链接
一、提议描述。
给定一个无向图,边存在边权;
给定起点终点,求一条路径;
将路径上任意边的边权减去一些数,这些数权值和<=k;
设f为修改后路径上的最大边权;
要求最小化f。
对于m=n-1,路径唯一,贪心修改路径上边权最大值即可。
对于k=0,求最小生成树,则答案为树上路径的边权最大值。
正解:此问题直接求解不好做,可转化为判定性问题。
二分答案,判断答案可行性。
时间复杂度n^2*log_n。
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#define R register
#define max_n 50010
using namespace std;
struct ED{int to,nex,c;}edge[max_n<<1];
int n,m,et,kk;
int st[max_n],dis[max_n];
int vis[max_n],q[30000010],h,t;
int read()
{
R int xx;R int ch;
while(ch=getchar(),ch<'0'||ch>'9');xx=ch-'0';
while(ch=getchar(),ch>='0'&&ch<='9')xx=xx*10+ch-'0';
return xx;
}
bool check(int bound)
{
memset(dis,63,sizeof(dis));
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
q[0]=1,dis[1]=0;
h=0,t=1;
R int u,v,e,cost;
while(h<t)
{
u=q[h++],vis[u]=0;
for(e=st[u];e!=-1;e=edge[e].nex)
{
v=edge[e].to;
cost=dis[u]+(edge[e].c>bound?(edge[e].c-bound):0);
if(cost<dis[v])
{
dis[v]=cost;
if(vis[v]==0)vis[v]=1,q[t++]=v;
}
}
}
if(dis[n]<=kk)return true;
else return false;
}
int main()
{
freopen("1.txt","r",stdin);
n=read(),m=read(),kk=read();
R int i,x,y,v;
R int l,r,mid;
memset(st,-1,sizeof(st));
et=1;
for(i=1;i<=m;++i)
{
x=read(),y=read(),v=read();
edge[et]=(ED){y,st[x],v},st[x]=et++;
edge[et]=(ED){x,st[y],v},st[y]=et++;
}
l=0,r=max_n;
while(r>l)
{
mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(check(mid))r=mid;
else l=mid+1;
}
printf("%d",r);
return 0;
}









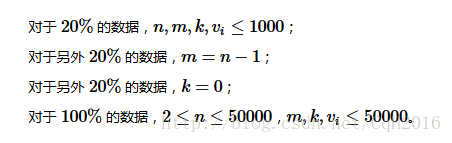














 78
78

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








