第一章Map集合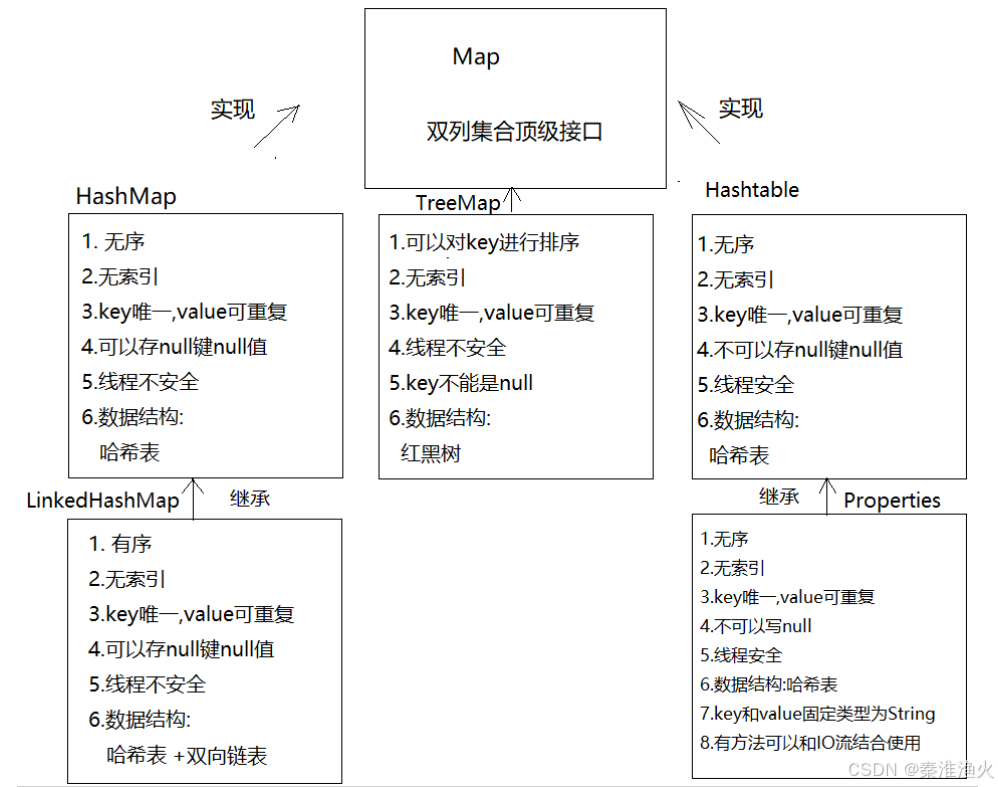
Map是双列集合顶级接口
什么叫做双列集合:一个元素有两部分构成:key和value -> 键值对
1.1.HashMap
常用方法:
V put(K key, V value) -> 添加元素,返回的是被替换的value值
V remove(Object key) ->根据key删除键值对,返回的是被删除的value
V get(Object key) -> 根据key获取value
boolean containsKey(Object key) -> 判断集合中是否包含指定的key
Collection<V> values() -> 获取集合中所有的value,转存到Collection集合中
Set<K> keySet()->将Map中的key获取出来,转存到Set集合中
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()->获取Map集合中的键值对,转存到Set集合中
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
//V put(K key, V value) -> 添加元素,返回的是被替换的value值
map.put("刘彦昌","三圣母");
map.put("唐僧","女儿国国王");
map.put("猪八戒","高翠兰");
map.put("后羿","嫦娥");
map.put("猪八戒", "嫦娥");
System.out.println(map);
//V remove(Object key) ->根据key删除键值对,返回的是被删除的value
String value = map.remove("刘彦昌");
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println(map);
//V get(Object key) -> 根据key获取value
String value1 = map.get("猪八戒");
System.out.println("value1 = " + value1);
//boolean containsKey(Object key) -> 判断集合中是否包含指定的key
System.out.println(map.containsKey("唐僧"));
//Collection<V> values() -> 获取集合中所有的value,转存到Collection集合中
Collection<String> collection = map.values();
System.out.println("collection = " + collection);
}1.1.1HashMap的两种遍历方式
方式1:获取key,根据key再获取value
Set<K> keySet()->将Map中的key获取出来,转存到Set集合中
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("刘彦昌","三圣母");
map.put("唐僧","女儿国国王");
map.put("猪八戒","高翠兰");
map.put("后羿","嫦娥");
map.put("猪八戒", "嫦娥");
Set<String> set = map.keySet();
for (String key : set) {
System.out.println(key+"..."+map.get(key));
}
}方式2:同时获取key和value
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()->获取Map集合中的键值对,转存到Set集合中
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("刘彦昌","三圣母");
map.put("唐僧","女儿国国王");
map.put("猪八戒","高翠兰");
map.put("后羿","嫦娥");
map.put("猪八戒", "嫦娥");
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> set = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : set) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"..."+entry.getValue());
}
}1.1.2LinkedHashMap
HashMap的子类
使用:和HashMap一样
1.2.TreeMap
是Map接口的实现类
方法:和HashMap一样
构造:
TreeMap()
TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator)
1.3.Hashtable集合
Hashtable和HashMap区别:
相同点: 元素无序,无索引,key唯一
不同点: HashMap线程不安全,Hashtable线程安全
HashMap可以存储null键null值;Hashtable不能
1.3.1Properties集合
Properties是Hashtable的子类
特有方法(但是HashMap中的方法它都能使用)
Object setProperty(String key, String value) -> 存键值对
String getProperty(String key) -> 根据key获取value
Set<String> stringPropertyNames() -> 获取所有的key,存储到set集合中,类似于keySet
void load(InputStream inStream) -> 将流中的数据加载到Properties集合中,用于读取配置文件->IO流再说
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("username","root");
properties.setProperty("password","1234");
//类似于keySet,将所有的key获取出来放到 set集合中
Set<String> set = properties.stringPropertyNames();
for (String key : set) {
String value = properties.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key+"..."+value);
}
}





















 997
997

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








