一、发布探店笔记
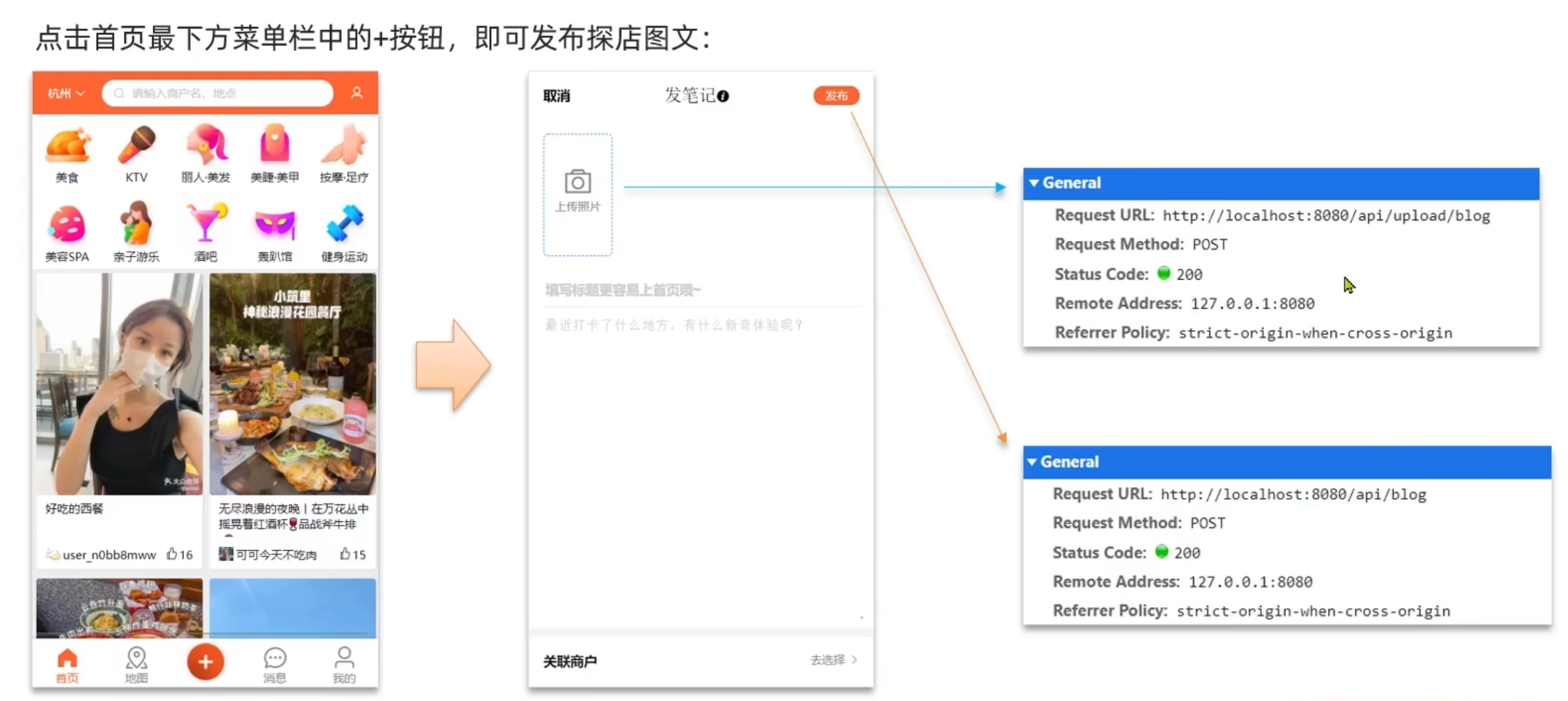


案例--实现查看发布探店笔记的接口:
映射到对应数据库

BLOG类中存在和对应数据库表不相关的属性,使用@TableField注解表示该字段并不在表中,需要在后续进行手动维护
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Result queryBlogById(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
return blogService.queryBlogById(id);
}
@Override
public Result queryBlogById(Long id) {
//1.查询Blog
Blog blog = getById(id);
if (blog == null ){
return Result.fail("笔记不存在!");
}
//2.查询blog有关的用户
queryBlogUser(blog);
return Result.ok(blog);
}
private void queryBlogUser(Blog blog){
Long userId = blog.getUserId();
User user = userService.getById(userId);
blog.setName(user.getNickName());
blog.setIcon(user.getIcon());
}案例--完善点赞功能:


@Override
public Result likeBlog(Long id) {
//1. 获取当前用户
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
//2. 判断用户是否已经点赞
String key = BLOG_LIKED_KEY + id;
Boolean isMember = stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember(key, userId.toString());
//防止为空 使用BooleanUtill
if (BooleanUtil.isFalse(isMember)){
//3. 如果未点赞,可以点赞
//3.1 数据库点赞数+1
boolean isSuccess = update().setSql("liked = liked + 1").eq("id", id).update();
//3.2 保存用户到Redis的set集合
if (isSuccess) {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add(key, userId.toString());
}
}else {
//4. 如果已经点赞,则取消点赞
//4.1. 数据库点赞数-1
boolean isSuccess = update().setSql("liked = liked - 1").eq("id", id).update();
//4.2. 把用户从Redis中的set集合移除
if (isSuccess) {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().remove(key, userId.toString());
}
}
return Result.ok();
}案例--点赞排行榜:



Set集合无序,因此采用SortedSet 修改相关代码
源代码中所有有关Set的操作改为SortedSet 对应的分数 使用时间戳System.currentTimeMillis()

@GetMapping("/likes/{id}")
public Result queryBlogLikes(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
return blogService.queryBlogLikes(id);
}
@Override
public Result queryBlogLikes(Long id) {
String key = BLOG_LIKED_KEY + id;
//1. 查询top5的点赞用户 zrange key 0 4
Set<String> top5 = stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().range(key, 0, 4);
if(top5 == null || top5.isEmpty()){
return Result.ok();
}
//2. 解析出其中的用户id
List<Long> ids = top5.stream().map(Long::valueOf).collect(Collectors.toList());
//3. 根据用户id查询用户
List<UserDTO> userDTOS = userService.listByIds(ids)
.stream()
.map(user -> BeanUtil.copyProperties(user, UserDTO.class))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
//4. 返回
return Result.ok(userDTOS);
}结果点赞用户展示顺序出现错误
![]()
原因,数据库使用in关键字进行查询时自动根据id调整了顺序
修改代码:.last表示在原有SQL语句最后拼接一句SQL语句
@Override
public Result queryBlogLikes(Long id) {
String key = BLOG_LIKED_KEY + id;
//1. 查询top5的点赞用户 zrange key 0 4
Set<String> top5 = stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().range(key, 0, 4);
if(top5 == null || top5.isEmpty()){
return Result.ok();
}
//2. 解析出其中的用户id
List<Long> ids = top5.stream().map(Long::valueOf).collect(Collectors.toList());
String idStr = StrUtil.join(",", ids);
//3. 根据用户id查询用户
List<UserDTO> userDTOS = userService.query()
.in("id",ids).last("order by field(id,"+idStr+")").list()
.stream()
.map(user -> BeanUtil.copyProperties(user, UserDTO.class))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
//4. 返回
return Result.ok(userDTOS);
}二、好友关注
关注和取关:

案例---实现关注和取关功能:

@Override
public Result follow(Long followUserId, Boolean isFollow) {
//1. 获取登录用户
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
//2. 判断是关注还是取关
if(isFollow){
//3. 关注,新增数据
Follow follow = new Follow();
follow.setUserId(userId);
follow.setFollowUserId(followUserId);
save(follow);
}else{
//4. 取关,删除 delete * from tb_follow where userId = ? and follow_user_id = ?
remove(new QueryWrapper<Follow>()
.eq("user_id",userId).eq("follow_user_id",followUserId));
}
return Result.ok();
}
@Override
public Result isFollow(Long followUserId) {
//1. 获取登录用户
UserDTO user = UserHolder.getUser();
if(user == null){
//用户未登录
return Result.ok(false);
}
Long userId = user.getId();
//查询是否关注 selec * from tb_follow where user_id = ? and follow_user_id = ?
//.count 表示数据数量 >0 表示关注了 反之一样
Integer count = query().eq("user_id", userId).eq("follow_user_id", followUserId).count();
return Result.ok(count>0);
}共同关注:
方案---实现共同关注功能:

在关注相关代码中 增加 写入关注数据 Redis 功能

@GetMapping("/common/{id}")
public Result followCommons(@PathVariable("id") Long followUserId){
return followService.followCommons(followUserId);
}
@Override
public Result followCommons(Long followUserId) {
//1. 先获取当前登录用户
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
String key = "follows:" + userId;
//2. 求交集
String key2= "follows:" + followUserId;
Set<String> intersect = stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().intersect(key, key2);
if (intersect == null || intersect.isEmpty()){
//无交集
return Result.ok(Collections.emptyList());
}
//3. 解析id集合
List<Long> ids = intersect.stream().map(Long::valueOf).collect(Collectors.toList());
//4. 查询用户
List<UserDTO> users = userService.listByIds(ids)
.stream()
.map(user -> BeanUtil.copyProperties(user, UserDTO.class))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return Result.ok(users);
}关注推送:




拉模式:
推模式:

推拉结合模式:

案例---基于推模式实现关注推送:
 传统分页问题:
传统分页问题:

解决办法--Feed流的滚动分页:

根据Feed流滚动分页的特性,关注推送采用SortedSet数据结构在Redis中存储查询(设置时间戳为分数)
代码实现:
修改发送笔记代码
发送笔记后,查询发送者的粉丝,向所有粉丝推送信息
@Override
public Result saveBlog(Blog blog) {
//1.获取登录用户
UserDTO user = UserHolder.getUser();
blog.setUserId(user.getId());
//2.保存探店笔记
boolean isSuccess = save(blog);
if (!isSuccess){
return Result.fail("新增笔记失败!");
}
//3.查询笔记作者的粉丝 select * from tb_follow where follow_user_id = ?
List<Follow> follows = followService.query().eq("follow_user_id", user.getId()).list();
//4.推送笔记给所有粉丝
for (Follow follow : follows) {
//4.1 获取粉丝id
Long userId = follow.getUserId();
//4.2 推送
String key = FEED_KEY + userId;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add(key,blog.getId().toString(),System.currentTimeMillis());
}
//5. 返回id
return Result.ok(blog.getId());
}
 案例---实现关注推送页面的分页查询:
案例---实现关注推送页面的分页查询:

@Override
public Result queryBlogofFollow(Long max, Integer offset) {
//1. 获取当前用户
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
//2. 查询收件箱
String key= FEED_KEY + userId;
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> typedTuples = stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet()
.reverseRangeByScoreWithScores(key, 0, max, offset, 2);
//3.判断非空
if (typedTuples == null || typedTuples.isEmpty()){
return Result.ok();
}
//4. 解析数据: blogId + minTime(时间戳) + offset(跟上次查询的最小值一样的元素的个数)
long minTime = 0;
int os = 1;
List<Long> ids = new ArrayList<>(typedTuples.size());
for (ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> typedTuple : typedTuples) {
//4.1 获取id
ids.add(Long.valueOf(typedTuple.getValue()));
//4.2 获取分数(时间戳)
long time = typedTuple.getScore().longValue();
if (time == minTime){
os++;
}else {
minTime = time;
os=1;
}
}
//5. 根据blogId查询blog
String idStr = StrUtil.join(",", ids);
List<Blog> blogs = query()
.in("id", ids).last("order by field(id," + idStr + ")").list();
for (Blog blog : blogs) {
//5.1.查询blog有关的用户
queryBlogUser(blog);
//5.2.查询blog是否点过赞
isBlogLiked(blog);
}
//6. 封装并返回
ScrollResult r = new ScrollResult();
r.setList(blogs);
r.setOffset(os);
r.setMinTime(minTime);
return Result.ok(r);
}三、附近商铺
GEO数据结构:
 案例---联系Redis的GEO功能:
案例---联系Redis的GEO功能:



![]()

附近商户搜索:
 数据存储方式:
数据存储方式:

支持版本:
 实现:
实现:
@GetMapping("/of/type")
public Result queryShopByType(
@RequestParam("typeId") Integer typeId,
@RequestParam(value = "current", defaultValue = "1") Integer current,
@RequestParam(value = "x",required = false) Double x,
@RequestParam(value = "y",required = false) Double y
) {
return shopService.queryShopByType(typeId,current,x,y);
} @Override
public Result queryShopByType(Integer typeId, Integer current, Double x, Double y) {
//1. 判断 是否需要根据坐标查询
if (x == null || y == null){
//不需要坐标查询,按数据库查询
// 根据类型分页查询
Page<Shop> page = query()
.eq("type_id", typeId)
.page(new Page<>(current, SystemConstants.DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE));
// 返回数据
return Result.ok(page.getRecords());
}
//2. 计算分页参数
int from = (current - 1)*SystemConstants.DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE;
int end = current * SystemConstants.DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE;
//3. 查询redis 按照距离排序+分页 结果: shipId、distance
String key = SHOP_GEO_KEY + typeId;
GeoResults<RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation<String>> results = stringRedisTemplate.opsForGeo() //GEOSEARCH key BYLONLAT(圆心) x y BYRADIUS(半径) 10 WITHDISTANCE(带距离)
.search(key, GeoReference.fromCoordinate(x, y),
new Distance(5000),
RedisGeoCommands.GeoSearchCommandArgs.newGeoSearchArgs().includeDistance().limit(end)
);
//4. 解析shopId
if (results==null){//判空
return Result.ok(Collections.emptyList());
}
List<GeoResult<RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation<String>>> list = results.getContent();
if (list.size() <= from){
//没有下一页了
return Result.ok(Collections.emptyList());
}
//4.1 截取 from - end 的部分
List<Long> ids = new ArrayList<>(list.size());
Map<String,Distance> distanceMap = new HashMap<>(list.size());
list.stream().skip(from).forEach(result ->{
//4.2 获取店铺id
String shopIdStr = result.getContent().getName();
ids.add(Long.valueOf(shopIdStr));
//4.3 获取距离
Distance distance = result.getDistance();
distanceMap.put(shopIdStr,distance);
});
//5. 根据shopId查询店铺
String idStr = StrUtil.join(",", ids);
List<Shop> shops = query().in("id", ids).last("order by field(id," + idStr + ")").list();
for (Shop shop : shops) {
shop.setDistance(distanceMap.get(shop.getId().toString()).getValue());
}
//6. 返回
return Result.ok(shops);
}由于GEO查询没有办法查询对应范围数据,只能指定数量,因此分页查询需要手动截取对应部分
四、用户签到

BitMap用法:



案例--实现签到功能 :

@Override
public Result sign() {
//1. 获取当前登录的用户
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
//2. 获取日期
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
//3. 拼接key
String keySuffix = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(":yyyy-MM"));
String key = USER_SIGN_KEY + userId +keySuffix;
//4. 获取今天是当月第几天(填充bit的位置)
int dayOfMonth = now.getDayOfMonth(); //这个月第一天返回值为1
//5. 写入Redis SETBIT key offset 1
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setBit(key,dayOfMonth-1,true);
return Result.ok();
}案例--实现签到统计:

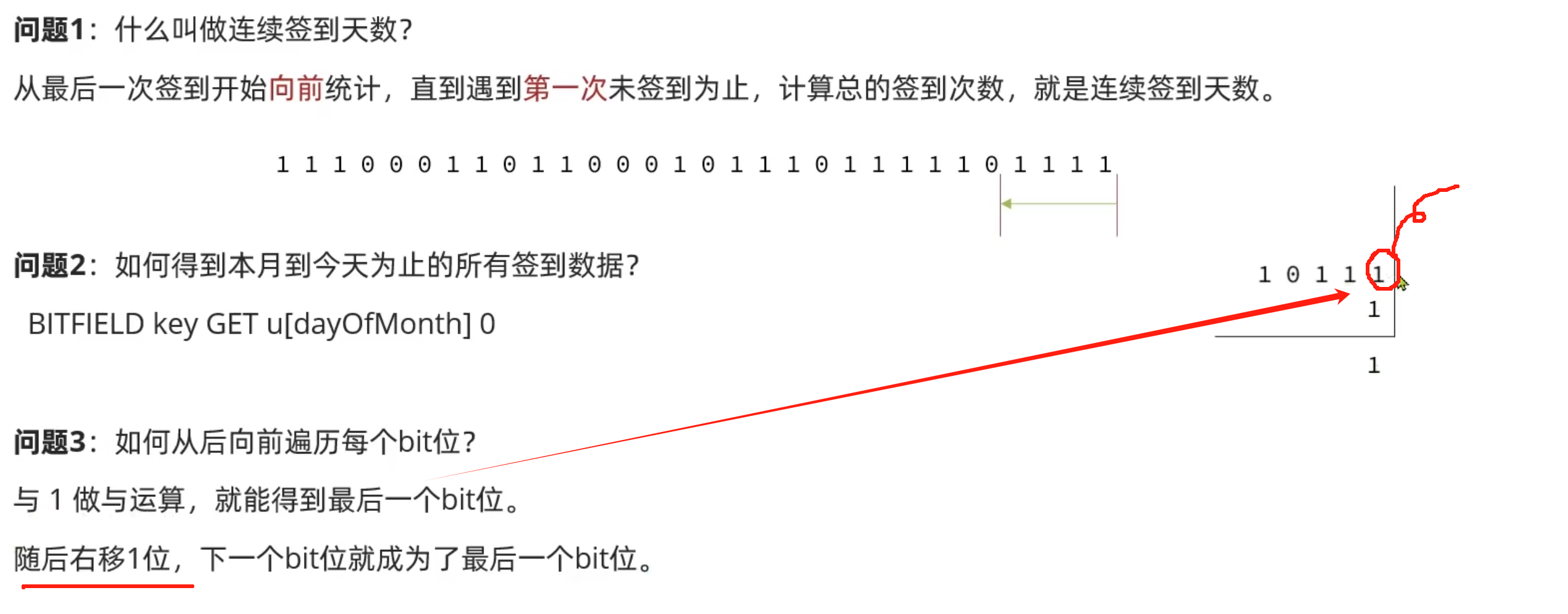
@GetMapping("/sign/count")
public Result signCount(){
return userService.signCount();
}
} @Override
public Result signCount() {
//1. 获取当前登录的用户
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
//2. 获取日期
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
//3. 拼接key
String keySuffix = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(":yyyy-MM"));
String key = USER_SIGN_KEY + userId +keySuffix;
//4. 获取今天是当月第几天
int dayOfMonth = now.getDayOfMonth(); //这个月第一天返回值为1
//5. 获取本月截至今天为止的所有签到记录 返回的是一个十进制数字 BITFIELD sign:5:202505 GET U14 0
List<Long> results = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().bitField(
key, BitFieldSubCommands.create()
.get(BitFieldSubCommands.BitFieldType.unsigned(dayOfMonth)).valueAt(0)
);
if(results == null || results.isEmpty()){
//没有任何结果
return Result.ok(0);
}
Long num = results.get(0);
if(num == null || num == 0){
return Result.ok();
}
//6. 循环遍历
int count=0;
while(true){
//6.1.让这个数字与1做与运算,得到数字的最后一个bit位
if((num & 1)==0){
//如果为0 说明未签到 结束
break;
}else{
//不为0,说明已经签到,计数器+1
count ++;
}
//把数字右移一位,抛弃最后一个bit位,继续下一个bit位
num = num>>>1;
}
return Result.ok(count);
}五、UV统计

HyperLogLog用法:
 HyperLogLog 算法的原理讲解以及 Redis 是如何应用它的聪明的你可能会马上想到,用 HashMap 这种数 - 掘金
HyperLogLog 算法的原理讲解以及 Redis 是如何应用它的聪明的你可能会马上想到,用 HashMap 这种数 - 掘金

























 1542
1542

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








