昨天面试完字节跳动头条的测试开发,我更是想要规划写一篇应届生校园招聘的面经,做一个总结。不管你面试哪个方向,主要考察内容都是C++软件知识、操作系统、计算机网络、数据库这几类。
因此,我以字节跳动面试的主要内容按这几类分类整理,供大家参考,之后也会在此基础上进行整理完善。
面试系列文章: 点击这里 直接跳转面试经验贴专栏
《数据结构与算法》上机实验专栏 链接:https://blog.csdn.net/charmve/category_9579957.html
快速排序的衍生应用——Partition函数
想直接看Partition函数的应用,可直接跳接到第二部分。
1. 原版快排1
1.1 算法原理
Like Merge Sort, QuickSort is a Divide and Conquer algorithm(分治算法). It picks an element as pivot and partitions the given array around the picked pivot. There are many different versions of quickSort that pick pivot in different ways.
- Always pick first element as pivot.
- Always pick last element as pivot (implemented below)
- Pick a random element as pivot.
- Pick median as pivot.
The key process in quickSort is partition(). Target of partitions is, given an array and an element x of array as pivot, put x at its correct position in sorted array and put all smaller elements (smaller than x) before x, and put all greater elements (greater than x) after x. All this should be done in linear time.
Pseudo Code for recursive QuickSort function :
/* low --> Starting index, high --> Ending index */
quickSort(arr[], low, high)
{
if (low < high)
{
/* pi is partitioning index, arr[pi] is now
at right place */
pi = partition(arr, low, high);
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1); // Before pi
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high); // After pi
}
}
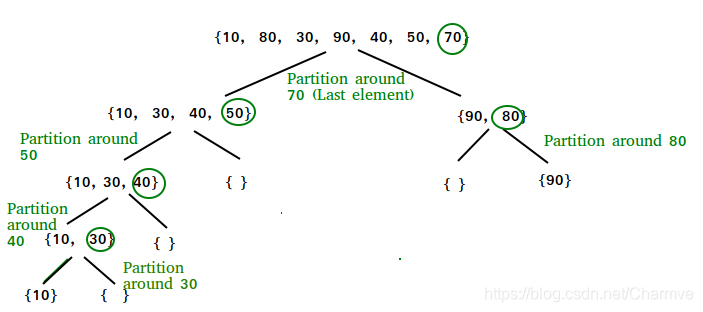
1.2 Partition Algorithm
There can be many ways to do partition, following pseudo code adopts the method given in CLRS book. The logic is simple, we start from the leftmost element and keep track of index of smaller (or equal to) elements as i. While traversing, if we find a smaller element, we swap current element with arr[i]. Otherwise we ignore current element.
Pseudo code for partition()
/* This function takes last element as pivot, places
the pivot element at its correct position in sorted
array, and places all smaller (smaller than pivot)
to left of pivot and all greater elements to right
of pivot */
partition (arr[], low, high)
{
// pivot (Element to be placed at right position)
pivot = arr[high];
i = (low - 1) // Index of smaller element
for (j = low; j <= high- 1; j++)
{
// If current element is smaller than the pivot
if (arr[j] < pivot)
{
i++; // increment index of smaller element
swap arr[i] and arr[j]
}
}
swap arr[i + 1] and arr[high])
return (i + 1)
}
Illustration of partition() :
arr[] = {10, 80, 30, 90, 40, 50, 70}
Indexes: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
low = 0, high = 6, pivot = arr[h] = 70
Initialize index of smaller element, i = -1
Traverse elements from j = low to high-1
j = 0 : Since arr[j] <= pivot, do i++ and swap(arr[i], arr[j])
i = 0
arr[] = {10, 80, 30, 90, 40, 50, 70} // No change as i and j
// are same
j = 1 : Since arr[j] > pivot, do nothing
// No change in i and arr[]
j = 2 : Since arr[j] <= pivot, do i++ and swap(arr[i], arr[j])
i = 1
arr[] = {10, 30, 80, 90, 40, 50, 70} // We swap 80 and 30
j = 3 : Since arr[j] > pivot, do nothing
// No change in i and arr[]
j = 4 : Since arr[j] <= pivot, do i++ and swap(arr[i], arr[j])
i = 2
arr[] = {10, 30, 40, 90, 80, 50, 70} // 80 and 40 Swapped
j = 5 : Since arr[j] <= pivot, do i++ and swap arr[i] with arr[j]
i = 3
arr[] = {10, 30, 40, 50, 80, 90, 70} // 90 and 50 Swapped
We come out of loop because j is now equal to high-1.
Finally we place pivot at correct position by swapping
arr[i+1] and arr[high] (or pivot)
arr[] = {10, 30, 40, 50, 70, 90, 80} // 80 and 70 Swapped
Now 70 is at its correct place. All elements smaller than
70 are before it and all elements greater than 70 are after
it.
1.3 源程序
/*************A.QuickSort for integers array deal *************
Editor:Zhang Tony
Date:2017/7/16
Decription:QuickSort to sort the integers array
***************************************************************/
/* C implementation QuickSort */
#include<stdio.h>
// A utility function to swap two elements
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
/* This function takes last element as pivot, places
the pivot element at its correct position in sorted
array, and places all smaller (smaller than pivot)
to left of pivot and all greater elements to right
of pivot */
int partition (int arr[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high]; // pivot
int i = (low - 1); // Index of smaller element
int j;
for (j = low; j <= high- 1; j++)
{
// If current element is smaller than or
// equal to pivot
if (arr[j] <= pivot)
{
i++; // increment index of smaller element
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);
return (i + 1);
}
/* The main function that implements QuickSort
arr[] --> Array to be sorted,
low --> Starting index,
high --> Ending index */
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high)
{
if (low < high)
{
/* pi is partitioning index, arr[p] is now
at right place */
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
// Separately sort elements before
// partition and after partition
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
/* Function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i=0; i < size; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
quickSort(arr, 0, n-1);
printf("Sorted array: \n");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Output:
Sorted array:
1 5 7 8 9 10
1.4 Analysis of QuickSort
Time taken by QuickSort in general can be written as following.
T ( n ) = T ( k ) + T ( n − k − 1 ) + θ ( n ) T(n) = T(k) + T(n-k-1) + \theta(n) T(n)=T(k)+T(n−k−1)+θ(n)
The first two terms are for two recursive calls, the last term is for the partition process. k is the number of elements which are smaller than pivot.
The time taken by QuickSort depends upon the input array and partition strategy. Following are three cases.
- Worst Case: The worst case occurs when the partition process always picks greatest or smallest element as pivot. If we consider above partition strategy where last element is always picked as pivot, the worst case would occur when the array is already sorted in increasing or decreasing order. Following is recurrence for worst case.
T ( n ) = T ( 0 ) + T ( n − 1 ) + θ ( n ) T(n) = T(0) + T(n-1) + \theta(n) T(n)=T(0)+T(n−1)+θ(n)
which is equivalent to
T ( n ) = T ( n − 1 ) + θ ( n ) T(n) = T(n-1) + \theta(n) T(n)=T(n−1)+θ(n)
The solution of above recurrence is θ ( n 2 ) \theta(n2) θ(n2).
- Best Case: The best case occurs when the partition process always picks the middle element as pivot. Following is recurrence for best case.
T ( n ) = 2 T ( n / 2 ) + θ ( n ) T(n) = 2T(n/2) + \theta(n) T(n)=2T(n/2)+θ(n)
The solution of above recurrence is θ ( n L o g n ) \theta(nLogn) θ(nLogn). It can be solved using case 2 of Master Theorem.
- Average Case:
To do average case analysis, we need to consider all possible permutation of array and calculate time taken by every permutation which doesn’t look easy.
We can get an idea of average case by considering the case when partition puts O(n/9) elements in one set and O(9n/10) elements in other set. Following is recurrence for this case.
T ( n ) = T ( n / 9 ) + T ( 9 n / 10 ) + θ ( n ) T(n) = T(n/9) + T(9n/10) + \theta(n) T(n)=T(n/9)+T(9n/10)+θ(n)
Solution of above recurrence is also O ( n L o g n ) O(nLogn) O(nLogn)
Although the worst case time complexity of QuickSort is O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) which is more than many other sorting algorithms like Merge Sort and Heap Sort, QuickSort is faster in practice, because its inner loop can be efficiently implemented on most architectures, and in most real-world data. QuickSort can be implemented in different ways by changing the choice of pivot, so that the worst case rarely occurs for a given type of data. However, merge sort is generally considered better when data is huge and stored in external storage.
2.快排的衍生应用——Partition函数
2.1 Partition函数浅谈
如上述快速排序算法中的核心,选取数组中Pivot的值,大于它的值都放在一边,小于它的值都放在 另一边,这样就可以快速讲数组中的元素二分。
基于此思想,我们有几种实现思路。
- 思路I
1.算法思路
- 使用第一个数组元素作为枢轴点,即为pivot;
- 使用一个指针去扫描整个数组,凡是小于pivot的全部放到数组左端;
- 最后将pivot放到数组中间的位置,pivot左边全部都是小于它的数字,右边反之,最后返回pivot的位置信息;
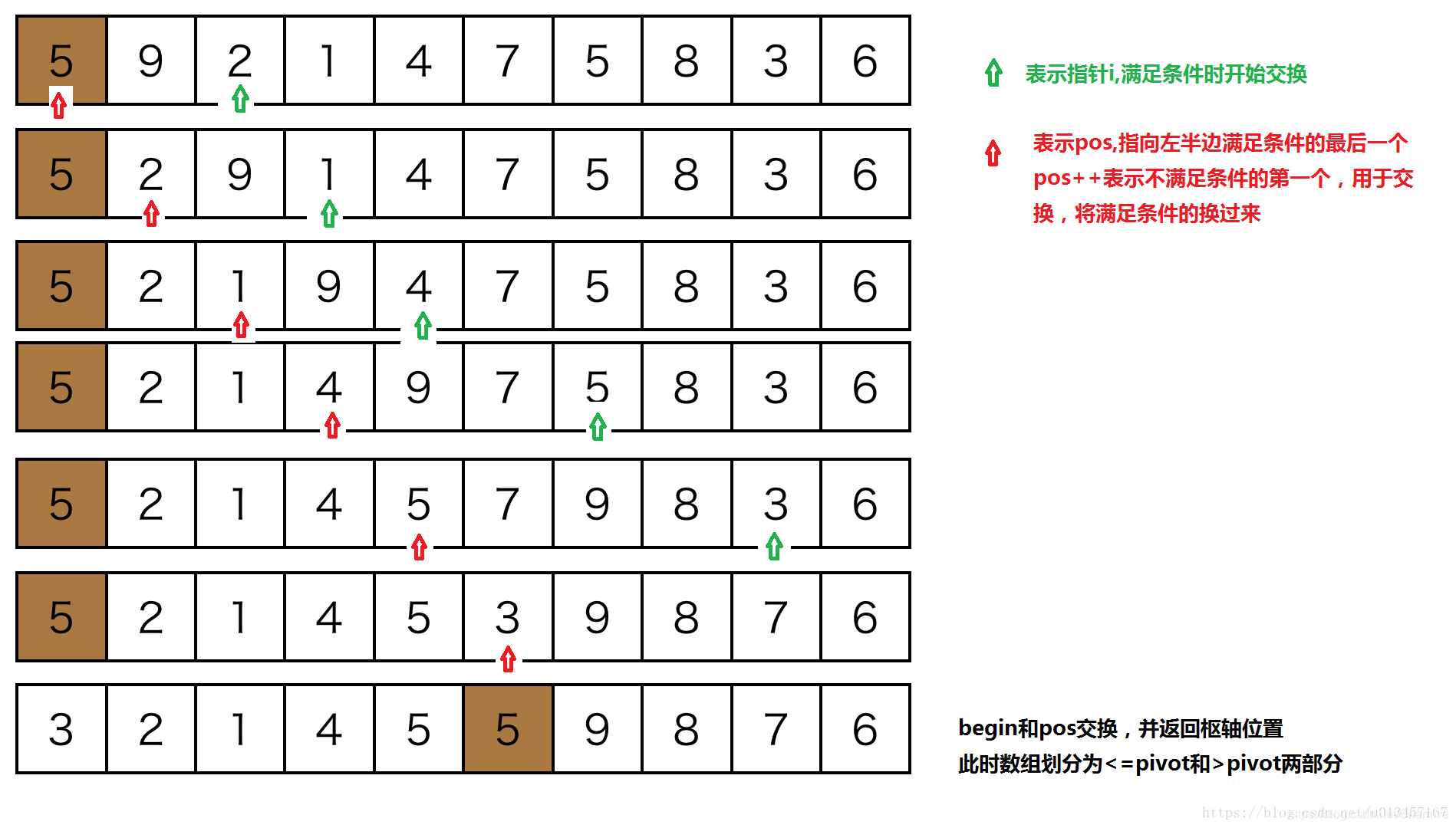
2. 实现代码:
void swap(int &x, int &y)
{
int t = x;
x = y;
y = t;
}
int partition(vector<int> &nums, int begin, int end)
{
int pivot = nums[begin];//枢轴(也可以是在begin和end之间的随机数)
// Last position where puts the no_larger element.
//凡是小于pivot的全部放到数组左端,pos指向<枢轴值的最后一个
//pos++指向不满足条件的(用于交换,将满足条件的换过来)
int pos = begin;
for (int i = begin + 1; i < end; ++i)
{
if (nums[i] < pivot)
{
pos++;
if (i != pos) //避免自身交换
swap(nums[pos], nums[i]);
}
}
swap(nums[pos], nums[begin]);
return pos;
}
注意: i < end表示并没有访问end值。此时若快排,end=元素个数。
3.算法分析
这种实现思路比较直观,但是其实并不高效。从直观上来分析一下,每个小于pivot的值基本上(除非到现在为止还没有遇见大于pivot的值)都需要一次交换,大于pivot的值(有可能需要被交换多次才能到达最终的位置。
- 思路II
1.算法思路
- 就如快速排序中最常使用的那样,使用两个指针分别从头部和尾部进行扫描,头部遇到大于pivot的数和尾部遇到小于pivot的数进行交换;
- 使用了两个指针,效率更高一点;避免使用swap函数
如果我们考虑用 Two Pointers 的思想,保持头尾两个指针向中间扫描,每次在头部找到大于pivot的值,同时在尾部找到小于pivot的值,然后将它们做一个交换,就可以一次把这两个数字放到最终的位置。一种比较明智的写法如下:
2.实现代码
//Two Pointers思想的分割函数(begin为0,end为n-1)
int Partition(vector<int> &nums, int begin, int end)
{
int pivot = nums[begin];//第一个记录作为枢轴(也可是在begin和end之间的随机数)
while (begin < end)
{
while (begin < end && nums[end] >= pivot)
{
end--;
}
nums[begin] = nums[end];//尾部找到小于pivot的值,移到低端
while (begin < end && nums[begin] <= pivot)
{
begin++;
}
nums[end] = nums[begin];//头部找到大于pivot的值,移到高端
}
nums[begin] = pivot;//枢轴基准归位
return begin;
}
注意: 这里访问了end值,此时若快排,end=最大下标n-1。
3.算法分析
直观上来看,赋值操作的次数不多,比前面单向扫描的swap次数都少,效率应该会更高。
2.2 衍生应用案例分析
根据上述的分析,我们发现:
- Partition函数交换了数组中的元素,也就是修改了原数组(这一点我们需要在选择方案时注意)
- 对于已经排好序的数组,这个函数的时间复杂度太高,特殊情况下我们可以特殊处理,可直接采用取中间值等的方法。
接下来,我们以《剑指Offer》中的两道题作为分析。
(1)剑指offer39:数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
题目:数组中由一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。例如,输入一个长度为9的数组{1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2}。由于数字2在数组中出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2.
解法1:基于Partiton函数的时间复杂度为O(n)的算法
这道题除了使用排序的方法(时间复杂度 O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn)),我们根据数组中元素的特性:数组中由一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半。如果把这个数组排序,那么排序之后位于数组中间的数字就是我们要找的那个。统计学上的中位数。
想到这里,我们就能采用Partition函数的思想,我们先在数组中随机选择一个数字,然后调整数组中数字的顺序,使得比选中的数字小的数字都排在它的左边,比选中的数字大的数字都排在它的右边。
- 如果这个选中的数字的下标刚好是n/2,那么这个数字就是数组的中位数。
- 如果它的下标大于n/2,那么中位数应该位于它的左边,我们可以接着在它的左边部分的数组中查找。
- 如果它的下标小于n/2,那么中位数应该位于它的右边,我们可以接着在它的右边部分的数组中查找。
这是一个典型的递归过程,实现代码如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
bool g_bInputInvalid = false;
bool CheckInvalidArray(int* numbers, int length)
{
bool g_bInputInvalid = false;
if(numbers == NULL || length <= 0)
bool g_bInputInvalid = true;
return g_bInputInvalid;
}
bool CheckMoreThanHalf(int*numbers, int length, int number)
{
int times = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
if(numbers[i] == number)
times++;
}
bool isMoreThanHalf = true;
if(times*2 <= length)
{
g_bInputInvalid = true;
isMoreThanHalf = false;
}
return isMoreThanHalf;
}
// A utility function to swap two elements
void Swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
int Partition (int arr[], int low, int high) // low~high : 0~n-1
{
int pivot = arr[high]; // pivot
int i = (low - 1); // Index of smaller element
for (int j = low; j <= high - 1; j++)
{
// If current element is smaller than the pivot
if (arr[j] < pivot)
{
i++; // increment index of smaller element
Swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
Swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);
return (i + 1);
}
int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int* numbers, int length)
{
if(CheckInvalidArray(numbers, length))
return 0;
int start = 0;
int end = length - 1;
int middle = length >> 1;
int index = 0;
//利用
while (start != middle)
{
if(index > middle)
{
end = index - 1;
index = Partition(numbers, start, end);
}
else
{
start = index + 1;
index = Partition(numbers, start, end);
}
}
int result = numbers[middle];
if(!CheckMoreThanHalf(numbers, length, result))
return 0;
return result;
}
int main()
{
int a[] = {1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2};//{3,4,5,1,2};
int length = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
cout<<MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(a,length);
return 0;
}
解法2:根据数组特点找出时间复杂度为O(n)的算法
数组中由一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,也就是说它出现的次数比其他所有数字出现次数的总和还要多。
因此,我们可以考虑在便利数组的时候记录两个值:一个是数组中的一个数字,另一个是次数。
当我们遍历到下一个数字的时候,如果下一个数字和我们之前保存的数字相同,则次数加1;如果下一个数字与我们之前保存的数字不同, 则次数减1。如果次数为零,那么我们需要保存下一个数字,并把次数设为1.
由于我们要找的数字出现的次数比其他所有数字出现的次数之和还要多,那么我们要找的数字肯定是最后一次把次数设为1时的数字。
下面是这种思路的参考代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
bool g_bInputInvalid = false;
bool CheckInvalidArray(int* numbers, int length)
{
bool g_bInputInvalid = false;
if(numbers == NULL || length <= 0)
bool g_bInputInvalid = true;
return g_bInputInvalid;
}
bool CheckMoreThanHalf(int*numbers, int length, int number)
{
int times = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
if(numbers[i] == number)
times++;
}
bool isMoreThanHalf = true;
if(times*2 <= length)
{
g_bInputInvalid = true;
isMoreThanHalf = false;
}
return isMoreThanHalf;
}
int MoreThanHalfNum(int* numbers, int length)
{
if(CheckInvalidArray(numbers, length))
return 0;
int result = numbers[0];
int times = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < length; i++)
{
if(times == 0)
{
result = numbers[i];
times = 1;
}
else if(numbers[i] == result)
times++;
else
times--;
}
if(!CheckMoreThanHalf(numbers, length, result))
return 0;
return result;
}
int main()
{
int a[] = {1,2,3,2,2,2,5,4,2};//{3,4,5,1,2};
int length = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
cout<<MoreThanHalfNum(a,length);
return 0;
}
类似于数组中数字出现的次数这样的题目还有很多,下一期我会归纳整理后发布。
(2)剑指offer40:最小的k个数
题目:输入n个整数,找出其中最小的k个数。例如,输入4,5,1,6,2,7,3,8这个8个数,则最小的4个数是1,2,3,4.
解法1:基于Partiton函数的时间复杂度为O(n)的算法
基于数组的第k个数字来调整,使得比第k个数字小的所有数字都位于数组的左边,比第k个数字大的所有数字都位于数组的右边。调整之后,位于数组左边的k个数字就是最小的k个数字(这k个数字不一定是排序的)。时间复杂度O(N)
void GetLeastKNumbers(int* input, int n, int* output, int k)
{
if(input == nullptr || output == nullptr || k > n || n<=0 ||k<=0)
return;
int start = 0;
int end = n - 1;
int index = Partition(input, n, start, end);
while(index != k)
{
if(index > k-1)
{
end = index - 1;
index = Partition(input, n, start, end);
}
else
{
start = index + 1;
index = Partition(input, n, start, end);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i<k; i++)
output[i] = input[i];
}
解法2:时间复杂度为 O ( n l o g k ) O(nlogk) O(nlogk)的算法,特别适合海量数据
创建一个大小固定为k的数据容器来存储最小的k个数字。接下来每次从输入的n个整数读入一个数,如果容器中已有的数字个数小于k,则直接把这次读入的数字放入容器;如果容器中已有k个数字(容器满了),此时我们需要换出这k个数字中的最大值或抛弃这次输入的数字。
因此,当容器满了之后,我们需要做3件事:
- 在k个整数中找到最大数;
- 有可能在这个容器中删除最大数;
- 有可能要插入一个新的数字。
如果用一棵二叉树来实现这个数据容器,那么我们能在 O ( l o g k ) O(logk) O(logk)时间内实现这3步。因此输入n个数而言,总的时间复杂度就是 O ( n l o g k ) O(nlogk) O(nlogk)。
我们可以选择用不同的二叉树来实现这个数据容器。由于每次都需要找到k个整数的最大数字,我们很容易想到用最大堆。在最大堆中,根结点的值总是大于它的子树中任意节点的值。但是,我们自己从头实现一个最大堆需要一定的代码量,这在面试短短的几十分钟内很难完成。(限于篇幅,本文就不详细介绍,有兴趣的读者可以详细实现一下最大堆,主要是它的思想。)
我们还可以采用红黑树来实现我们的容器。红黑树把节点分为红、黑两种颜色并根据一些规则确保输在一定程度上是平衡的,从而保证在红黑树中的查找、删除和插入操作都只需要
O
(
l
o
g
k
)
O(logk)
O(logk)时间。在STL中,set和multiset都是基于红黑树实现的。


3. 精选大厂面试实战
(1)阿里云笔试
题目:数组中比第x个值大的放在左边,比它小的放在右边,如果左边的最小值f是右边的最大值g的倍数就计数,输出最终满足条件的个数。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int count = 0;
int RandomInRange(int a, int b)
{
int temp = 0;
do
{
temp = rand()%(b-1);
}
while(temp < a || temp > b);
return temp;
}
void Swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
int Partition(int data[], int length, int start, int end, int k)
{
if(data == NULL || length <= 0 || start < 0 || end > length)
printf("Invalid Parameters");
//throw new std::exception("Invalid Parameters");
int temp = data[k];
int dat = data[0];
//cout<<"\ntemp: "<<temp<<endl;
int i,j;
i = start-1, j = end-1;
do
{
while(data[j] < temp && i < j) j--;
if(i<j) data[i++] = data[j];
while(data[i] > temp && i < j) i++;
if(i<j) data[j--] = data[i];
}while(i != j);
data[i] = dat;
return i+1;
}
int max(int a[], int start, int end)
{
int max = a[start-1];
for(int i = start-1; i < end; i++)
{
if(a[i] > max)
max = a[i];
}
return max;
}
int min(int a[], int start, int end)
{
int min = a[start-1];
for(int i = start-1; i < end; i++)
{
if(a[i] < min)
min = a[i];
}
return min;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin>>n;
int count = 0;
int i,j;
int* a = new int(n+1);
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
cin>>a[j];
for(int k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
int* b = new int(n+1);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
b[i] = a[i];
int index = Partition(b, n, 1, n, k);
//cout<<index<<endl;
for(j = 0; j < n-1; j++)
cout<<b[j]<<" ";
cout<<b[j]<<endl;
int fmin = min(b, 1, index);
int gmax = max(b, index, n);
if(fmin % gmax == 0)
count++;
}
cout<<count<<endl;
delete[] a;
return 0;
}
(2)乐鑫科技笔试
题目:一个村庄里有n个人,假如有m个富人,请问这m个富人所占的财富比重是多少。如用到排序算法请说明时间复杂度。
本题跟找出数组中最小的k个数是一样的,所以Partition实现可以参考前一题。
这里给出采用冒泡排序的方法,但是这个时间复杂度太高 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)。
分析: 要得出这m个富人,肯定得用到排序的逻辑,但是如何排序使得时间复杂度更低,这是一个需要考虑的问题。
这里,我首先想到的是冒泡排序,只需要找出这较不富裕的n-m个人就可以顺利解决这题。那么可以缩短这个n!次比较次数,缩短为n*m! (这里m<n).
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define DateType int
void swap(int *xp, int *yp)
{
int temp = *xp;
*xp = *yp;
*yp = temp;
}
void BobbleSort(DateType arr[], int len, int m) //第n-m个最小值放在数据末尾
{
int i,j,count = 0;
int max = 0;
if(len>=m)
{
for (i = 0; i<len-m; i++)
for(j = i; j<len-i-1; j++)
if(arr[j]<arr[j+1])
swap(&arr[j], &arr[j+1]);
}
else
printf("given 'm' is illegal\n");
}
void myprint(int arr[], int len)
{
for(int i = 0; i<len; i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<' ';
cout<<endl;
}
int main(void)
{
int m,n; //总人数n,m个富人
cin>>n;
cin>>m;
double sum_n,sum_m;
sum_n = sum_m = 0;
int *arr=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
//int arr[] = {10, 5, 7, 5, 9, 3, 6, 7, 8, 4};
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
cin>>*(arr+i);
sum_n += *(arr+i);
}
myprint(arr, n);
BobbleSort(arr, n, m);
myprint(arr, n);
for(int j = 0; j<m; j++)
sum_m += *(arr+j);
printf("%.2f\n", sum_m/sum_n);
return 0;
}
4. 进阶应用
三分partition算法,顾名思义,也就是将数组按照规则分为三个部分,比如非常经典的国旗问题Dutch national flag problem,就是要给定的红、白、蓝三色随机颜色小球按照红、白、蓝的顺序进行排序,利用partition算法,使用一个指针进行扫描,红色的小球就用swap()放到左边,白色的保持位置不变,蓝色的同样使用swap()放到右边,最后就得到要求的序列了。
LeetCode中有恰好有这么一个题:75. Sort Colors!
class Solution
{
public:
void sortColors(vector<int> &nums)
{
int len = nums.size();
int left = 0;
int right = len - 1;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
if(i > right)
break;
if(nums[i] == 1)
continue;
else if(nums[i] == 0)
{
swap(nums[i], nums[left]);
left++;
}
else
{
swap(nums[i], nums[right]);
right--;
i--;
}
}
}
};
LeetCode 324. Wiggle Sort II
LeetCode中的第324题中也同样可以使用三分partition算法,该题的discuss中,StefanPochmann大神提出一种O(n)+O(1)复杂度的高效算法,原链接为:
解题思路:

class Solution
{
public:
void wiggleSort(vector<int>& nums)
{
int n = nums.size();
// Find a median.
auto midptr = nums.begin() + n / 2;
nth_element(nums.begin(), midptr, nums.end());
int mid = *midptr;
// Index-rewiring.
#define A(i) nums[(1+2*(i)) % (n|1)]
// 3-way-partition-to-wiggly in O(n) time with O(1) space.
int i = 0, j = 0, k = n - 1;
while (j <= k)
{
if (A(j) > mid)
swap(A(i++), A(j++));
else if (A(j) < mid)
swap(A(j), A(k--));
else
j++;
}
}
};
更多关于排序算法的变式应用,我将会在之后的文章中继续更新。
推荐阅读:
[1] 数据结构与算法 | 二分查找:剑指offer53 在排序数组中查找数字
[2] 数据结构与算法 | 数据结构中到底有多少种“树”?一文告诉你
关注微信公众号:迈微电子研发社,获取更多精彩内容,首发于个人公众号。

知识星球
专为求职面试中算法与数据结构的小伙伴,创了学习交流/刷题群(知识星球)!想要最快的提升算法与数据结构技能,和更多小伙伴一起来吧!
进群获取互联网大厂高频coding题库,告别刷题400道,分类整理的题库,算法思路和源代码实现配套,各个类型总结出来的解题模板,远比你一个人要强!












 这篇博客探讨了快速排序算法中的Partition函数,包括其原理、实现方式和时间复杂度分析。作者提到了Partition函数在已排序数组中的效率问题,并讨论了它的衍生应用,如在《剑指Offer》题目中的解决方案。此外,还分享了在阿里云和乐鑫科技笔试中涉及的相关问题,以及快速排序的进阶应用,如三分partition算法在LeetCode题目中的应用。
这篇博客探讨了快速排序算法中的Partition函数,包括其原理、实现方式和时间复杂度分析。作者提到了Partition函数在已排序数组中的效率问题,并讨论了它的衍生应用,如在《剑指Offer》题目中的解决方案。此外,还分享了在阿里云和乐鑫科技笔试中涉及的相关问题,以及快速排序的进阶应用,如三分partition算法在LeetCode题目中的应用。




















 7882
7882

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










