An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
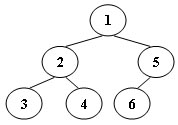
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
static int counts = 0;
static int sum = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
sum = n;
Stack<Integer> integerStack = new Stack<>();
int pre[] = new int[n], in[] = new int[n], preIndex = 0, inIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * n; ++i) {
String[] inputStrings = br.readLine().split("\\s+");
if (inputStrings[0].equals("Push")) {
int inStack = Integer.parseInt(inputStrings[1]);
integerStack.add(inStack);
pre[preIndex++] = inStack;
} else {
int outStack = integerStack.pop();
in[inIndex++] = outStack;
}
}
TreeNode root = create(pre, 0, preIndex-1,
in, 0, inIndex-1);
postOrder(root);
}
public static TreeNode create(int[] pre, int preLeft, int preRight,
int[] in, int inLeft, int inRight) {
if (preLeft > preRight) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pre[preLeft]);
int findIndex = -1;
// 找出中序遍历中的根节点位置
for (int i = inLeft; i <= inRight; ++i) {
if (in[i] == root.data) {
findIndex = i;
break;
}
}
// 计算左子树的数量
int leftNum = findIndex - inLeft;
root.left = create(pre, preLeft + 1, preLeft + leftNum,
in, inLeft, findIndex - 1);
root.right = create(pre, preLeft + leftNum + 1, preRight,
in, findIndex + 1, inRight);
return root;
}
public static void postOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root!=null) {
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
++counts;
if (counts<sum){
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
} else {
System.out.print(root.data);
}
}
}
}
class TreeNode {
int data;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}











 博客介绍了非递归方式用栈实现二叉树中序遍历,给出栈操作序列可生成唯一二叉树。要求根据输入的栈操作(Push和Pop),输出对应二叉树的后序遍历序列,还给出了输入和输出的规格说明。
博客介绍了非递归方式用栈实现二叉树中序遍历,给出栈操作序列可生成唯一二叉树。要求根据输入的栈操作(Push和Pop),输出对应二叉树的后序遍历序列,还给出了输入和输出的规格说明。
















 429
429

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








