520507288
pool-1-thread-2 - userName=2 - end:1490520509289
pool-1-thread-3 - userName=3 - end:1490520509289
pool-1-thread-2 - userName=4 - begin:1490520509289
pool-1-thread-3 - userName=5 - begin:1490520509289
pool-1-thread-1 - userName=1 - end:1490520509289
pool-1-thread-3 - userName=5 - end:1490520511289
pool-1-thread-2 - userName=4 - end:1490520511289可以看到池中最多可允许有三个线程同时在线,当thread-2和thread-3 end后立马接着运行。
TP_5:使用newFixedThreadPool(int, ThreadFactory)定制线程工厂
有界线程池中的Thread类还可以有程序员自己定制,方法newFixedThreadPool(int nThread, ThreadFactory threadFactory)就是解决这个问题的。
创建项目newFixedThreadPoolFactory,创建MyThreadFactory.java线程工厂类代码如下:
得到某一次的测试结果如下:
package com.yc.executors_2;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
public class MyThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory{
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread mThread = new Thread(r);
mThread.setName("定制的有界线程工厂->" + Math.random());
return mThread;
}
}
package com.yc.executors_2;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class TPNewFixThreadPoolFactoryTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThreadFactory threadFactory = new MyThreadFactory();
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3, threadFactory);
for(int i = 5; i > 0; i --){
executorService.execute(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我正在运行-" +Thread.currentThread().getName() );
}
});
}
}
}
得到某一次的测试结果如下:
我正在运行-定制的有界线程工厂->0.34551172025115573
我正在运行-定制的有界线程工厂->0.7745731609040991
我正在运行-定制的有界线程工厂->0.6848389479731579
我正在运行-定制的有界线程工厂->0.7745731609040991
我正在运行-定制的有界线程工厂->0.34551172025115573TP_6:使用newSingleThreadExecutor()方法创建单一线程池
使用newSingleThreadExecutor()方法可以创建单一线程池。单一线程池可以实现以队列的方式来执行任务。
创建项目Executors_4,类MyRunnable.java代码如下:
package com.yc.executors_3;
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
private String StringName;
public MyRunnable(String StringName){
this.StringName = StringName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " and - StringName=" + StringName + " -begin-> " + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(1* 1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " and - StringName=" + StringName + " -end-> " + System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package com.yc.executors_3;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class TPNewSingleThreadExecutorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i ++){
executorService.execute(new MyRunnable( "" + (i + 1)));
}
}
}
pool-1-thread-1 and - StringName=1 -begin-> 1490522664356
pool-1-thread-1 and - StringName=1 -end-> 1490522665356
pool-1-thread-1 and - StringName=2 -begin-> 1490522665356
pool-1-thread-1 and - StringName=2 -end-> 1490522666356
pool-1-thread-1 and - StringName=3 -begin-> 1490522666356
pool-1-thread-1 and - StringName=3 -end-> 1490522667356
TP7:使用newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory)定制线程工厂单一线程池
此方法的使用和前面的newFixedThreadPool(int , ThreadFactory)相似。





























 235
235

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








