ϵ−SVR
SVR回归中,基本思路和SVM中是一样的,在
ϵ−SVR
[Vapnic,1995] 需要解决如下的优化问题。
min 12||w||2+C∑i=1l(ξi+ξ∗i)
s.t. ⎧⎩⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪yi−(wTxi+b)<ϵ+ξi(wTxi+b)−yi<ϵ+ξ∗iξi,ξ∗i≥0
细心的读者可能已经发现了与 C−SVM 中的具有相似的地方,但又不太一样,那么如何理解上述公式呢?
假设我们的训练数据集是 {(x1,y1),(x2,y2),...(xn,yl)}
我们的目标是找到一个函数,比如线性函数 f(x)=wTx+b ,使得
如果数据离回归函数的偏差 |yi−wTx−b|<ϵ| (下图非色区域),我们是能接受的,不需要付出任何代价(即不需要在代价函数中体现)。我们只关注偏差大于 ϵ 的代价。举个例子来说,就好比我们在换外币时,我们并不关注少量 ϵ 损失,这部分损失是汇率引起的合理损失。
所以约束条件是保证更多多的数据点都在灰色范围内(拟合最佳的线性回归函数,使得更多的点落在我们接受的精度范围内),即 |yi−wTx−b|<ϵ| 。但是我们发现,还是会有一部分点,偏差比较大,落在灰色区域之外,所以类似SVM中使用的方法,引入松弛因子,采取软边界的方法,而且上下采取不同的松弛因子 ξi,ξ∗i≥0 ,这样就不难得出约束条件为:
s.t. ⎧⎩⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪yi−(wTxi+b)<ϵ+ξi(wTxi+b)−yi<ϵ+ξ∗iξi,ξ∗i≥0
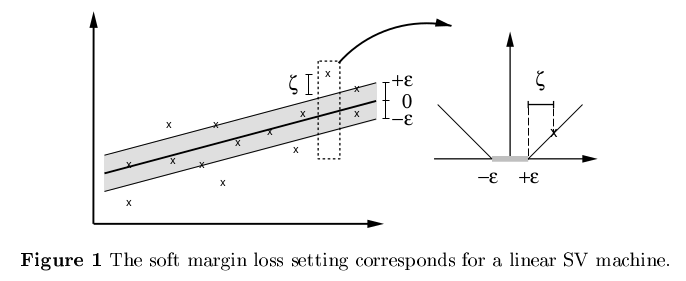
如同SVM中一样的,在多数情况下转换为对偶问题更容易计算。同时还可以计算出 w 和 b ,直接看文献1吧。
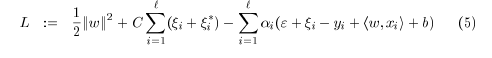

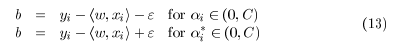
详细推导过程看文献1。
使用核函数的 ϵ−SVR
文献2
ν−SVR

Chang and Lin (2002) prove that
ϵ
-SVR with parameters
(C¯¯¯̄ ,ϵ)
has the same solution as
ν
-SVR with parameters
(lC¯¯¯̄ ,ν)
.
其实两种SVR在满足一定条件下,具有相同的解。
优缺点分析
Scikit代码
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
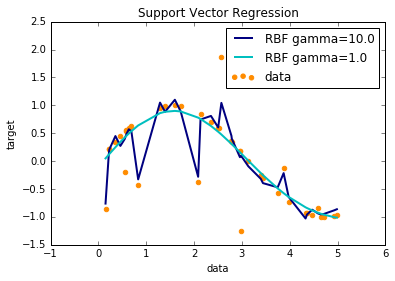
RBF不同参数:
不同核函数:






















 3040
3040

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








