JAVA——IO流
File类
- File类的一个对象,代表一个文件或一个文件目录(俗称:文件夹)
- 声明在java.io下
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-0DQzf0Ci-1636451757423)(C:\Users\10153\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20211104185752333.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a3857319a5aa4a4ca2b2d4d7cabe1251.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZHJvaWRzYW5zZmFsbGJhY2s,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA57-U5LuU5bCP6aaS5aS0,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
-
相对路径:相较于某个路径下,指明的路径。举例:
File file = new File("hello.txt"); -
绝对路径:包含盘符在内的文件或文件目录的路径。举例:
File file1 = new File("D:\\JDK8\\1project\\IO\\src\\File\\hello.txt"); -
四种构造器
public void test1(){
//构造器1
//public File(String filepath) 指明相对路径
File file1 = new File("hello.txt");
File file = new File("hello.txt");
File file2 = new File("D:\\JDK8\\1project\\IO\\src\\File\\hi.txt");
System.out.println(file1);//hello.txt
System.out.println(file2);//D:\JDK8\1project\IO\src\File\hi.txt
//构造器2
//public File(String parentPath,String childPath) parentPath目录下的childPath文件夹
File file3 = new File("D:\\JDK8\\1project\\IO\\src","File");
System.out.println(file3);//D:\JDK8\1project\IO\src\File
//构造器3
//public File(File file,String filePath) file目录下的filePath文件
File file4 = new File(file3,"hi.txt");
System.out.println(file4);//D:\JDK8\1project\IO\src\File\hi.txt
}
常用方法
获取
public void test3(){
File file = new File("D:\\JDK8\\1project\\IO\\src\\File");
//获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件目录的名称数组:file.list()
String[] list = file.list();
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}//FileTest.java
//hello.txt
// hi.txt
//获取指定目录下的所有文件或文件目录的File数组
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File file1 : files) {
System.out.println(file1);
}
/*
D:\JDK8\1project\IO\src\File\FileTest.java
D:\JDK8\1project\IO\src\File\hello.txt
D:\JDK8\1project\IO\src\File\hi.txt
*/
}
public void test2(){
File file = new File("hello.txt");
File file1 = new File("D:\\JDK8\\1project\\IO\\src\\File\\hi.txt");
//获取绝对路径:public String getAbsoluteFile()
System.out.println(file.getAbsoluteFile());//D:\JDK8\1project\IO\hello.txt
System.out.println(file1.getAbsoluteFile());//D:\JDK8\1project\IO\src\File\hi.txt
System.out.println();
//获取路径String getPath()
System.out.println(file.getPath());//hello.txt
System.out.println(file1.getPath());//D:\JDK8\1project\IO\src\File\hi.txt
System.out.println();
//获取名称 String getName()
System.out.println(file.getName());//hello.txt
System.out.println(file1.getName());//hi.txt
System.out.println();
//获取上层文件目录,若无返回null String getParent()
System.out.println(file.getParent());//null
System.out.println(file1.getParent());//D:\JDK8\1project\IO\src\File
System.out.println();
//获取文件长度(字节数) length()
System.out.println(file.length());//12
System.out.println(file1.length());//9
System.out.println();
//获取最后一次修改时间(毫秒值)lastModified())
System.out.println(file.lastModified());//1636024940645
System.out.println(new Date(file.lastModified()));//Thu Nov 04 19:22:20 GMT+08:00 2021
System.out.println(file1.lastModified());//1636024816752
System.out.println(new Date(file1.lastModified()));//Thu Nov 04 19:20:16 GMT+08:00 2021
}
重命名
public void test4(){
//把文件重命名为指定的文件路径:相当于重命名并移动位置
File file1 = new File("hello1.txt");
File file11 = new File("D:\\JDK8\\1project\\IO");
File file2 = new File("D:\\JDK8\\1project\\IO\\src\\File\\hi.txt");
boolean b = file1.renameTo(file2);
System.out.println(b);//false
//要想保证成功,需要保证file1在硬盘中是存在的,且file2不能存在
File file3 = new File("D:\\JDK8\\1project\\IO\\src\\File\\hahaha.txt");
File file33 = new File("D:\\JDK8\\1project\\IO\\src\\File");
String[] list11 = file11.list();
for (String s1 : list11) {
System.out.println(s1);
}
/*
.idea
hello.txt
hello1.txt
IO.iml
out
src
*/
System.out.println();
String[] list33 = file33.list();
for (String s3 : list33) {
System.out.println(s3);
}
/*
FileTest.java
hello.txt
hi.txt
*/
boolean b1 = file1.renameTo(file3);
System.out.println(b1);//true
String[] list111 = file11.list();
for (String s1 : list111) {
System.out.println(s1);
}
/*
.idea
hello.txt
IO.iml
out
src
*/
System.out.println();
String[] list333 = file33.list();
for (String s3 : list333) {
System.out.println(s3);
}
/*
FileTest.java
hahaha.txt
hello.txt
hi.txt
*/
}
判断
public void test6(){
File file1 = new File("hello.txt");
File file2 = new File("D:\\JDK8\\1project\\IO\\src\\File");
//判断是否是文件目录 file1.isDirectory()
System.out.println(file1.isDirectory());//false
System.out.println(file2.isDirectory());//true
System.out.println();
//判断是否是文件file1.isFile()
System.out.println(file1.isFile());//true
System.out.println(file2.isFile());//false
System.out.println();
//判断是否存在file1.exists()
System.out.println(file1.exists());//true
System.out.println(file2.exists());//true
System.out.println();
//判断是否可读file1.canRead()
System.out.println(file1.canRead());//true
System.out.println(file2.canRead());//true
System.out.println();
//判断是否可写 file1.canWrite()
System.out.println(file1.canWrite());//true
System.out.println(file2.canWrite());//true
System.out.println();
//判断是否隐藏 file1.isHidden()
System.out.println(file1.isHidden());//false
System.out.println(file2.isHidden());//false
}
创建和删除
public void test7() throws IOException {
File file1 = new File("hi.txt");
//创建文件,若文件存在,则不创建,返回false :file1.createNewFile()
//删除:delete(); 若文件不存在,返回false
if(!file1.exists()){
file1.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建"+file1.getName()+"文件成功");
} else{
/*file1.delete();
System.out.println("删除"+file1.getName()+"文件成功");*/
System.out.println("创建"+file1.getName()+"文件失败");
}
//创建文件目录,若文件目录存在,则不创建,若上层文件目录不存在,则不创建,返回false
File file2 = new File("D:\\JDK8\\1project\\IO\\src\\File1");
boolean mkdir = file2.mkdir();
if(mkdir){
System.out.println("创建"+file2.getName()+"文件成功");
} else{
/*file1.delete();
System.out.println("删除"+file1.getName()+"文件成功");*/
System.out.println("创建"+file2.getName()+"文件失败");
}
//创建文件目录,若上层文件目录不存在,则一并创建
File file3 = new File("D:\\JDK8\\1project\\IO11\\src\\File1");
boolean mkdirs = file3.mkdirs();
if(mkdirs){
System.out.println("创建"+file3.getName()+"文件成功");
} else{
/*file3.delete();
System.out.println("删除"+file3.getName()+"文件成功");*/
System.out.println("创建"+file3.getName()+"文件失败");
}
}
IO流
IO原理

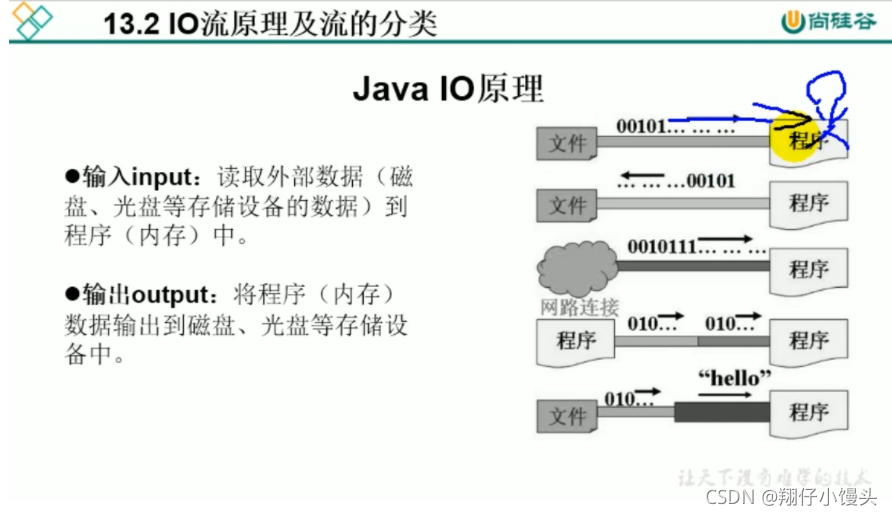
流的分类
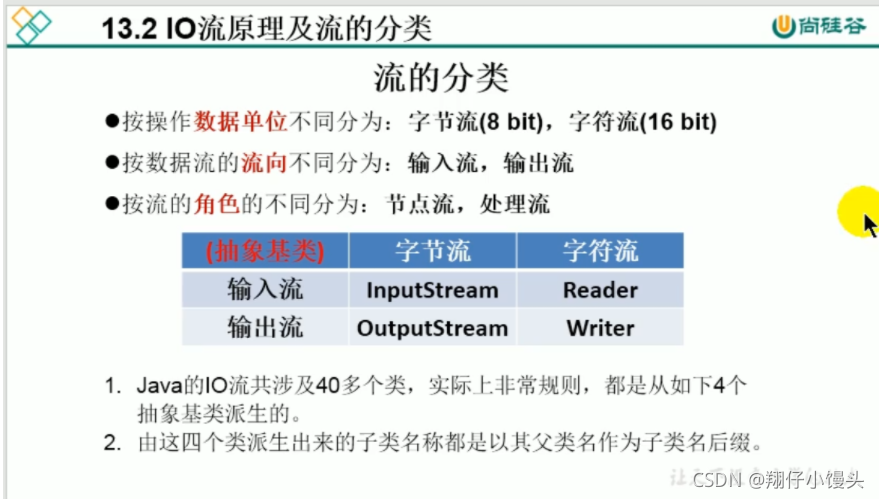
IO流体系
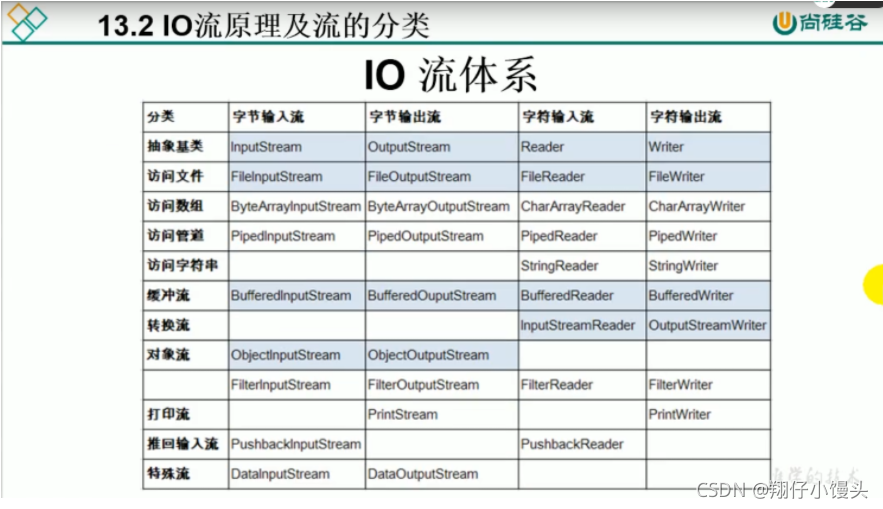
-
节点流(文件流):
FileInputStream,FileOutputStream,FileReader,FileWriter
-
缓冲流(处理流的一种):
BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream,BufferedReader,BufferedWriter
字符流示例
-
注:异常的处理:为了保证流资源一定可以执行关闭操作,需要使用try-catch-final处理
读入的文件一定要存在,否则会报FileNotFoundException
读入
/*
异常的处理:为了保证流资源一定可以执行关闭操作,需要使用try-catch-final处理
读入的文件一定要存在,否则会报FileNotFoundException
*/
public void test1(){
FileReader fileReader = null;
try {
//1.实例化File类的对象,指明要操作的文件
File file = new File("hello.txt");//相较于当前module
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
//D:\JDK8\1project\IO\IO流\hello.txt
//2.提供具体的流
fileReader = new FileReader(file);
//3.数据的读入过程
//read():返回读入的一个字符,如果达到文件末尾,返回-1
int data;
while((data = fileReader.read())!= -1){
System.out.print((char)data);
}//helloworld!
System.out.println();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.流的关闭操作
try {
if(fileReader != null)
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
-
更好的读入
public void test2() { FileReader fileReader = null; try { //1.实例化File类的对象,指明要操作的文件 File file = new File("hello.txt");//相较于当前module //2.提供具体的流 fileReader = new FileReader(file); //3.数据的读入过程 //read(char[] cbuffer):返回每次读入cbuffer数组中的字符的个数,如果达到文件末尾,返回-1 char[] cbuf = new char[5]; int len; while((len = fileReader.read(cbuf)) != -1){ //错误的写法,利用cbuf.length判断,输出的字符串只为5的整数倍,将文件中的字符读入时优先占用下标低的位置 /* for (int i = 0; i < cbuf.length; i++) { System.out.print(cbuf[i]);//输出为:helloworld!orld }*/ //方式1: for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { System.out.print(cbuf[i]); } } System.out.println(); //方式2 while((len = fileReader.read(cbuf)) != -1){ String s = new String(cbuf,0,len);//从cbuf数组取,从0开始取len个 System.out.print(s); } System.out.println(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(fileReader != null){ //4.资源的关闭 try { fileReader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
写出
-
输出操作:对应的File可以不存在,
如果不存在,在输出的过程中会自动创建此文件
如果存在,fileWriter = new FileWriter(file,true); 不会覆盖原有文件,在原有文件基础上追加内容,fileWriter = new FileWriter(file); /fileWriter = new FileWriter(file,false); 会覆盖原有文件
@Test
public void test3() {
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
try {
//1. 提供File类的对象,指明写出到的文件
File file = new File("hi.txt");
//2. 提供的对象用于数据的写出
fileWriter = new FileWriter(file,true);
//3.写出的操作
fileWriter.write("I have a dream!\n");
fileWriter.write("You need to have a dream!\n");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fileWriter != null){
try {
//4.流资源的关闭
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
读入加写出
public void test4() {
FileReader fileReader = null;
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
try {
//1. 提供File类的对象,指明读入和写出到的文件
File srcFile = new File("hello.txt");
File destFile= new File("hello1.txt");
//2.创建输入流和输出流的对象
fileReader = new FileReader(srcFile);
fileWriter = new FileWriter(destFile);
//3.数据的读入写入操作
char[] cbuf = new char[5];
int len;//记录每次读入到cbuf数组中的字符的个数
while((len = fileReader.read(cbuf)) != -1){
//每次写出len个字符
fileWriter.write(cbuf,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.关闭流资源
try {
if(fileWriter != null)
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(fileReader != null)
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字节流示例
-
复制图片(不能使用字符流处理图片视频等文件)
public void test5() { FileInputStream fi = null; FileOutputStream fo = null; try { //1. 提供File类的对象,指明读入和写出到的文件 File srcfile = new File("伊蕾娜.jpg"); File destfile = new File("伊蕾娜1.jpg"); //2. 提供字节流对象 fi = new FileInputStream(srcfile); fo = new FileOutputStream(destfile); //3. 读入写出数据 byte[] bbuf = new byte[5]; int len; while((len = fi.read(bbuf)) != -1){ fo.write(bbuf,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4. 关闭流资源 try { if(fo != null) fo.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(fi != null) fi.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } -
利用字节流读文本文字,中文会出乱码(txt,java,c,cpp),但是可以利用字节流复制文本文字
public void test2() { FileInputStream fi = null; try { //1. 提供File类的对象,指明读入和写出到的文件 File file = new File("hello.txt"); //2. 提供字节流对象 fi = new FileInputStream(file); //3. 读入写出数据 byte[] bbuf = new byte[5]; int len; while((len = fi.read(bbuf)) != -1){ String s = new String(bbuf, 0, len); System.out.print(s); }//helloworld!我���中国�� 中文会乱码 应该为:helloworld!我是中国人 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4. 关闭流资源 try { if(fi != null) fi.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } -
复制写成一个函数
public void testCopyFile(){ long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); String strpath = "伊蕾娜.jpg"; String destpath = "伊蕾娜2.jpg"; copyFile(strpath,destpath); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("操作花费的时间为:" + (end - start) + "ms"); } public void copyFile(String strpath,String destpath){//复制指定路径下文件的操作 FileInputStream fi = null; FileOutputStream fo = null; try { //1. 提供File类的对象,指明读入和写出到的文件 File srcfile = new File(strpath); File destfile = new File(destpath); //2. 提供字节流对象 fi = new FileInputStream(srcfile); fo = new FileOutputStream(destfile); //3. 读入写出数据 byte[] bbuf = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len = fi.read(bbuf)) != -1){ fo.write(bbuf,0,len); } //复制成功 System.out.println("复制成功"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4. 关闭流资源 try { if(fo != null) fo.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(fi != null) fi.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
缓冲流示例
-
作用:提高流的读取、写入的速度
-
原因:内部提供了一个缓冲区
-
flush():刷新缓冲区
-
示例:
public void BufferedStreamTest(){ BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try { //1.造文件对象 File srcfile = new File("伊蕾娜.jpg"); File destfile = new File("伊蕾娜3.jpg"); //2.1 造节点流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcfile); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destfile); //2.2 造缓冲流 bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); //3.读取和写入 byte[] buffers = new byte[10]; int len; while((len = bis.read(buffers)) != -1){ bos.write(buffers,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.资源关闭:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流 try { if(bos != null) bos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(bis != null) bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //说明:关闭外层流的同时:内层流也会自动的进行关闭,内层流可以省略 // fos.close(); // fis.close(); } -
字节流缓冲流速度对比:
public void testCopyFile(){ long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); String strpath = "伊蕾娜.jpg"; String destpath = "伊蕾娜4.jpg"; copyFileWithBufferd(strpath,destpath); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("处理流操作花费的时间为:" + (end - start) + "ms"); //76ms long start1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); String strpath1 = "伊蕾娜.jpg"; String destpath1 = "伊蕾娜5.jpg"; FileInputOutputTest fiot = new FileInputOutputTest(); fiot.copyFile(strpath1,destpath1); long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("节点流操作花费的时间为:" + (end1 - start1) + "ms"); //332ms }
//缓冲流实现文件复制的方法
public void copyFileWithBufferd(String srcPath,String destPath){
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
//1.造文件对象
File srcfile = new File(srcPath);
File destfile = new File(destPath);
//2.1 造节点流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcfile);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destfile);
//2.2 造缓冲流
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//3.读取和写入
byte[] buffers = new byte[10];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(buffers)) != -1){
bos.write(buffers,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.资源关闭:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流
try {
if(bos != null)
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(bis != null)
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//说明:关闭外层流的同时:内层流也会自动的进行关闭,内层流可以省略
// fos.close();
// fis.close();
}
//字节流实现文件复制的方法
public void copyFile(String strpath,String destpath){//复制指定路径下文件的操作
FileInputStream fi = null;
FileOutputStream fo = null;
try {
//1. 提供File类的对象,指明读入和写出到的文件
File srcfile = new File(strpath);
File destfile = new File(destpath);
//2. 提供字节流对象
fi = new FileInputStream(srcfile);
fo = new FileOutputStream(destfile);
//3. 读入写出数据
byte[] bbuf = new byte[10];
int len;
while((len = fi.read(bbuf)) != -1){
fo.write(bbuf,0,len);
}
//复制成功
System.out.println("复制成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4. 关闭流资源
try {
if(fo != null)
fo.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(fi != null)
fi.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
-
字符流示例:
public void testBufferedReadertest(){ BufferedReader br = null; BufferedWriter bw = null; try { //造文件造流 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("hello.txt"))); bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File("hello1.txt"))); //读写操作 //方式1: // char[] cbuf = new char[10]; // int len; // while((len = br.read(cbuf)) != -1){ // bw.write(cbuf,0,len); // } //方式2: String data; while((data = br.readLine()) != null){ //方法一: //bw.write(data + "\n");//data中不包含换行符 //方法二: bw.write(data);//data中不包含换行符 bw.newLine();//提供换行的操作 } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭资源 try { if(bw != null) bw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(br != null) br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
练习
-
实现图片的加密解密
//图片的加密 @Test public void test1() { BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try { bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("伊蕾娜.jpg"))); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("伊蕾娜(加密).jpg"))); //实现加密 byte[] bytes = new byte[20]; int len; while((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1){ //字节数组进行修改 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { bytes[i] = (byte) (bytes[i] ^ 5); //每一个位置上的数与5(0101)异或 } bos.write(bytes,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //资源关闭 try { if(bis != null) bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(bos != null) bos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }//图片的解密 public void test2() { BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try { bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("伊蕾娜(加密).jpg"))); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("伊蕾娜(解密).jpg"))); //实现加密 byte[] bytes = new byte[20]; int len; while((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1){ //字节数组进行修改 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { bytes[i] = (byte) (bytes[i] ^ 5); //每一个位置上的数与5(0101)异或 } bos.write(bytes,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //资源关闭 try { if(bis != null) bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(bos != null) bos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } -
获取文本上每个字符的出现的次数,并写入到另一个文本里
@Test public void test3() { FileReader fr = null; FileWriter fw = null; try { fr = new FileReader("hello.txt");//此处填想要识别的文件路径 HashMap<Character,Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); int len; while((len = fr.read()) != -1){ char ch = (char) len; if(hashMap.get(ch) == null){ hashMap.put(ch,1); }else { hashMap.put(ch,hashMap.get(ch)+1); } } //把map中数据存在文件count.txt中 fw = new FileWriter(new File("count.txt"));//此处填想要输出的文件路径 Set<Map.Entry<Character, Integer>> entrySet = hashMap.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry : hashMap.entrySet()) { switch (entry.getKey()){ case ' ': fw.write("空格=" + entry.getValue()); System.out.println("空格=" + entry.getValue()); break; case '\t': fw.write("tab键=" + entry.getValue()); System.out.println("tab键=" + entry.getValue()); break; case '\r': fw.write("回车=" + entry.getValue()); System.out.println("回车=" + entry.getValue()); break; case '\n': fw.write("换行=" + entry.getValue()); System.out.println("换行=" + entry.getValue()); break; default: fw.write(entry.getKey() +"="+ entry.getValue()); System.out.println(entry.getKey()+ "=" + entry.getValue()); break; } fw.write("\n"); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if(fr != null) fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(fw != null) fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
处理流中的转换流
-
属于字符流
InputStreamReader:将一个字节的输入流转换为字符的输入流
OutputStreamReader:将一个字符的输出流转换为字节的输出流
-
作用:提供字节流与字符流之间的转换
-
InputStreamReader的使用示例
public void test1(){ InputStreamReader isr = null; try { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("hello.txt")); //InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);//使用系统默认的字符集 isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"UTF-8"); //使用UTF-8的字符集,具体使用哪个取决于文件保存时使用的字符集 char[] cbuf = new char[20]; int len; while((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1){ for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { System.out.print(cbuf[i]); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if(isr != null) isr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } -
InputStreamReader,OutputStreamReader的使用示例
public void test2(){ InputStreamReader isr = null; OutputStreamWriter osw = null; try { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("hello.txt")); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("hello_gbk.txt")); //InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);//使用系统默认的字符集 isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"UTF-8"); osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk"); //使用UTF-8的字符集,具体使用哪个取决于文件保存时使用的字符集 char[] cbuf = new char[20]; int len; while((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1){ osw.write(cbuf,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if(isr != null) isr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(osw != null) osw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
其他流
标准输入输出流
import org.junit.Test;
import java.awt.peer.SystemTrayPeer;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.StringReader;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class OtherStreamTest {
// System.in;
// System.out;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//方法1:
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入字符串:");
while(scanner.hasNextLine()){
String s = scanner.nextLine();
if(("e".equalsIgnoreCase(s)) || ("exit".equalsIgnoreCase(s))){
System.out.println("退出程序");
break;
}else {
String s1 = s.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(s+"对应的大写字母为:"+s1);
}
System.out.println("请输入字符串:");
}
//方法2:
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
while (true){
System.out.println("请输入字符串");
String data = br.readLine();
if(data.equalsIgnoreCase("e") || data.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")){
System.out.println("结束");
break;
}else {
System.out.println(data+"对应的大写字母为:"+data.toUpperCase());
}
}
}
}
打印流
数据流
对象流

- 要想一个java对象是可序列化的,需要满足相应的要求:
- 重写Serializable接口
- 需要当前类提供一个常量:public final long serialVersionUID = 3214321412L;\
- 当前类的所有属性都是可序列化的
- 不能序列化static 和 transient的成员变量
@Test
//序列化过程
public void testObjectOutputStream() {
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("object.dat")));
oos.writeObject(new String("我们是冠军!"));
oos.flush();//刷新操作
oos.writeObject(new Person("Scout",23));
oos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(oos != null)
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Test
//反序列化过程:将磁盘文件中的对象还原为内存中的一个java对象
public void testObjectInputStream(){
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("object.dat")));
Object o = ois.readObject();
String str = (String) o;
Person p = (Person) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(p);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(ois != null)
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
-
- Person类:
import java.io.Serializable; public class Person implements Serializable { public final long serialVersionUID = 3214321412L; //定义序列版本号 private String name; private int age; public Person() { } public Person(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Person person = (Person) o; if (age != person.age) return false; return name != null ? name.equals(person.name) : person.name == null; } @Override public int hashCode() { int result = name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0; result = 31 * result + age; return result; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
随机存取文件流
- RandomAccessFile直接继承与java.lang.Object类,实现了DataInput和DataOutput接口
- RandomAccessFile既可以作为一个输入流,又可以作为一个输出流

public void testRandomAccessFile(){
RandomAccessFile raf1 = null;
RandomAccessFile raf2 = null;
try {
raf1 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("伊蕾娜.jpg"),"r");
raf2 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("伊蕾娜1.jpg"),"rw");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = raf1.read(buffer)) != -1){
raf2.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (raf1 != null)
raf1.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (raf2 != null)
raf2.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 如果RandomAccessFile作为输出流时,写出到的文件如果不存在,则在执行过程中自动创建
- 如果写出到的文件存在,则会对原有文件内容进行覆盖,默认情况下从头覆盖
public void test1(){
RandomAccessFile raf1 = null;
RandomAccessFile raf2 = null;
RandomAccessFile raf3 = null;
try {
raf1 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("hello.txt"),"rw");
raf2 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("hello.txt"),"r");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = raf2.read(buffer)) != -1){
String s = new String(buffer, 0, len);
System.out.println(s);
}
//abcdefghijklmn
raf1.write("opq".getBytes());
raf3 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("hello.txt"),"r");
byte[] buffer1= new byte[1024];
while ((len = raf3.read(buffer1)) != -1){
String s = new String(buffer1, 0, len);
System.out.println(s);
}
//opqdefghijklmn
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (raf1 != null)
raf1.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
-
实现从指定位置写入字符串
public void test2() { RandomAccessFile raf1 = null; try { raf1 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("hello.txt"), "rw"); //0123456789 raf1.seek(3);//将指针调到角标为3的位置 raf1.write("abc".getBytes());//从3开始覆盖 //012abc6789 raf1.seek(raf1.length());//将指针调到最后 raf1.write("哦哦哦".getBytes());//从最后开始写入 //012abc6789哦哦哦 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if(raf1 != null) raf1.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } -
实现插入字符串
//实现插入效果 public void test3() { RandomAccessFile raf1 = null; try { raf1 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("hello.txt"), "rw"); //0123456789 raf1.seek(3);//将指针调到角标为3的位置 //保存指针3后的所有数据到builder中 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder((int) new File("hello.txt").length()); byte[] buffer = new byte[20]; int len; while((len = raf1.read(buffer)) != -1){ builder.append(new String(buffer,0,len)); } //调回指针,写入 raf1.seek(3); raf1.write("我是插入的字符串".getBytes()); //将StringBuilder中的数据写到后面 raf1.write(builder.toString().getBytes()); //012我是插入的字符串3456789 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if(raf1 != null) raf1.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }






















 124
124











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








