数组是相同类型的数据放在一起存储的结果。可以通过序号来引用任何一个元素。
通过如下方式声明数组:
int[] a;//此时a-->null,因为没有初始化
int d[];//效果同上
int[] b = new int[100];//此时b的长度是100,可以存放100个int元素,但是内部每个元素是没有初始化的
//声明数组,设置数组长度,并对每个元素进行初始化
int[] c = new int[20];
for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
c[i] = 0;
boolean[] e = new boolean[50];
char[] f = new char[0];//长度为0,表明没有元素,但是不是null啊
String[] g = new String[5];//其他类型也可以声明数组的
for(int i = 0; i < g.length; i++)//而且可以通过数组的length属性获取数组的长度
{
g[i] = "";
}
1 for each 循环
for(变量:集合)语句
数组是一种集合。
int[] c = new int[20];
for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
c[i] = 0;
for(int i : c)
System.out.println(i);
//上面就使用了foreach循环提示:可以使用System.out.println(Arrays.toString(c));把数组输出
2 数组初始化和匿名数组
int[] a;
a = { 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13};//初始化了一个数组
a = new int[]{ 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13};//效果同上
//采用这样的匿名数组,可以直接对数组初始化。这样得到的数组就是确定长度的,而且每个元素都被初始化了3 数组的复制
int[] a = {1, 2, 3};
int[] b = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length);//复制数组,
int[] c = Arrays.copyOf(a, 1);//只复制了a的第一个元素
int[] d = Arrays.copyOf(a, 5);//复制了数组,后面的用0填充,如果是布尔型的化用false填充注意:幅值的数组和原数组有这相同的元素引用,对于基本类型还好,如果是非基本类型,那么只要改变复制数组中被复制的元素的属性什么的,那么原数组也会改变的。必须尤其注意这点,不然产生的bug有你找的了。
4 命令行数组
其实我们早就见过数组了
public class Welcome
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Hello, world!");
}
}main方法传入的就是数组。
具体是通过执行.class文件的命令后面的参数就会被输入到args里面。
java Welcome a b ccc
//等同于 args = {"a", "b", "ccc"};5 数组排序
int[] a = {5, 7, 3, 2, 5, 8, 9, 0};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[5, 7, 3, 2, 5, 8, 9, 0]
Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));//[0, 2, 3, 5, 5, 7, 8, 9]一些Arrays类的方法。
- static String toString(type[] a)
a可以是 int、long、short、char、byte、boolean、float、double、 - static type[] copyOf(type[] a, int length)
- static type[] copyOf(type[] a, int start, int end)
复制数组 - static void sort(type[] a)
排序 - static int binarySearch(type[] a, type v)
- static int binarySearch(type[] a, int start, int end, type v)
二分搜索算法查找v,找到则返回序号,找不到就返回-1 - static void fill(type[] a, type v)
用v填充数组 - static boolean equals(type[] a,type[] b)
比较
6 多维数组
double[][] balances = new double[5][6];
int[][] magicSquare =
{
{16, 3, 2, 13},
{6, 3, 12, 13},
{9, 13, 2, 13},
{4, 15, 14, 1}
};
for(double[] row : a)
for(double value : row)
//做一些事情,这是用foreach循环的哦多维数组的理解很简单,就是数组的数组嘛。
7 不规则数组
还是那句话“数组的数组”
先定义多维数组,再对每一个数组进行不等长的初始化,那就是不规则的喽。
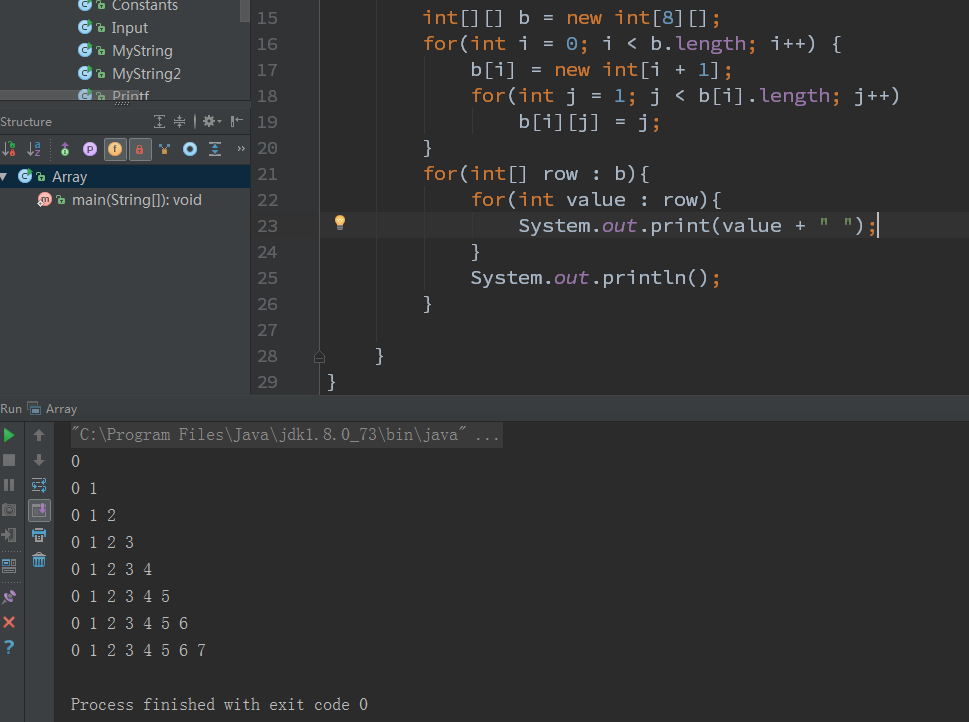
int[][] b = new int[8][];
for(int i = 0; i < b.length; i++)
{
b[i] = new int[i + 1];
for(int j = 1; j < b[i].length; j++)
b[i][j] = j;
}
for(int[] row : b)
{
for(int value : row)
{
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}





















 218
218

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








