- 在Linux系统中,绑定双网卡可以实现网络负载均衡和故障容错。当一张网卡出现故障时,系统可以自动切换到另一张网卡,保证网络的稳定性和可靠性。本文将介绍如何在Linux系统中进行双网卡绑定。
-
一、双网卡绑定方式
- 在Linux系统中,双网卡绑定的方式有多种,如bonding、teaming等。其中,bonding是一种比较常用的方式,它可以将多张网卡绑定成一个虚拟网卡,实现负载均衡和故障容错。
-
二、bonding模式
- bonding模式包括7种模式:mode-0、mode-1、mode-2、mode-3、mode-4、mode-5、mode-6。其中,mode-0是负载均衡模式,mode-1到mode-6是故障容错模式。
-
1、mode-0
- mode-0是负载均衡模式,它将数据包通过各个网卡分别发送,从而实现网络负载均衡。mode-0可以细分为多种模式:round-robin、active-backup、xor、broadcast、802.3ad、balance-tlb和balance-alb。
-
2、mode-1
- mode-1是主备模式,也称为active-backup模式。在这种模式下,只有一张网卡处于工作状态,另一张网卡处于备份状态。当工作网卡出现故障时,备份网卡会自动接管,从而实现网络故障容错。
-
3、mode-2
- mode-2是双向绑定模式,也称为balance-xor模式。在这种模式下,数据包会通过其中一张网卡发送,而接收数据包则通过另一张网卡。这种方式可以提高网络的吞吐量和可靠性。
-
4、mode-3
- mode-3是广播模式,也称为broadcast模式。在这种模式下,数据包会通过所有的网卡进行广播,从而实现网络广播功能。
-
5、mode-4
- mode-4是802.3ad模式,也称为动态链接聚合模式。在这种模式下,网卡之间会进行协商,根据网络状况自动分配负载,从而实现网络负载均衡和故障容错。
-
6、mode-5
- mode-5是平衡负载透明模式,也称为balance-tlb模式。在这种模式下,数据包通过各个网卡发送,但接收数据包只通过其中一张网卡。这种方式可以提高网络的吞吐量和可靠性。
-
7、mode-6
- mode-6是平衡负载适应模式,也称为balance-alb模式。在这种模式下,数据包通过各个网卡发送,但接收数据包则根据MAC地址和IP地址的映射关系进行选择,从而实现网络负载均衡和故障容错。
-
- bonding模式包括7种模式:mode-0、mode-1、mode-2、mode-3、mode-4、mode-5、mode-6。其中,mode-0是负载均衡模式,mode-1到mode-6是故障容错模式。
-
三、配置双网卡绑定
-
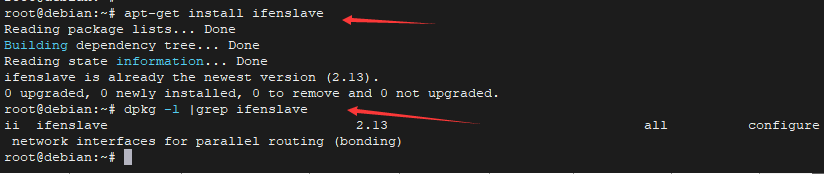
1.安装负载均衡软件 ifenslave
- apt-get install ifenslave
- dpkg -l | grep ifenslave
-
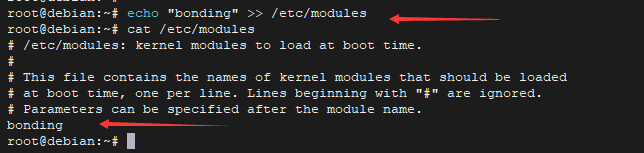
2.添加 bonding 模块,使之可以开机自动加载该模块
- echo "bonding" >> /etc/modules
- cat /etc/modules
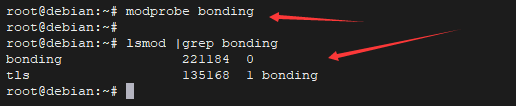
- 接着可以手动加载绑定内核模块,也可以重启
- modprobe bonding
- lsmod | grep bonding
-
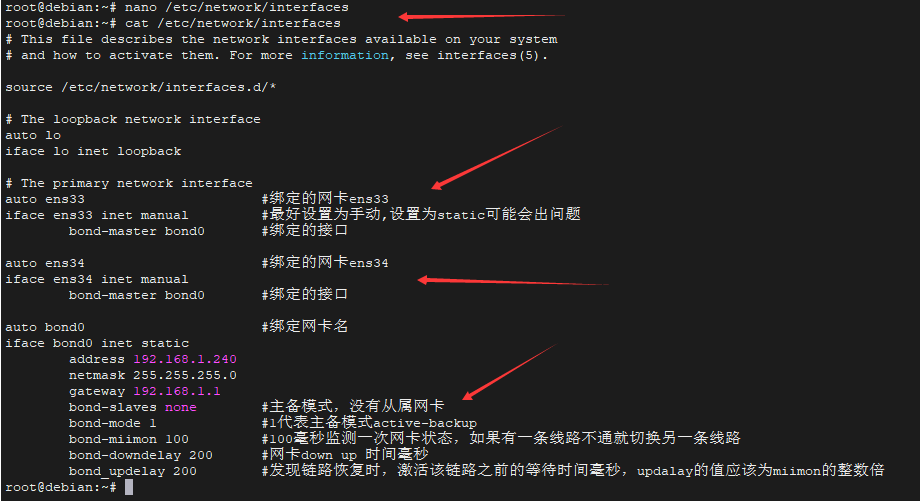
3.编辑 /etc/network/interfaces 配置文件
-
设置主备模式 (active-backup)
- nano /etc/network/interfaces
- cat /proc/net/bonding/bond0
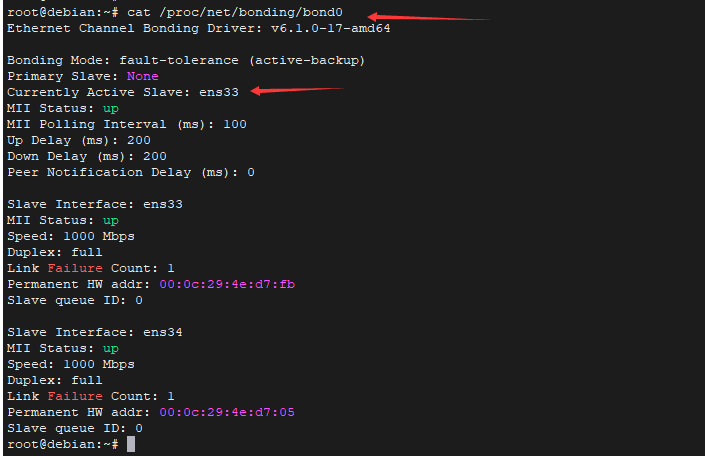
- nano /etc/network/interfaces
-
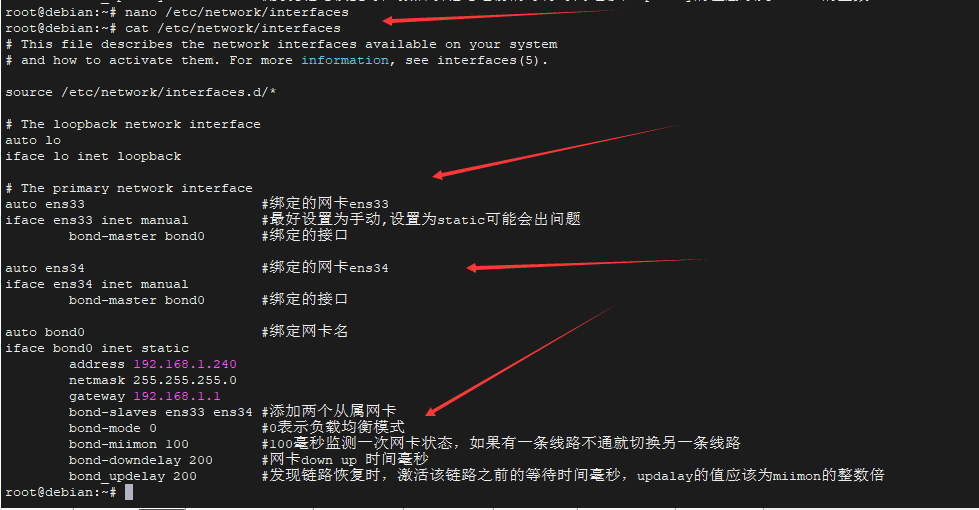
设置负载均衡模式 (balace-rr)
- nano /etc/network/interfaces
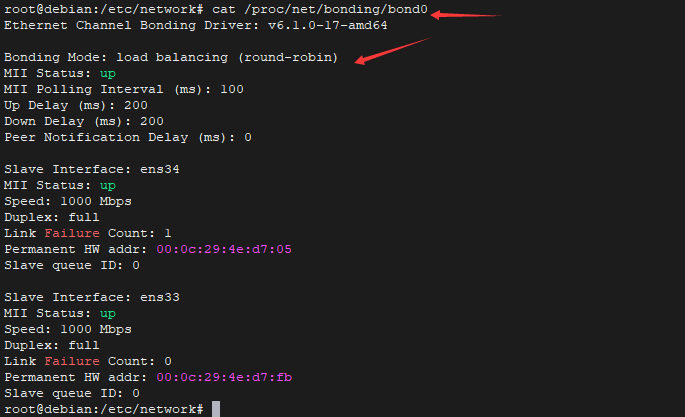
- cat /proc/net/bonding/bond0
- nano /etc/network/interfaces
-
-
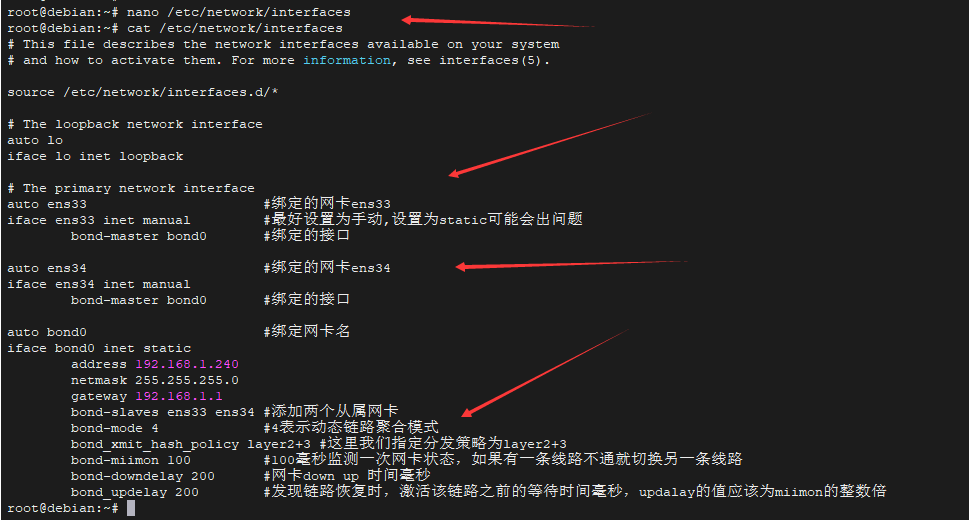
设置动态链路聚合模式(802.3ad模式)
- nano /etc/network/interfaces
- cat /proc/net/bonding/bond0

- nano /etc/network/interfaces
-
4.重启网络服务
- /etc/init.d/networking restart
-
5.查看bond
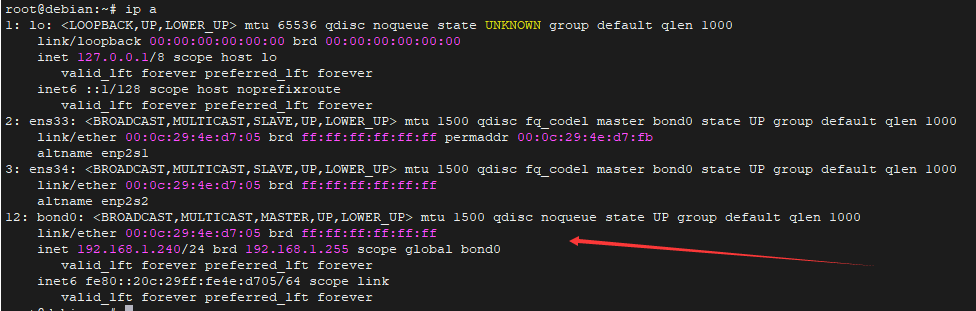
-
Debian系统双网卡 bonding操作
于 2024-01-19 11:09:03 首次发布


























 1674
1674

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










