目录
一. 关于Dijkstra 算法与 Prim 算法
1. 关于Dijkstra 算法
当图是带权图时,把从一个顶点到图中其余任意一个顶点
的一条路径(可能不止一条)所经过边上的权值之和,定义为该路径的带权路径长度,把带权路径长度最短的那条路径成为最短路径,求解最短路径的算法通常都依赖于一种性质,即两点之间的最短路径也包含了路径上其他顶点间的最短路径。带权有向图G的最短路径问题一般可分为两类:一是单源最短路径,即求图中某一顶点到其他各顶点的最短路径,可通过Dijkstra算法求解;二是求每对顶点间的最短路径,可通过Floyd算法来求解,针对于Floyd算法我在这一小节不进行讨论,有兴趣的读者欢迎看数据结构图这一部分。
2. 关于Prim 算法
一个连通图的最小生成树包含图的所有顶点,并且只含尽可能少的边。对于生成树来说,若砍去它的一条边,则会使生成树变成非连通图;若给它增加一条边,则会形成图中的一条回路。对于一个带权连通无向图G=(V,E),生成树不同,每棵树的全(即树中所有边上的权值之和)也可能不同。设O是G的所有生成树的集合,若T为O中边的权值之和最小的那颗生成树,则T称为G的最小生成树。
不难看出,最小生成树具有如下性质:
最小生成树不是惟一的,即最小生成树的树形不唯一,O中可能有多个最小生成树。当图G中的各边权值互不相等时,G的最小生成树是惟一的;若无向连通图G的边数比顶点数少1,即G本身是一棵树时,则G的最小生成树就是它本身。
最小生成树的边的权值之和总是唯一的,虽然最小生成树不唯一,但其对应边的权值之和总是唯一的,而且是最小的。
最小生成树的边数为顶点数减1。
基于以上三条性质的最小生成树算法主要有Prim算法,它是基于贪心算法的策略。
二. 如何实现Dijkstra 算法与 Prim 算法
1. Dijkstra算法的实现
Dijkstra算法设置一个集合S记录已求的的最短路径的顶点,初始时把源点放入S,集合S每并入一个新的顶点
,都要修改源点
到集合V-S中顶点当前的最短路径长度值(这里可能不太好理解,没关系,等下就可以明白)。
除此之外,构造两个矩阵:
dist[ ]:记录从源点到其他各个顶点当前的最短路径长度,它的初始化为:从
到
的邻接矩阵的值(第
行的值),当然若
暂时没有到其他各个节点的路径,则初始化为
∞。
path[ ]:path[ i ]表示从源点,到顶点
之间的最短路径的前驱节点,在算法结束时,可根据其值追溯得到源点
到顶点
的最短路径。
假设从顶点0出发即=0,集合S最初只包含顶点0,邻接矩阵arcs表示带权有向图,arcs[i][j]表示有向边<i,j>的权值,若不存在有向边<i,j>,则arcs[i][j]=∞。
Dijkstra算法步骤如下:
step1:初始化集合S初始化为{0},dist[ ]的初始值为dist[i]=arcs[0][i],i=1,2...n-1。
step2:从集合V-S中选出,满足dist[j]=min{dist[i] |
V-S},
就是当前求得的一条从
出发的最短路径的终点,令S=S∪{
}。
step3:修改从出发到集合V-S上任意一个顶点
可达的最短路径长度:若dist[j]+arcs[j][k]<dist[k],则更新dist[k]=dist[j]+arcs[j][k]。
step4:重复step2-step3操作共n-1次,直到所有的顶点都包含在S中。
(ps:step3就是当一个新的节点并入集合S后,修改dist矩阵最短路径长度的值)
为了更清晰的表述先有如下图H所示,求v1源点到各个点的最短路径
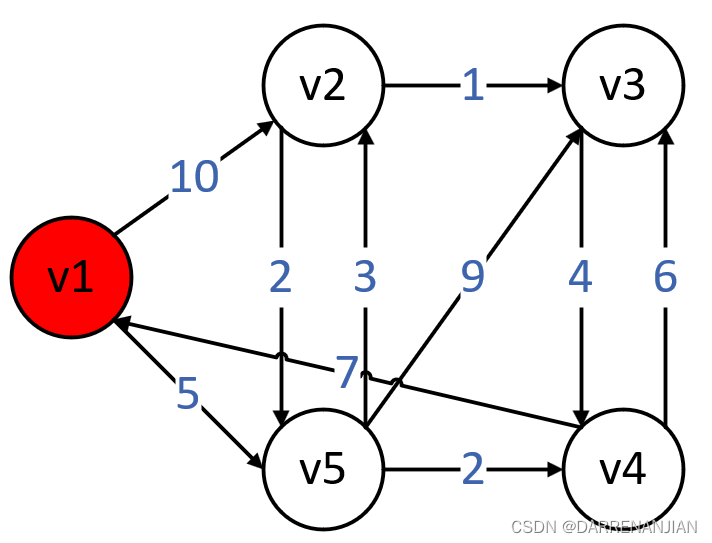
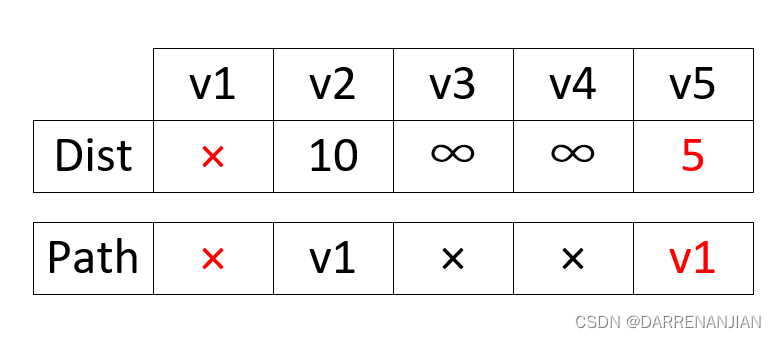
初始化集合S中有{v1},dist矩阵和path矩阵如下图H1所示。
这时选取最小的dist[i]=5,故我们现在已经可以确定源点1到节点5的最小路径是5,路径是1->5,这时将5号节点纳入集合S{v1,v5},接着我们更新dist矩阵和path矩阵如图H2所示(由于v2,v3,v4都改变了dist的值,所以他们的前驱节点都应该改变为5,这一点非常重要,后面我们也会有不改变前驱节点的情况,那就是由于在这次循环中没有改变dist矩阵的值)。
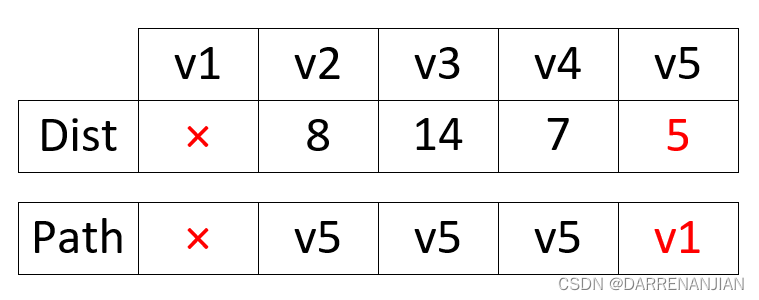
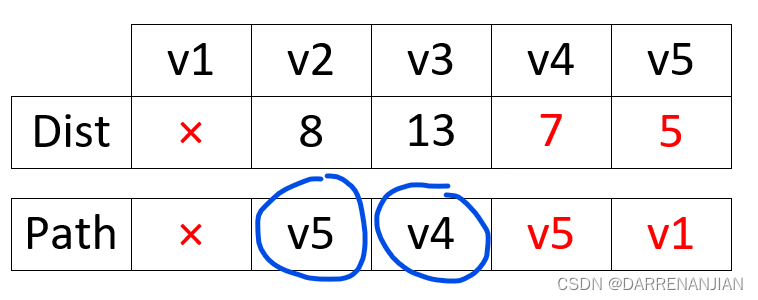
这时选取最小的dist[i]=7,确定源点1到节点4的最小路径是7,路径是1->5->4这时将4号节点纳入集合S{v1,v5,v4},接着我们更新dist矩阵和path矩阵如图H3所示,这里我们就没有改变2号节点的值,这是由于引入节点4之后,并没有使节点2到源点1的距离变得更小,于是我们就没有改变2号节点的前驱节点,即没有改变path矩阵2号节点的值。
这时选取最小的dist[i]=8,确定源点1到节点2的最小路径是8,路径是1->5->2这时将2号节点纳入集合S{v1,v5,v4,v2},接着我们更新dist矩阵和path矩阵如图H4所示。
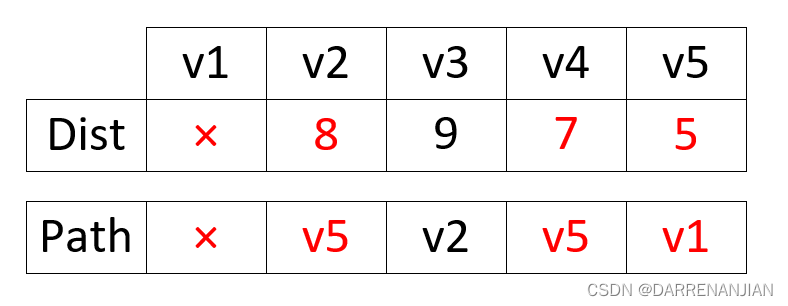
这时选取最小的dist[i]=9,确定源点1到节点3的最小路径是9,路径是1->5->2->3这时将3号节点纳入集合S{v1,v5,v4,v2,v3},故最终我们完成了图H的Dijkstra算法,并且得到了源点1到各个节点的最小路径长度和源点1到各个节点的路径。
2. Prim算法的实现
Prim算法构造最小生成树的过程如图P1-P6所示。初始时,从图中任取一个顶点加入树T,此时树中只含有一个顶点,之后选择一个与当前T中顶点集合距离最近的顶点,并将该顶点和对应的边加入T,每次操作之后T中的顶点数和边数都增加1。以此推类,直到图中所有的顶点都并入T,得到的T就是最小生成树。此时T中必然有n-1条边。
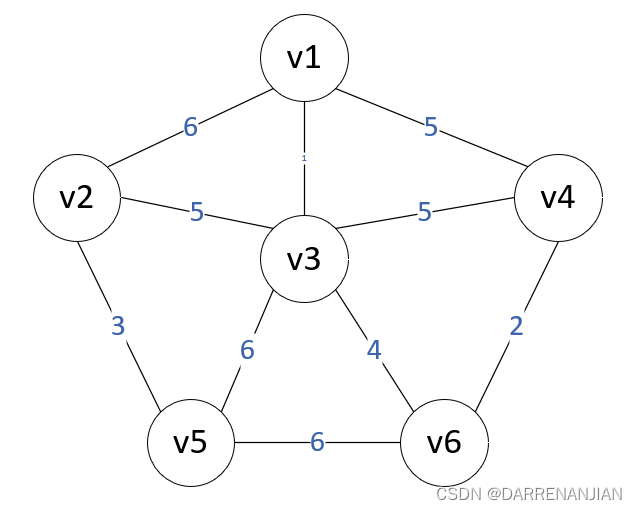
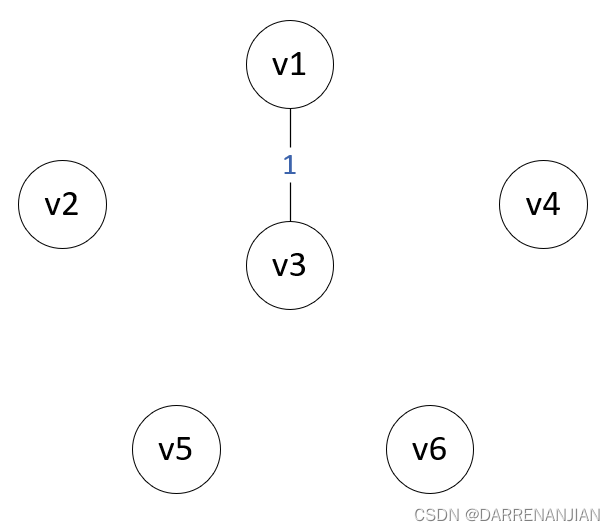
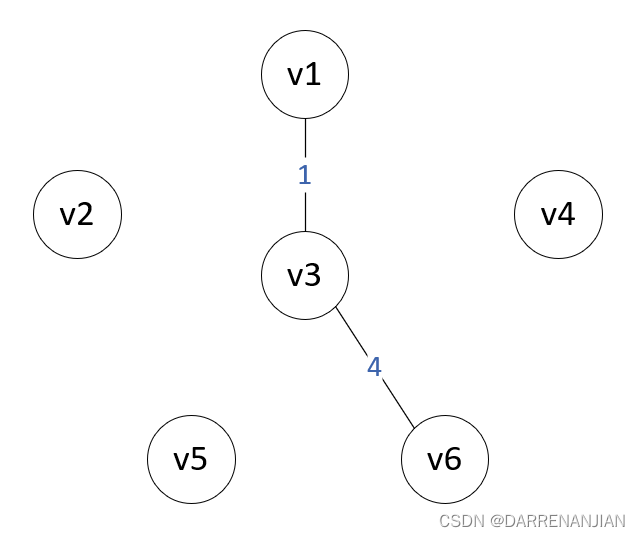
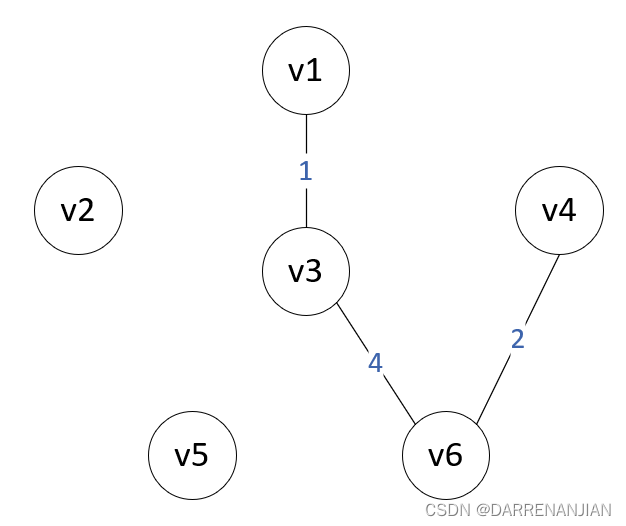
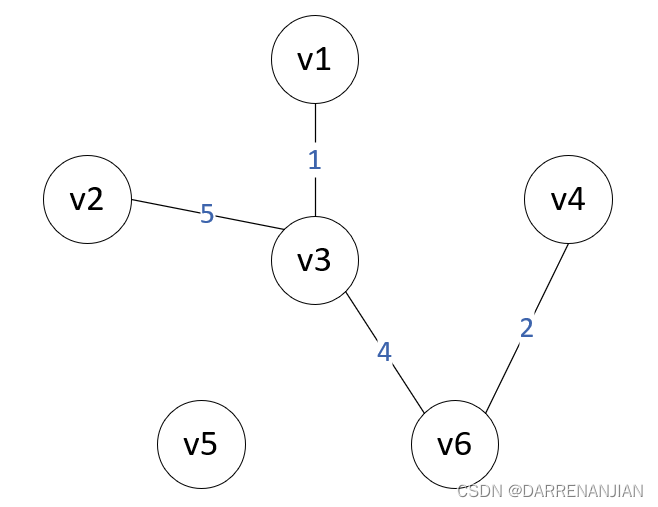
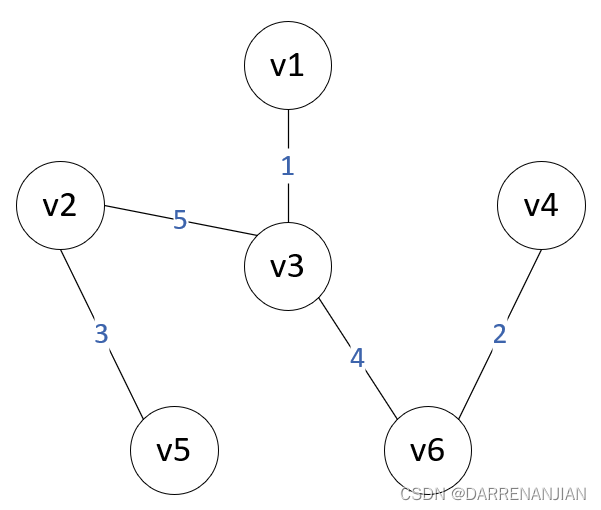
算法步骤:
初始化一个树T;
添加任意一个顶点U;
while(树T中不含全部顶点){
当(u,v)是权值最小的边:
边归入树;
顶点归入树;
}
三. 代码实现
1. Dijkstra算法
1.1 Dijkstra的初始化:
构造距离矩阵tempDistanceArray,其初始值等于第1号节点直接到各个节点的值,构造路径矩阵tempParentArray,初始值除了1号节点,1号节点的值设置为-1,其他的都设置为1(若邻接矩阵有1号节点不能直接到达的节点,则设置为-1),构造一个访问矩阵(相当于集合S的作用),用来存储某个节点是否已经接入集合S。
// Step 1. Initialize.
int[] tempDistanceArray = new int[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempDistanceArray[i] = weightMatrix.getValue(paraSource, i);
} // Of for i
int[] tempParentArray = new int[numNodes];
Arrays.fill(tempParentArray, paraSource);
// -1 for no parent.
tempParentArray[paraSource] = -1;
// Visited nodes will not be considered further.
boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[paraSource] = true;
1.2 Dijkstra的核心代码:
由于总共有n个节点,但是要除开源节点,所以总共循环n-1次,临时变量tempMinDistance记录此时最短的路径长度,tempBestNode记录此时最短路径的前驱节点,开始第一层循环。首先设置tempMinDistance为∞,在tempDistanceArray矩阵里面寻找没有被访问,且距离值最小的节点,用tempBestNode记录节点的值,用tempMinDistance记录最短的路径,接着更新节点最短路径节点tempBestNode的访问位为true。开始更新下一个节点的情况。
还是开始第三轮循环,这次循环的主要目的是将tempBestNode纳入集合S后下一个节点的路径情况和距离情况。寻找没有被访问过的节点,寻找且与更新节点tempBestNode直接相连的节点,当原来距离矩阵的tempDistanceArray[j](j是第三轮循环其他没有被访问的节点)>集合S到新节点tempBestNode的距离+新节点tempBestNode到 j 节点的距离(由于先前直接相连的判断,这时的距离是一个有限值),则更新距离矩阵tempDistanceArray[j]=集合S到新节点tempBestNode的距离+新节点tempBestNode到 j 节点的距离,并且节点 j 的前驱节点为tempBestNode,按照上述一直更新所有的节点,完成第三轮循环。
// Step 2. Main loops.
int tempMinDistance;
int tempBestNode = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes - 1; i++) {
// Step 2.1 Find out the best next node.
tempMinDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
if (tempMinDistance > tempDistanceArray[j]) {
tempMinDistance = tempDistanceArray[j];
tempBestNode = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
tempVisitedArray[tempBestNode] = true;
// Step 2.2 Prepare for the next round.
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
// This node cannot be reached.
if (weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j) >= MAX_DISTANCE) {
continue;
} // Of if
if (tempDistanceArray[j] > tempDistanceArray[tempBestNode]
+ weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j)) {
// Change the distance.
tempDistanceArray[j] = tempDistanceArray[tempBestNode]
+ weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j);
// Change the parent.
tempParentArray[j] = tempBestNode;
} // Of if
} // Of for j2. Prim算法
2.1 Prim算法的初始化:
初始化和Dijkstra几乎一致(默认从0号节点开始计算),构建距离矩阵(邻接矩阵的第0行),前驱矩阵(0列为-1,其他列都为0),访问矩阵(0列设置为已访问,其他列设置为未访问)。
// Step 1. Initialize.
// Any node can be the source.
int tempSource = 0;
int[] tempDistanceArray = new int[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempDistanceArray[i] = weightMatrix.getValue(tempSource, i);
} // Of for i
int[] tempParentArray = new int[numNodes];
Arrays.fill(tempParentArray, tempSource);
// -1 for no parent.
tempParentArray[tempSource] = -1;
// Visited nodes will not be considered further.
boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[tempSource] = true;2.2 Prim算法的核心代码:
大循环(第一轮循环)循环n-1次(总共有n个节点,除了源节点,故次数为n-1),在距离矩阵里面寻找没有被访问过,且距离最小的节点,用tempBestNode记录节点,tempMinDistance记录最小的距离。找到最小的节点,改变访问矩阵的值tempVisitedArray[tempBestNode] = true。接着改变并入节点tempBestNode的情况,第三轮循环:如果距离矩阵tempDistanceArray的某个节点j 对应的值>从节点tempBestNode到节点 j 的值,则改距离矩阵tempDistanceArray[j]的值等于邻接矩阵tempBestNode行,j列的值。j节点的前驱为tempBestNode(empParentArray[j] = tempBestNode)。按照上述过程一直直到大循环结束,得到最终结果。
// Step 2. Main loops.
int tempMinDistance;
int tempBestNode = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes - 1; i++) {
// Step 2.1 Find out the best next node.
tempMinDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
if (tempMinDistance > tempDistanceArray[j]) {
tempMinDistance = tempDistanceArray[j];
tempBestNode = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
tempVisitedArray[tempBestNode] = true;
// Step 2.2 Prepare for the next round.
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
// This node cannot be reached.
if (weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j) >= MAX_DISTANCE) {
continue;
} // Of if
// Attention: the difference from the Dijkstra algorithm.
if (tempDistanceArray[j] > weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j)) {
// Change the distance.
tempDistanceArray[j] = weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j);
// Change the parent.
tempParentArray[j] = tempBestNode;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// For test
System.out.println(
"The selected distance for each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempDistanceArray));
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
} // Of for i
四. 代码展示
主类:
package Day_38;
public class deom1 {
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args
* Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
int MAX_DISTANCE = 1000;
Net tempNet0 = new Net(3);
System.out.println(tempNet0);
int[][] tempMatrix1 = { { 0, 9, 3, 6 }, { 5, 0, 2, 4 }, { 3, 2, 0, 1 }, { 2, 8, 7, 0 } };
Net tempNet1 = new Net(tempMatrix1);
System.out.println(tempNet1);
// Dijkstra
tempNet1.dijkstra(1);
// An undirected net is required.
int[][] tempMatrix2 = { { 0, 7, MAX_DISTANCE, 5, MAX_DISTANCE }, { 7, 0, 8, 9, 7 },
{ MAX_DISTANCE, 8, 0, MAX_DISTANCE, 5 }, { 5, 9, MAX_DISTANCE, 0, 15 },
{ MAX_DISTANCE, 7, 5, 15, 0 } };
Net tempNet2 = new Net(tempMatrix2);
tempNet2.prim();
}// Of main
}调用类:
package Day_38;
import Day_31.IntMatrix;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Weighted graphs are called nets.
*
* @author An Jian 2569222191@qq.com.
*/
public class Net {
/**
* The maximal distance. Do not use Integer.MAX_VALUE.
*/
public static final int MAX_DISTANCE = 10000;
/**
* The number of nodes.
*/
int numNodes;
/**
* The weight matrix. We use int to represent weight for simplicity.
*/
IntMatrix weightMatrix;
/**
* ********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraNumNodes The number of nodes in the graph.
* ********************
*/
public Net(int paraNumNodes) {
numNodes = paraNumNodes;
weightMatrix = new IntMatrix(numNodes, numNodes);
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
// For better readability, you may need to write fill() in class
// IntMatrix.
Arrays.fill(weightMatrix.getData()[i], MAX_DISTANCE);
} // Of for i
}// Of the first constructor
/**
* ********************
* The second constructor.
*
* @param paraMatrix The data matrix.
* ********************
*/
public Net(int[][] paraMatrix) {
weightMatrix = new IntMatrix(paraMatrix);
numNodes = weightMatrix.getRows();
}// Of the second constructor
/**
* ********************
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
* ********************
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "This is the weight matrix of the graph.\r\n" + weightMatrix;
return resultString;
}// Of toString
/**
* ********************
* The Dijkstra algorithm: shortest path from the source to all nodes.
*
* @param paraSource The source node.
* @return The distances to all nodes.
* ********************
*/
public int[] dijkstra(int paraSource) {
// Step 1. Initialize.
int[] tempDistanceArray = new int[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempDistanceArray[i] = weightMatrix.getValue(paraSource, i);
} // Of for i
int[] tempParentArray = new int[numNodes];
Arrays.fill(tempParentArray, paraSource);
// -1 for no parent.
tempParentArray[paraSource] = -1;
// Visited nodes will not be considered further.
boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[paraSource] = true;
// Step 2. Main loops.
int tempMinDistance;
int tempBestNode = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes - 1; i++) {
// Step 2.1 Find out the best next node.
tempMinDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
if (tempMinDistance > tempDistanceArray[j]) {
tempMinDistance = tempDistanceArray[j];
tempBestNode = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
tempVisitedArray[tempBestNode] = true;
// Step 2.2 Prepare for the next round.
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
// This node cannot be reached.
if (weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j) >= MAX_DISTANCE) {
continue;
} // Of if
if (tempDistanceArray[j] > tempDistanceArray[tempBestNode]
+ weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j)) {
// Change the distance.
tempDistanceArray[j] = tempDistanceArray[tempBestNode]
+ weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j);
// Change the parent.
tempParentArray[j] = tempBestNode;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// For test
System.out.println("The distance to each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempDistanceArray));
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
} // Of for i
// Step 3. Output for debug.
System.out.println("Finally");
System.out.println("The distance to each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempDistanceArray));
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
return tempDistanceArray;
}// Of dijkstra
/**
* ********************
* The minimal spanning tree.
*
* @return The total cost of the tree.
* ********************
*/
public int prim() {
// Step 1. Initialize.
// Any node can be the source.
int tempSource = 0;
int[] tempDistanceArray = new int[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempDistanceArray[i] = weightMatrix.getValue(tempSource, i);
} // Of for i
int[] tempParentArray = new int[numNodes];
Arrays.fill(tempParentArray, tempSource);
// -1 for no parent.
tempParentArray[tempSource] = -1;
// Visited nodes will not be considered further.
boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[tempSource] = true;
// Step 2. Main loops.
int tempMinDistance;
int tempBestNode = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes - 1; i++) {
// Step 2.1 Find out the best next node.
tempMinDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
if (tempMinDistance > tempDistanceArray[j]) {
tempMinDistance = tempDistanceArray[j];
tempBestNode = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
tempVisitedArray[tempBestNode] = true;
// Step 2.2 Prepare for the next round.
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
// This node cannot be reached.
if (weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j) >= MAX_DISTANCE) {
continue;
} // Of if
// Attention: the difference from the Dijkstra algorithm.
if (tempDistanceArray[j] > weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j)) {
// Change the distance.
tempDistanceArray[j] = weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j);
// Change the parent.
tempParentArray[j] = tempBestNode;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// For test
System.out.println(
"The selected distance for each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempDistanceArray));
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
} // Of for i
int resultCost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
resultCost += tempDistanceArray[i];
} // Of for i
// Step 3. Output for debug.
System.out.println("Finally");
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
System.out.println("The total cost: " + resultCost);
return resultCost;
}// Of prim
}// Of class Net五. 数据测试
第一个Dijkstra方法的测试矩阵如下图G1所示,第二个Prim方法的测试矩阵如下如G2所示


Dijkstra的测试结果:

Prim的测试结果:

六. 总结与反思
Dijkstra算法和Prim算法本质上是用贪心算法,在不断的迭代中找到最优解。






















 1004
1004

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








