蓝桥杯书的笔记
https://www.lanqiao.cn/courses/3993/learning/?id=248897
将一段字符串转换成整数并存放在一个变量中(只能转数字)
//将一段字符串转换成整数并存放在一个变量中
int chnum(char str[])
{
int i,n,num=0;
for(i=0;str[i]!='\0';i++)
{
if(str[i]>='0' && str[i]<='9')
num=num*10+str[i]-'0';
}
return num;
}
链表
小王子问题(含单双链表)
题意:
小王子有一天迷上了排队的游戏,桌子上有标号为 1-10 按顺序摆放的 10 个玩具,现在小王子想将它们按自己的喜好进行摆放。小王子每次从中挑选一个好看的玩具放到所有玩具的最前面。已知他总共挑选了 M 次,每次选取标号为 X 的玩具放到最前面,求摆放完成后的玩具标号。
给出一组输入,M=8 共计排了 8 次,这 8 次的序列为 9,3,2,5,6,8,9,8。 求最终玩具的编号序列。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
};
Node *head = new Node; //先生成头结点
void init()
{
head->next = nullptr; //形成空链,由上文已知单链表最后一个结点的指针为空。
for (int i = 10; i >= 1; i--)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = i;
temp->next = head->next;
head->next = temp;
}
}
void del(int x)
{
Node *Befor = head; //用于存放当前节点的前驱,因为单链表单向遍历,我们不能从下一个找到上一个
for (Node *T = head->next; T != nullptr; T = T->next) //链表的遍历常用写法
{
if (T->data == x) //找到要的那个数了
{
Node *temp = T; //先临时保存结点
Befor->next = T->next; //将节点从链表上摘除
delete temp; //从内存中删除结点。
return; //删除结束后,结束函数。
}
Befor = T; //前驱改变
}
}
void insert(int x)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = x;
temp->next = head->next;
head->next = temp;
}
void show(int i)
{
cout << "这是第" << i << "次操作";
for (Node *T = head->next; T != nullptr; T = T->next) //链表的遍历常用写法
{
cout << T->data << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
init();
show(0);
int N;
cin >> N;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
del(x);
insert(x);
show(i);
}
}
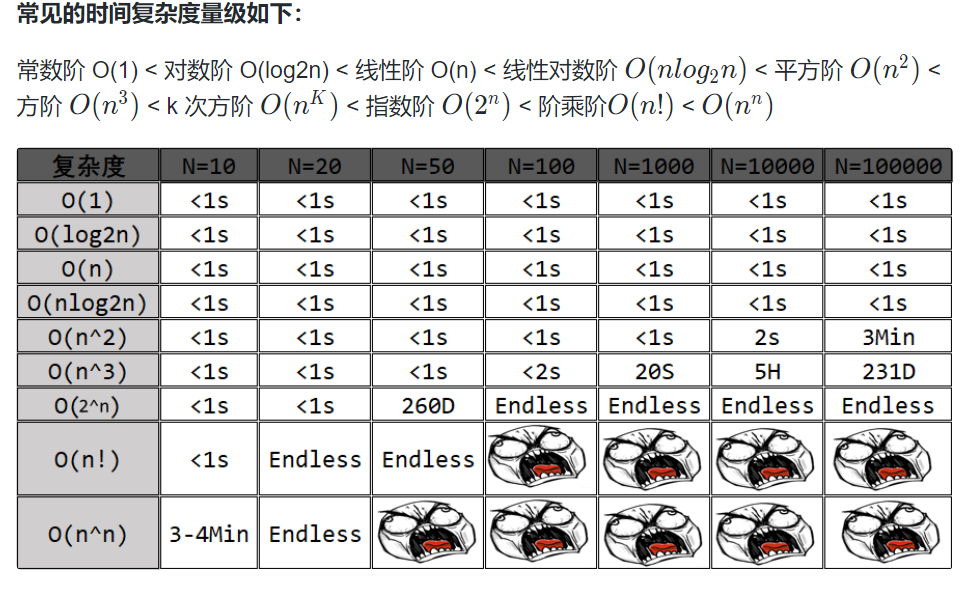
约瑟夫环问题
//头文件与命名空间
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *pNext;
};
int main()
{
int n, k, m, i; //n个人从k位置开始报数,数到m出列
Node *p, *q, *head;
cin >> n >> k >> m;
if (m == 1)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) //共计N个人
{
int left;
left = k - 1;
if (left == 0)
left = n;
cout << left;
}
}
else
{
Node * first = (Node *)new Node;
p = first;
first->data = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
q = new Node;
q->data = i;
p->pNext = q;
p = p->pNext;
}
p->pNext = first;
p = first;
for (i = 1; i <= k - 1; i++) //
p = p->pNext;
while (p != p->pNext) //只剩下一个结点的时候停止
{
for (i = 1; i < m - 1; i++)
{
p = p->pNext;
}
q = p->pNext; //q为要出队的元素
cout << q->data << endl;
p->pNext = q->pNext;
delete q;
p = p->pNext;
}
cout << p->data << endl; //输出最后一个元素
}
return 0;
}
小王子问题双链表
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *next;
Node *before;
};
Node* head = new Node; //先生成头结点
void insert(int x)
{
Node* temp=new Node;
temp->data=x;
temp->next=head->next;
head->next=temp;
temp->before=head;
if(temp->next) temp->next->before=temp;
}
void init() //为了美观,我们写个初始化函数
{
head->next=nullptr; //无论用什么方式,都不能省略该语句,不然无法正常使用。
head->before=nullptr;
for(int i=10; i>=1; i--) insert(i); //从10开始插入
}
void del(int x)
{
for(Node*T=head->next; T!=nullptr; T=T->next) //链表的遍历常用写法
{
if(T->data==x) //找到要的那个数了
{
T->before->next=T->next;//双向链表,就是如此简单方便。
T->next->before=T->before;
return; //删除结束后,结束函数。
}
}
}
void show(int i)
{
cout << "这是第" << i << "次操作";
for (Node *T = head->next; T != nullptr; T = T->next) //链表的遍历常用写法
{
cout << T->data << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
init();
show(0);
int N;
cin >> N;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
del(x);
insert(x);
show(i);
}
}
队列
思考一下:
为什么链式存储的方式的队列首尾指针与链表头尾刚好相反,是什么原因呢?
其实我们知道链表的表头是用来插入数据的,表尾处的数据才是最先插入的,先入先出原则,所以表尾出的数据最先出列,也就是队列的头啦!听到这里,可能有人迷糊了,什么头什么尾的?链表是数据存储的组织方式,他只是决定了数据在内存中怎么存储,而队列是说我们是按照什么顺序存储。可以理解为一群人排队,队列告诉他们先来的先吃饭,后来的得排队,而链表或顺序表是说,你可以站着排队蹲着排队等等。
银行排队问题(普通队列)
题意:
银行排队问题,CLZ 银行只有两个接待窗口,VIP 窗口和普通窗口,VIP 用户进入 VIP 用户窗口,剩下的进入普通窗口排队。
现在有以下操作:
第一行 M 次操作(M<1000)
第二行 到 第M+1行 输入操作
格式: IN name V
OUT V
IN name2 N
OUT N
即 第一个字符串为操作 是IN进入排队和OUT 出队
IN 排队 跟着两个字符串为姓名和权限V或N
OUT 为出队即完成操作,V和N代表那个窗口完成了操作
输出:M次操作后V队列和N队列中姓名,先输出V队列后输出N队列。
样例:
输入:
5
IN xiaoming N
IN Adel V
IN laozhao N
OUT N
IN CLZ V
输出:
Adel
CLZ
laozhao
//注意题意,输出队伍中现有的
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
string Vqueue[1005]; //V队列
int Vhead=0; //首指针
int Vtail=0; //尾指针
string Nqueue[1005]; //N队列
int Nhead=0; //首指针
int Ntail=0; //尾指针
void in(string name,string type)
{
if(type=="V"){
Vqueue[Vtail]=name;
Vtail++;
}
else
{
Nqueue[Ntail]=name;
Ntail++;
}
}
bool out(string type)
{
if(type=="V"){
if(Vhead==







 本文探讨了将字符串转换为整数的算法,以及链表在解决小王子排队和约瑟夫环问题中的应用。介绍了队列的实现,包括普通队列和循环队列,以及在银行排队问题中的应用。此外,详细阐述了散列表的概念、冲突处理和在解决弗里语言重复单词问题中的运用。最后,讨论了排序算法,包括简单排序和高效排序算法,并展示了C++内置模板在排序和数据结构操作中的便捷性。
本文探讨了将字符串转换为整数的算法,以及链表在解决小王子排队和约瑟夫环问题中的应用。介绍了队列的实现,包括普通队列和循环队列,以及在银行排队问题中的应用。此外,详细阐述了散列表的概念、冲突处理和在解决弗里语言重复单词问题中的运用。最后,讨论了排序算法,包括简单排序和高效排序算法,并展示了C++内置模板在排序和数据结构操作中的便捷性。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










