普通函数时,this指向window
<script>
function test() {
console.log('=== test this: ', this)
}
test()
const test1 = function () {
console.log('===test1 this: ', this)
}
test1()
</script>![]() 由结果可以看到普通函数中this指向window
由结果可以看到普通函数中this指向window
函数是对象属性或类方法时,this指向当前对象
<script>
const obj = {
// 方法
test2() {
console.log('===test2 this: ', this)
},
// 属性
test3: function () {
console.log('===test3 this: ', this)
},
test4() {
console.log('===test4 this: ', this)
// 方法中新定义的方法,就相当于是普通方法
function innerTest4() {
console.log('===innerTest4 this:', this)
}
innerTest4()
}
}
obj.test2()
obj.test3()
obj.test4()
class Test {
// 类方法
test5() {
console.log('===test5 this: ', this)
}
}
const testClass = new Test()
testClass.test5()
// 构造函数
function Test6(name) {
this.name = name
this.getName = function () {
console.log('===test6 this: ', this)
// 普通方法
function test7() {
console.log('===test7 this: ', this)
}
test7()
return this.name
}
}
const test6 = new Test6('zhangsan')
test6.getName()
</script>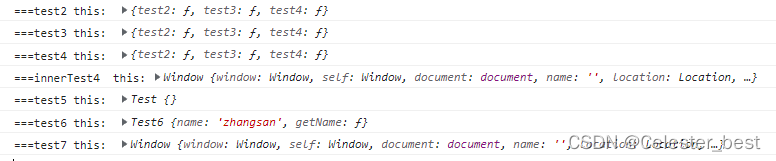
由结果可知,如果函数是对象属性或者是类方法时 ,this指向当前对象。但是如果是普通方法调用,this指向window。
箭头函数的this指向问题
<script>
let obj2 = {
arr: [1, 2, 3],
getArrData: function () {
console.log('=== getArrData this: ', this)
let arrStr1 = ''
this.arr.map(function (item) {
console.log('===map1 this: ', this)
arrStr1 = arrStr1 + item
})
let arrStr2 = ''
// 箭头函数
this.arr.map(item => {
console.log('===map2 this: ', this)
arrStr2 = arrStr2 + item
})
}
}
obj2.getArrData()
</script>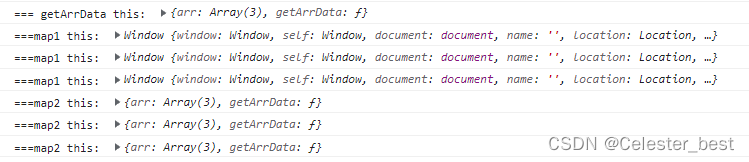
由结果可知,例子中第一个map的回调函数是普通函数,this指向window,第二个map的回调函数时箭头函数,this执行该对象。
所以可以理解为箭头函数中的this指向上下文,也可以理解为父级作用域中的this。
事件中的this指向问题
<div>
<button id="btn-wrap">点击</button>
</div>
<script>
const btnView = document.getElementById('btn-wrap')
btnView.addEventListener('click', function () {
console.log('=== this: ', this)
})
</script>![]()
可以看到虽然点击事件的回调函数是普通函数,但是this并没有指向window,为什么呢》
因为addEventListener('click')可以理解为给btnView添加了onClick属性
<div>
<button id="btn-wrap">点击</button>
</div>
<script>
const btnView = document.getElementById('btn-wrap')
btnView.onclick=function(){
console.log('==== 2 this: ',this)
}
</script>![]()
所以addEventListener ('click')的中回调函数的this指向是被点击的元素。也就是说事件中的回调函数其实是被点击对象的一个属性方法,属性方法中的this指向对象,所以上面的例子中的this指向btnView
如果点击事件的回调函数使用箭头函数,this会指向什么对象呢?
<div>
<button id="btn-wrap">点击</button>
</div>
<script>
const btnView = document.getElementById('btn-wrap')
btnView.onclick = function () {
console.log('==== 2 this: ', this)
}
const obj = {
show() {
console.log('3 this: ', this)
btnView.addEventListener('click', function () {
console.log('4 this: ', this)
})
btnView.addEventListener('click', () => {
console.log('5 this: ', this)
})
}
}
obj.show()
</script>
可以发现上例中的this指向了obj对象。
这是因为箭头函数的this指向父级作用域的this对象,父级作用域的this指向obj,所以该处箭头函数中的this就指向obj.
如果既想使用父级作用域的this又想使用被点击对象,该怎么办呢?
可以使用箭头函数,向箭头传递event,通过event.target获取被点击对象即可。
<div>
<button id="btn-wrap">点击</button>
</div>
<script>
const btnView = document.getElementById('btn-wrap')
btnView.onclick = function () {
console.log('==== 2 this: ', this)
}
const obj = {
show() {
console.log('3 this: ', this)
btnView.addEventListener('click', function () {
console.log('4 this: ', this)
})
btnView.addEventListener('click', () => {
console.log('5 this: ', this)
})
btnView.addEventListener('click', (event) => {
console.log('6 this: ', this,' event: ',event.target)
})
}
}
obj.show()
</script>
修改this指向
赋值修改this指向
<script>
let obj3 = {
arr: [1, 2, 3],
value: 'zhangsan',
getArrData2: function () {
console.log('=== getArrData2 this: ', this)
let arrStr1 = ''
this.arr.map(function (item) {
console.log('=== 1 value: ', this.value)
arrStr1 = arrStr1 + item
})
let arrStr2 = ''
// 将上下文this赋值给that
const that = this
this.arr.map(function (item) {
console.log('=== 2 value: ', that.value)
arrStr2 = arrStr2 + item
})
}
}
obj3.getArrData2()
</script>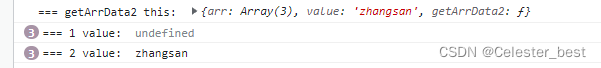
利用一些函数的特性
有些函数的参数有些特殊作用,例如map方法的第二个参数就可以是map的回调函数中的this指向第二个参数
<script>
let obj3 = {
arr: [1, 2, 3],
value: 'zhangsan',
getArrData2: function () {
console.log('=== getArrData2 this: ', this)
let arrStr1 = ''
this.arr.map(function (item) {
console.log('=== 1 value: ', this.value)
arrStr1 = arrStr1 + item
})
let arrStr2 = ''
//将上下文this赋值给that
const that = this
this.arr.map(function (item) {
console.log('=== 2 value: ', that.value)
arrStr2 = arrStr2 + item
})
// 利用map方法的第二个参数,将回调函数的this指向一个对象
let arrStr3 = ''
this.arr.map(function (item) {
console.log('=== 3 value: ', this)
arrStr3 = arrStr3 + item
}, {
a: '1',
b: '2'
})
// 利用map方法的第二个参数,将回调函数的this指向上下文
let arrStr4 = ''
this.arr.map(function (item) {
console.log('=== 4 value: ', this)
arrStr4 = arrStr4 + item
}, this) //将this传递给map的回调函数
}
}
obj3.getArrData2()
</script>
利用call和apply方法
<script>
const obj = {
data: '测试',
show() {
console.log('1 this: ', this)
}
}
const obj2 = {
data: '测试2',
}
obj.show()
obj.show.call(obj2)
obj.show.apply(obj2)
</script>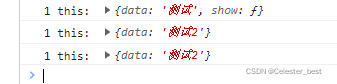
可以发现使用call和apply之后,this指向了obj2.





















 1510
1510











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








