1.解决方案
- 使用ConcurrentHashMap
package com.company.newtest;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class test30 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
map.put("key1", "value1");
map.put("key2", "value2");
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next();
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
if(key.equals("key1")){
map.put("sadasdasd",value);
iterator.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(map);
}
}
result::{key2=value2, sadasdasd=value1}
// 另一个Demo
Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
map.put("key1", "value1");
map.put("key2", "value2");
map.forEach((k, v) -> {
if(k.equals("key1")){
map.remove("key1");
map.put("key1", "213123123");
}
});
System.out.println(map);
- 使用ConcurrentSkipListMap
package com.company.newtest;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListMap;
public class test30 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();
map.put("key1", "value1");
map.put("key2", "value2");
map.forEach((k, v) -> {
if("key1".equals(k)){
map.remove("key1");
map.put("key1", "213123123");
}
});
System.out.println(map);
}
}
Java的ConcurrentSkipListMap是一种基于跳表算法实现的并发数据结构,它可以在多线程并发访问时保证数据的正确性和一定的性能。
跳表算法是一种高效的数据结构,可以在拥有n个元素的有序列表中进行快速的查找、插入和删除操作,其时间复杂度为O(logn)。ConcurrentSkipListMap通过使用跳表算法,实现了高效的并发访问。
与Java的其他Map实现不同的是,ConcurrentSkipListMap中的元素是按照键值有序排列的。在进行插入、删除或查找操作时,它会根据键值的大小关系,自动将元素插入到合适的位置。
ConcurrentSkipListMap是一种线程安全的数据结构,可以支持多个线程同时访问。它使用了一种乐观锁的机制来保证并发访问的正确性,当多个线程同时修改同一个元素时,只有一个线程会成功,其他线程则会进行重试,确保数据的正确性。
总的来说,ConcurrentSkipListMap是一个高效、线程安全的并发数据结构,适用于需要高并发访问的场景。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>();
map.put("key1", "value1");
map.put("key2", "value2");
map.forEach((k, v) -> {
if("key1".equals(k)){
map.remove("key1");
map.put("key1", "213123123");
}
});
System.out.println(map);
}
补充:
concurrentHashMap与ConcurrentSkipListMap性能测试
在4线程1.6万数据的条件下,ConcurrentHashMap 存取速度是ConcurrentSkipListMap 的4倍左右。
但ConcurrentSkipListMap有几个ConcurrentHashMap 不能比拟的优点:
1、ConcurrentSkipListMap 的key是有序的。
2、ConcurrentSkipListMap 支持更高的并发。ConcurrentSkipListMap 的存取时间是log(N),和线程数几乎无关。也就是说在数据量一定的情况下,并发的线程越多,ConcurrentSkipListMap越能体现出他的优势。
2.深入了解
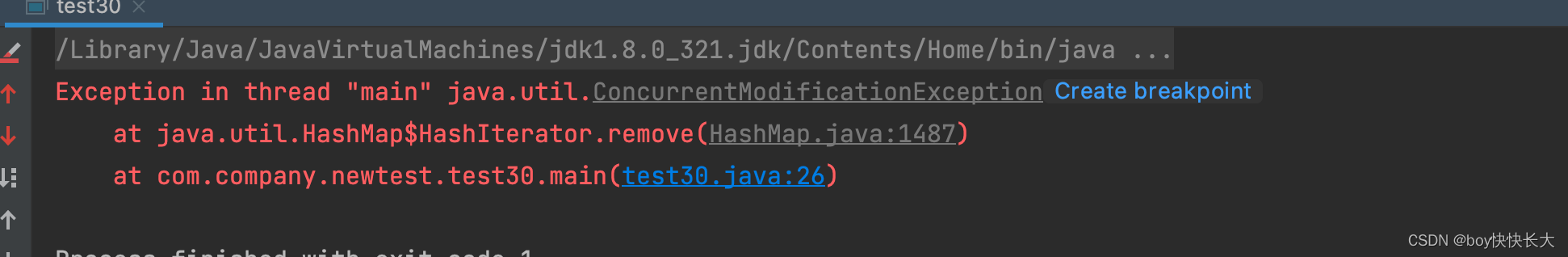
1.map在循环中如果直接修改自己的key value 会发生ConcurrentModificationException
即便是你已经在用iterator进行遍历修改也会发生并发修改异常,如下:
public class test30 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("key1", "value1");
map.put("key2", "value2");
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next();
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
if(key.equals("key1")){
map.put("sadasdasd",value);
iterator.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(map);
}
}
2.用Iterator迭代器可以删除数据,修改value,却修改不了key
// 删除数据
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, BigDecimal>> vendorStaffMealIterator = vendorStaffMealMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (vendorStaffMealIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Integer, BigDecimal> entry = vendorStaffMealIterator.next();
Integer staffId = entry.getKey();
BigDecimal mealFeeSum = entry.getValue();
if (vendorHcRecords.stream().anyMatch(item -> item.getStaffId().equals(staffId))) {
continue;
}
// 负责人id
String principalId = vendorManagerMap.getOrDefault(staffId, "");
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(principalId)) {
BigDecimal staffMealFee = staffMealMap.getOrDefault(Integer.valueOf(principalId), BigDecimal.ZERO);
staffMealFee = staffMealFee.add(mealFeeSum);
staffMealMap.put(Integer.valueOf(principalId), staffMealFee);
vendorStaffMealIterator.remove();
}
}
// 修改value
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("key1", "value1");
map.put("key2", "value2");
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next();
String key = entry.getKey();
if(key.equals("key1")){
map.put(key,"asdasdsda");
}
}
System.out.println(map);
}
- removeIf删除
map.keySet().removeIf(key -> key.equals("CCC"));
map.values().removeIf(value -> value.equals("123"));
3. 最新可用
// 订单Map key:Date时间,yyyy-MM-dd格式 value:List<CtOrdersEntity> 将departure_time转化为yyyy-MM-dd类型Date进行分类
Map<Date, List<CtOrdersEntity>> orderMap = evectionRecords.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(entity -> DateUtils.convertDifferentDate(entity.getDepartureTime())));
Iterator<Map.Entry<Date, List<CtOrdersEntity>>> iterator = orderMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<Date, List<CtOrdersEntity>> next = iterator.next();
Date keyDate = next.getKey();
List<CtOrdersEntity> valueList = next.getValue();
Date startDate = DateUtils.addOrDecreaseDay(keyDate, -1);
Date endDate = DateUtils.addOrDecreaseDay(keyDate, 1);
List<Integer> staffIds = valueList.stream()
.filter(item -> null != item.getStaffId())
.map(CtOrdersEntity::getStaffId)
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
Map<Integer, AttendanceAppliesEntity> bpmInfoMap = attendanceAppliesDao.bpmInfoMap(staffIds, AttendanceAppliesTypeEnum.EVECTION.getName(), startDate, endDate);
List<CtOrdersEntity> checkResList = valueList.stream()
.map(item -> {
if (!bpmInfoMap.containsKey(item.getStaffId())) {
String status = String.format("%s无%s的OA审批", DateUtils.format(keyDate, "yyyy-MM-dd"), AttendanceAppliesTypeEnum.EVECTION.getName());
item.setLocalStatus(status);
item.setCheckResult(status);
} else {
item.setLocalStatus("正常");
item.setCheckResult("正常");
}
return item;
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 修改Map
orderMap.put(keyDate,checkResList);
}























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










