二叉树
提供的主要操作集有:
- 三种递归遍历
- 三种非递归遍历
- 层序遍历
- 输出叶子节点
- 递归求二叉树的高度
- 从一个数组中建立一棵二叉树
- 销毁二叉树
- 由后缀表达式构造表达式树
代码实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "linkQueue.c"
#include "linkStack.c"
#define BinTreeElemType char
#define NOINFO '0'
struct TreeNode {
BinTreeElemType data;
struct TreeNode* left;
struct TreeNode* right;
};
typedef struct TreeNode TreeNode;
typedef struct TreeNode* BinTree;
void PreOrderTraversal_recursively(BinTree t, void (*visit)(BinTreeElemType x)) {
if (t != NULL) {
visit(t->data);
PreOrderTraversal_recursively(t->left, visit);
PreOrderTraversal_recursively(t->right, visit);
}
}
void InOrderTraversal_recursively(BinTree t, void (*visit)(BinTreeElemType x)) {
if (t != NULL) {
InOrderTraversal_recursively(t->left, visit);
visit(t->data);
InOrderTraversal_recursively(t->right, visit);
}
}
void PostOrderTraversal_recursively(BinTree t, void (*visit)(BinTreeElemType x)) {
if (t != NULL) {
PostOrderTraversal_recursively(t->left, visit);
PostOrderTraversal_recursively(t->right, visit);
visit(t->data);
}
}
void PreOrderTraversal_iteratively(BinTree t, void (*visit)(BinTreeElemType x)) {
Stack s = CreateStack();
BinTree curr = t;
while (curr != NULL || !StackEmpty(s)) {
if (curr) {
visit(curr->data);
Push(s, curr);
curr = curr->left;
} else {
Pop(s, &curr);
curr = curr->right;
}
}
DestoryStack(s);
}
void InOrderTraversal_iteratively(BinTree t, void (*visit)(BinTreeElemType x)) {
Stack s = CreateStack();
BinTree curr = t;
while (curr != NULL || !StackEmpty(s)) {
if (curr) {
Push(s, curr);
curr = curr->left;
} else {
Pop(s, &curr);
visit(curr->data);
curr = curr->right;
}
}
DestoryStack(s);
}
void PostOrderTraversal_iteratively(BinTree t, void (*visit)(BinTreeElemType x)) {
Stack s = CreateStack();
BinTree curr = t;
BinTree prev;
while (curr != NULL || !StackEmpty(s)) {
while (curr != NULL) {
Push(s, curr);
curr = curr->left;
}
if (!StackEmpty(s)) {
Pop(s, &curr);
//访问节点的条件:当前经过节点是叶子节点||当前经过节点的右子节点是上一次访问的节点。
if (curr->right == NULL || curr->right == prev) {
visit(curr->data);
prev = curr;
curr = NULL;
} else {
Push(s, curr);
curr = curr->right;
}
}
}
DestoryStack(s);
}
void LevelOrderTraversal(BinTree t, void (*visit)(BinTreeElemType x)) {
if (t == NULL)
return;
Queue q = CreateQueue();
BinTree curr = t;
EnQueue(q, curr);
while (!QueueEmpty(q)) {
DeQueue(q, &curr);
visit(curr->data);
if (curr->left != NULL)
EnQueue(q, curr->left);
if (curr->right != NULL)
EnQueue(q, curr->right);
}
DestoryQueue(q);
}
//输出二叉树的叶子节点
void PreOrderPrintLeaves(BinTree t) {
if (t != NULL) {
if (t->left == NULL && t->right == NULL) {
printf("%2c ", t->data);
}
PreOrderPrintLeaves(t->left);
PreOrderPrintLeaves(t->right);
}
}
//求二叉树的高度
int BinTreeHeight(BinTree t) {
int hl, hr;
if (t != NULL) {
hl = BinTreeHeight(t->left);
hr = BinTreeHeight(t->right);
return (hl > hr) ? (hl + 1) : (hr + 1);
} else {
return 0;
}
}
BinTree CreateBinTreeFromArray(BinTreeElemType* array) {
if (array == NULL || array[0] == NOINFO)
return NULL;
Queue q = CreateQueue();
BinTree root = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
root->data = array[0];
root->left = root->right = NULL;
EnQueue(q, root);
BinTree t;
int i = 1;
while (!QueueEmpty(q)) {
DeQueue(q, &t);
//t的左孩子
if (array[i] == NOINFO) {
t->left = NULL;
} else {
t->left = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
t->left->data = array[i];
t->left->left = t->left->right = NULL;
EnQueue(q, t->left);
}
i++;
//t的右孩子
if (array[i] == NOINFO) {
t->right = NULL;
} else {
t->right = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
t->right->data = array[i];
t->right->left = t->right->right = NULL;
EnQueue(q, t->right);
}
i++;
}
DestoryQueue(q);
return root;
}
void DestoryBinTree(BinTree t) {
if (t == NULL)
return;
Queue q = CreateQueue();
BinTree curr = t;
EnQueue(q, curr);
while (!QueueEmpty(q)) {
DeQueue(q, &curr);
if (curr->left != NULL)
EnQueue(q, curr->left);
if (curr->right != NULL)
EnQueue(q, curr->right);
free(curr);
}
DestoryQueue(q);
}
//构造表达式树,假定表达式一定合法
BinTree ExpressionTree(const char* postExp) {
if (postExp == NULL)
return NULL;
Stack s = CreateStack();
BinTree t = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
t->data = postExp[0];
t->left = t->right = NULL;
Push(s, t);
for (int i = 1; postExp[i] != '\0'; ++i) {
if (postExp[i] < 'z' && postExp[i] > 'a') {
BinTree t = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
t->data = postExp[i];
t->left = t->right = NULL;
Push(s, t);
} else {
BinTree t = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
t->data = postExp[i];
BinTree tr, tl;
Pop(s, &tr);
Pop(s, &tl);
t->left = tl;
t->right = tr;
Push(s, t);
}
}
Pop(s, &t);
DestoryStack(s);
return t;
}
测试代码
//gcc test_binaryTree.c -o main -Wno-incompatible-pointer-types
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "binaryTree.c"
void visit(char ch) {
printf("%2c ", ch);
}
void test_BinTree() {
printf("\n%s\n", __func__);
char arr[] = "ABCDFGI00E00H000000";
BinTree bt = CreateBinTreeFromArray(arr);
PreOrderTraversal_recursively(bt, visit);
printf("\n\n");
PreOrderTraversal_iteratively(bt, visit);
printf("\n\n");
InOrderTraversal_recursively(bt, visit);
printf("\n\n");
InOrderTraversal_iteratively(bt, visit);
printf("\n\n");
PostOrderTraversal_recursively(bt, visit);
printf("\n\n");
PostOrderTraversal_iteratively(bt, visit);
printf("\n\n");
LevelOrderTraversal(bt, visit);
printf("\n\n");
PreOrderPrintLeaves(bt);
printf("\n\n");
int height = BinTreeHeight(bt);
printf("height=%d\n", height);
char postExp[] = "abc*+de*f+g*+";
bt = ExpressionTree(postExp);
printf("\npostExp:%s\n", postExp);
printf("PostOrderTraversal:\n");
PostOrderTraversal_iteratively(bt, visit);
printf("\n\n");
DestoryBinTree(bt);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
test_BinTree();
return 0;
}
二叉搜索树
提供的主要操作集有:
- 递归查找和迭代查找
- 递归查找最大最小值和迭代查找最大最小值
- 向BST中插入元素
- 从BST中删除元素
代码实现
#include "binaryTree.c"
BinTree BST_Find_recursively(BinTree BST, BinTreeElemType X) {
if (!BST) {
return NULL;
}
if (X < BST->data) {
return BST_Find_recursively(X, BST->left);
} else if (X > BST->data) {
return BST_Find_recursively(X, BST->right);
} else {
return BST;
}
}
BinTree BST_Find_iteratively(BinTree BST, BinTreeElemType X) {
while (BST) {
if (X > BST->data) {
BST = BST->right;
} else if (X < BST->data) {
BST = BST->left;
} else {
return BST;
}
}
return NULL;
}
BinTree BST_FindMin_recursively(BinTree BST) {
if (BST == NULL) {
return NULL;
} else if (BST->left == NULL) {
return BST;
} else {
return BST_FindMin_recursively(BST->left);
}
}
BinTree BST_FindMin_iteratively(BinTree BST) {
if (BST) {
while (BST) {
BST = BST->right;
}
}
return BST;
}
BinTree BST_FindMax_recursively(BinTree BST) {
if (BST == NULL) {
return NULL;
} else if (BST->right == NULL) {
return BST;
} else {
return BST_FindMin_recursively(BST->right);
}
}
BinTree BST_FindMax_iteratively(BinTree BST) {
if (BST) {
while (BST) {
BST = BST->right;
}
}
return BST;
}
BinTree BST_Insert(BinTree BST, BinTreeElemType X) {
if (BST == NULL) {
BST = (BinTree)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
BST->data = X;
BST->right = BST->left = NULL;
} else {
if (X > BST->data) {
BST->right = BST_Insert(X, BST->right);
} else if (X < BST->data) {
BST->left = BST_Insert(X, BST->left);
}
}
return BST;
}
BinTree BST_Delete(BinTree BST, BinTreeElemType X) {
BinTree tmp;
if (BST == NULL) {
return;
} else if (X < BST->data) {
//X小,到左子树递归删除,注意接收返回值
BST->left = BST_Delete(X, BST->left);
} else if (X > BST->data) {
//X大,到右子树递归删除,注意接收返回值
BST->right = BST_Delete(X, BST->right);
} else {
//BST指向了要删除的节点
if (!BST->left && !BST->right) {
//左右子树都不空,去右子树找最小值
tmp = BST_FindMin_recursively(BST->right);
//替换到当前节点,相当于删除了
BST->data = tmp->data;
//去右子树把那个节点删掉
BST->right = BST_Delete(BST->data, BST->right);
} else {
//左右子树有一棵空,或都空
tmp = BST;
if (BST->left == NULL) {
//右子树非空,将其返回给上层
BST = BST->right;
} else {
//左子树非空,将其返回给上层
BST = BST->left;
}
free(tmp);
}
}
return BST;
}
测试代码
无
平衡二叉树
又称AVL树,是一种自平衡二叉树。插入节点时通过旋转操作保证左右子树高度之差≤1。
代码实现
提供的主要操作集有:
- 左单旋,右单旋,左右旋转,右左旋转四种平衡调整方式
- 向AVLTree中插入节点
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "linkQueue.c"
#define AVLTreeElemType int
struct AVLNode {
AVLTreeElemType data;
struct AVLNode* left;
struct AVLNode* right;
int height;
};
typedef struct AVLNode* AVLTree;
int max(int a, int b) {
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
int AVLTreeHeight(AVLTree t) {
if (t == NULL)
return 0;
else
return t->height;
}
void PrintAVLTreeLevelOrder(AVLTree t) {
printf("\n%s\n", __func__);
if (t == NULL)
return;
Queue q = CreateQueue();
EnQueue(q, t);
AVLTree x;
while (!QueueEmpty(q)) {
DeQueue(q, &x);
printf("%2d ", x->data);
if (x->left)
EnQueue(q, x->left);
if (x->right)
EnQueue(q, x->right);
}
printf("\n\n");
DestoryQueue(q);
}
//LL
AVLTree SingleLeftRotation(AVLTree A) {
AVLTree B = A->left;
A->left = B->right;
B->right = A;
A->height = max(AVLTreeHeight(A->left), AVLTreeHeight(A->right)) + 1;
B->height = max(AVLTreeHeight(B->left), AVLTreeHeight(B->right)) + 1;
return B;
}
//RR
AVLTree SingleRightRotation(AVLTree A) {
AVLTree B = A->right;
A->right = B->left;
B->left = A;
A->height = max(AVLTreeHeight(A->left), AVLTreeHeight(A->right)) + 1;
B->height = max(AVLTreeHeight(B->left), AVLTreeHeight(B->right)) + 1;
return B;
}
//LR
AVLTree DoubleLeftRightRotation(AVLTree A) {
//先对左子树RR旋转
A->left = SingleRightRotation(A->left);
//在对ALL旋转
return SingleLeftRotation(A);
}
//RL
AVLTree DoubleRightLeftRotation(AVLTree A) {
A->right = SingleLeftRotation(A->left);
return SingleRightRotation(A);
}
AVLTree AVLTree_Insert(AVLTree t, AVLTreeElemType x) {
if (t == NULL) {
t = (AVLTree)malloc(sizeof(struct AVLNode));
t->data = x;
t->height = 1;
t->left = t->right = NULL;
} else if (x < t->data) {
t->left = AVLTree_Insert(t->left, x);
if (AVLTreeHeight(t->left) - AVLTreeHeight(t->right) == 2) {
if (x < t->left->data) {
t = SingleLeftRotation(t);
} else {
t = DoubleLeftRightRotation(t);
}
}
} else if (x > t->data) {
t->right = AVLTree_Insert(t->right, x);
if (AVLTreeHeight(t->left) - AVLTreeHeight(t->right) == -2) {
if (x > t->right->data) {
t = SingleRightRotation(t);
} else {
t = DoubleRightLeftRotation(t);
}
}
} //else x==t->data,无需插入
t->height = max(AVLTreeHeight(t->left), AVLTreeHeight(t->right)) + 1;
return t;
}
测试代码
AVL树有着良好的性质,我们以任意顺序向树中插入节点,总能得到一棵很平衡的二叉树。
//gcc test_AVLTree.c -o main -Wno-incompatible-pointer-types
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "AVLTree.c"
void test_AVLTree() {
AVLTree t = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < 15; ++i) {
t = AVLTree_Insert(t, i);
}
printf("AVLTree height=%d\n", t->height);
PrintAVLTreeLevelOrder(t);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
test_AVLTree();
return 0;
}
堆
堆,又称优先队列(Priority Queue),是一种特殊的队列,取出元素的顺序是按照元素的优先权(关键字)的大小,而不是元素进入队列的先后顺序。
优先队列的用途广泛,比如堆排序就是借助堆实现的选择排序,还有操作系统的进程调度,也需要根据进程的优先级从就绪队列中选择下一个需要调度的进程。
虽然名字叫“优先队列”,听起来像是线性结构,但是实际上一般用完全二叉树实现堆。堆可分为大顶堆和小顶堆两种,顾名思义,大顶堆就是对于任意子树,根节点都比左右子节点大;小顶堆就是对于任意子树,根节点都比左右子节点小,二者的实现方式相同,逻辑结构都是完全二叉树,采用数组存储。
下面是4个堆的例子,前2个是大顶堆,后2个是小顶堆:

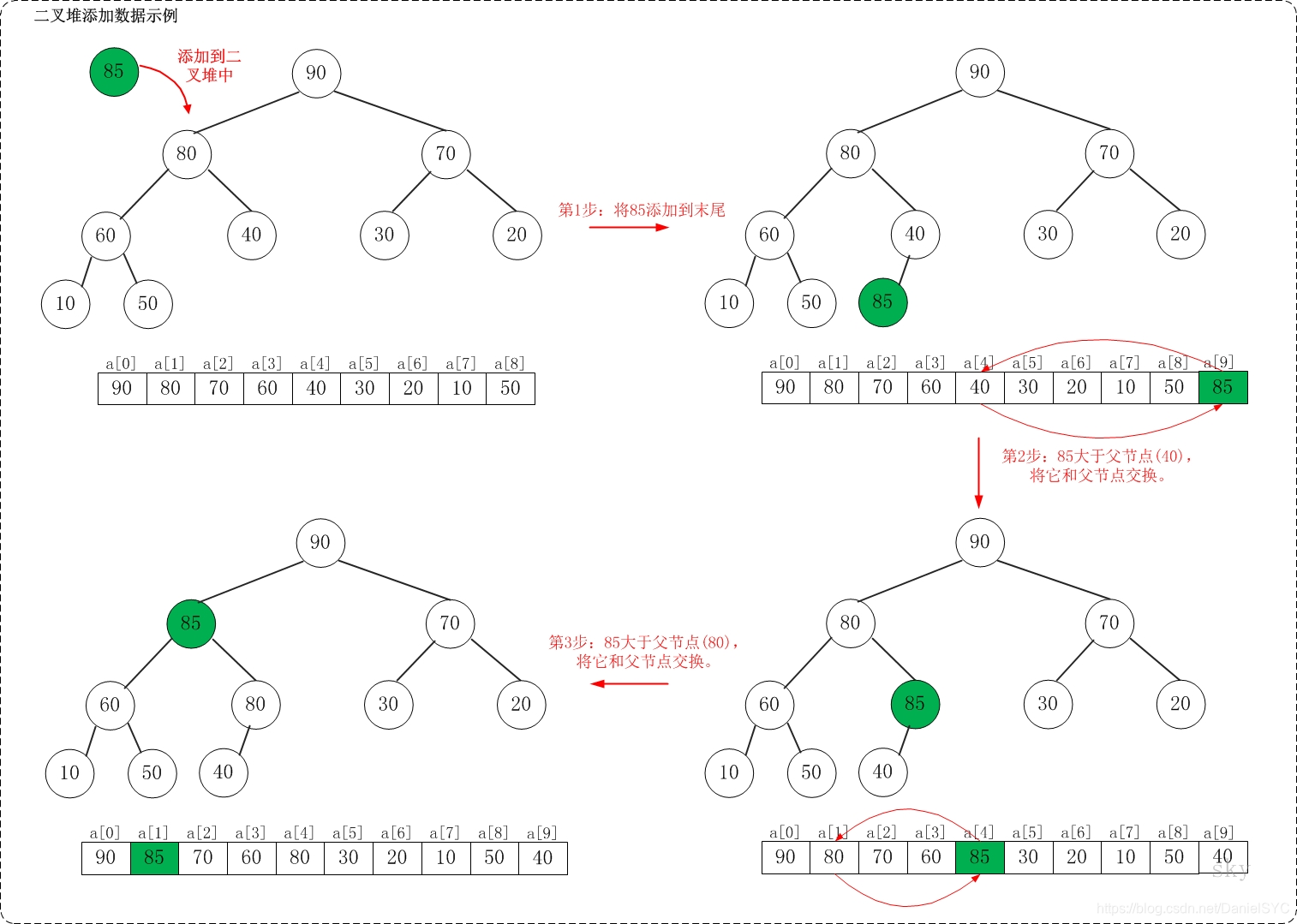
一个大顶堆的插入过程如下图所示:
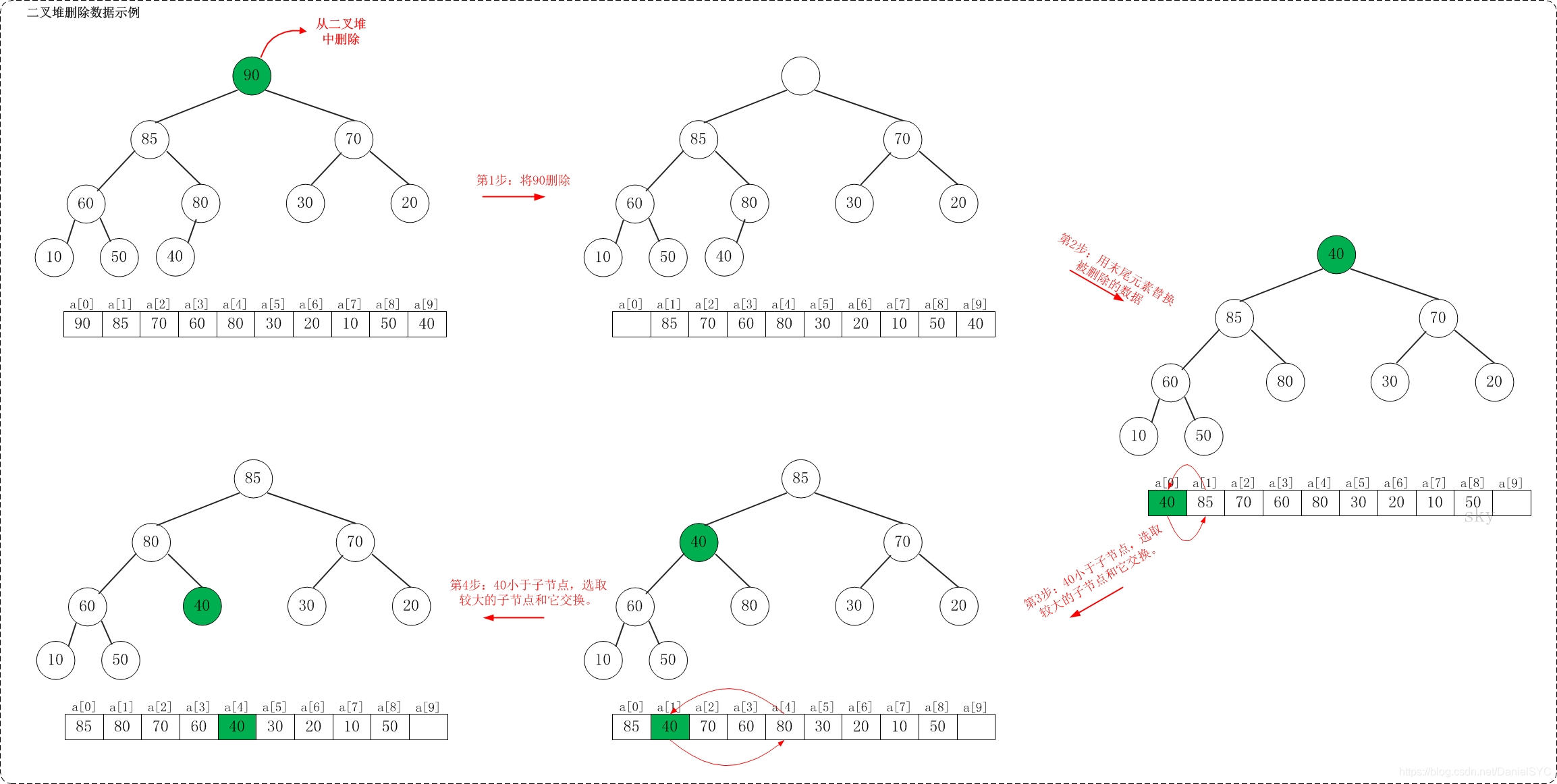
一个大顶堆的删除过程如下图所示:
提供的主要操作集有:
- 建立最大/最小堆
- 向最大/最小堆中插入元素
- 从最大/最小堆中删除元素
- 对最大/最小堆向下过滤节点
- 将堆中的元素调整为堆
代码实现
#include <limits.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//哨兵值
#define MAXDATA INT_MAX
#define MINDATA INT_MIN
typedef int HeapElemType;
struct HeapNode {
HeapElemType* data;
int size;
int capacity;
};
typedef struct HeapNode* MaxHeap;
typedef struct HeapNode* MinHeap;
MaxHeap CreateMaxHeap(int MaxSize) {
MaxHeap H = (MaxHeap)malloc(sizeof(struct HeapNode));
//为数组开空间,0号元素存的是哨兵,所以要+1
H->data = (HeapElemType*)malloc((MaxSize + 1) * sizeof(struct HeapNode));
H->size = 0;
H->capacity = MaxSize;
//哨兵
H->data[0] = MAXDATA;
return H;
}
MinHeap CreateMinHeap(int MaxSize) {
MinHeap H = (MinHeap)malloc(sizeof(struct HeapNode));
H->data = (HeapElemType*)malloc((MaxSize + 1) * sizeof(struct HeapNode));
H->size = 0;
H->capacity = MaxSize;
H->data[0] = MINDATA;
return H;
}
void DestoryHeap(struct HeapNode* h) {
if (h != NULL) {
if (h->data != NULL)
free(h->data);
free(h);
}
}
bool HeapFull(struct HeapNode* H) {
return H->size == H->capacity;
}
bool HeapEmpty(struct HeapNode* H) {
return H->size == 0;
}
void printHeap(struct HeapNode* H) {
printf("\n%s\n", __func__);
for (int i = 1; i <= H->size; ++i) {
printf("%2d ", H->data[i]);
}
printf("\n\n");
}
bool InsertMaxHeap(MaxHeap H, HeapElemType item) {
if (HeapFull(H)) {
return false;
}
//刚开始假设插入的位置在数组的最后
int i = ++H->size;
//只要item比父节点大:
while (item > H->data[i / 2]) {
//父节点下来
H->data[i] = H->data[i / 2];
//我上去
i = i / 2;
}
//跳出循环时i锚定了合适的插入位置,赋值
H->data[i] = item;
return true;
}
bool InsertMinHeap(MinHeap H, HeapElemType item) {
if (HeapFull(H)) {
return false;
}
int i = ++H->size;
while (item < H->data[i / 2]) {
H->data[i] = H->data[i / 2];
i = i / 2;
}
H->data[i] = item;
return true;
}
HeapElemType DeleteMax(MaxHeap H) {
if (HeapEmpty(H)) {
return H->data[0];
}
HeapElemType MaxItem = H->data[1];
HeapElemType tmp = H->data[H->size--];
int Parent = 1;
int Child;
//算法核心:给tmp找到合适的位置
while (Parent * 2 <= H->size) {
// Child指向左孩子
Child = 2 * Parent;
// Child指向左右孩子中最大者
if ((Child != H->size) && H->data[Child] < H->data[Child + 1]) {
Child++;
}
//如果tmp>左右孩子最大者,说明tmp在这里坐得住,跳出循环
if (tmp > H->data[Child]) {
break;
} else {
//让孩子上来
H->data[Parent] = H->data[Child];
//自己下去
Parent = Child;
}
}
H->data[Parent] = tmp;
return MaxItem;
}
HeapElemType DeleteMin(MinHeap H) {
if (HeapEmpty(H)) {
return H->data[0];
}
HeapElemType MinItem = H->data[1];
HeapElemType tmp = H->data[H->size--];
int Parent = 1;
int Child;
while (Parent * 2 <= H->size) {
Child = 2 * Parent;
if ((Child != H->size) && H->data[Child + 1] < H->data[Child]) {
Child++;
}
if (tmp < H->data[Child]) {
break;
} else {
H->data[Parent] = H->data[Child];
Parent = Child;
}
}
H->data[Parent] = tmp;
return MinItem;
}
void percDownMaxHeap(MaxHeap H, int n) {
HeapElemType top;
int Child;
int Parent = n;
top = H->data[n];
//向下过滤
for (Parent = n; Parent * 2 <= H->size; Parent = Child) {
Child = 2 * Parent;
if (Child != H->size && H->data[Child] < H->data[Child + 1]) {
Child++;
}
if (top >= H->data[Child]) {
break;
} else {
H->data[Parent] = H->data[Child];
}
}
H->data[Parent] = top;
}
void percDownMinHeap(MinHeap H, int n) {
HeapElemType top;
int Child;
int Parent = n;
top = H->data[n];
for (Parent = n; Parent * 2 <= H->size; Parent = Child) {
Child = 2 * Parent;
if (Child != H->size && H->data[Child + 1] < H->data[Child]) {
Child++;
}
if (top <= H->data[Child]) {
break;
} else {
H->data[Parent] = H->data[Child];
}
}
H->data[Parent] = top;
}
void initMaxHeap(struct HeapNode* H) {
//从最后一个有儿子的节点开始
for (int i = (H->size / 2); i > 0; i--) {
percDownMaxHeap(H, i);
}
}
void initMinHeap(struct HeapNode* H) {
//从最后一个有儿子的节点开始
for (int i = (H->size / 2); i > 0; i--) {
percDownMinHeap(H, i);
}
}
测试代码
#include "heap.c"
void test_MaxHeap_01() {
printf("\n%s:\n", __func__);
MaxHeap h0 = CreateMaxHeap(128);
InsertMaxHeap(h0, 78);
InsertMaxHeap(h0, 32);
InsertMaxHeap(h0, 53);
InsertMaxHeap(h0, 12);
InsertMaxHeap(h0, 90);
InsertMaxHeap(h0, 10);
InsertMaxHeap(h0, 99);
InsertMaxHeap(h0, 19);
InsertMaxHeap(h0, 79);
printHeap(h0);
initMaxHeap(h0);
printHeap(h0);
while (!HeapEmpty(h0)) {
printf("\nDeleteMax:%d\n", DeleteMax(h0));
printHeap(h0);
}
}
void test_MaxHeap_02() {
printf("\n%s:\n", __func__);
MaxHeap h0 = CreateMaxHeap(128);
//得到一个不是堆的东西
h0->data[1] = 79;
h0->data[2] = 66;
h0->data[3] = 43;
h0->data[4] = 83;
h0->data[5] = 30;
h0->data[6] = 87;
h0->data[7] = 38;
h0->data[8] = 55;
h0->data[9] = 91;
h0->data[10] = 72;
h0->data[11] = 49;
h0->data[12] = 9;
h0->size = 12;
printHeap(h0);
//调整为堆
initMaxHeap(h0);
printHeap(h0);
}
void test_MinHeap_01() {
printf("\n%s:\n", __func__);
MinHeap h0 = CreateMinHeap(128);
InsertMinHeap(h0, 78);
InsertMinHeap(h0, 12);
InsertMinHeap(h0, 32);
InsertMinHeap(h0, 53);
InsertMinHeap(h0, 90);
InsertMinHeap(h0, 10);
InsertMinHeap(h0, 99);
InsertMinHeap(h0, 19);
InsertMinHeap(h0, 79);
printHeap(h0);
initMinHeap(h0);
printHeap(h0);
while (!HeapEmpty(h0)) {
printf("\nDeleteMin:%d\n", DeleteMin(h0));
printHeap(h0);
}
}
void test_MinHeap_02() {
printf("\n%s:\n", __func__);
MinHeap h0 = CreateMinHeap(128);
//得到一个不是堆的东西
h0->data[1] = 79;
h0->data[2] = 66;
h0->data[3] = 43;
h0->data[4] = 83;
h0->data[5] = 30;
h0->data[6] = 87;
h0->data[7] = 38;
h0->data[8] = 55;
h0->data[9] = 91;
h0->data[10] = 72;
h0->data[11] = 49;
h0->data[12] = 9;
h0->size = 12;
printHeap(h0);
//调整为堆
initMinHeap(h0);
printHeap(h0);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
test_MaxHeap_01();
test_MaxHeap_02();
test_MinHeap_01();
test_MinHeap_02();
return 0;
}
哈夫曼树
提供的主要操作集有:
- 从一个
DataWeightPair数组中建立哈夫曼树
代码实现
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define HuffmanTreeElemType char
struct HTNode {
int weight;
HuffmanTreeElemType data;
struct HTNode* left;
struct HTNode* right;
};
typedef struct HTNode* HuffmanTree;
typedef struct {
HuffmanTreeElemType data;
int weight;
} DataWeightPair;
//存储哈夫曼树节点指针的最小堆
struct MinHeapNode {
HuffmanTree* data;
int size;
int capacity;
};
typedef struct MinHeapNode* MinHeap;
MinHeap CreateMinHeap(int c) {
MinHeap h = (MinHeap)malloc(sizeof(struct MinHeapNode));
if (h != NULL) {
h->data = (HuffmanTree*)malloc(sizeof(HuffmanTree) * (c + 1));
if (h->data == NULL) {
free(h);
return NULL;
}
h->capacity = c;
h->size = 0;
h->data[0] = (HuffmanTree)malloc(sizeof(struct HTNode));
h->data[0]->weight = -1;
h->data[0]->data = '\0';
}
return h;
}
void DestoryMinHeap(MinHeap h) {
if (h != NULL) {
if (h->data != NULL) {
free(h->data);
}
free(h);
}
}
bool HeapFull(MinHeap h) {
return h->capacity == h->size;
}
bool HeapEmpty(MinHeap h) {
return h->size == 0;
}
bool Insert(MinHeap h, HuffmanTree x) {
if (HeapFull(h))
return false;
int i = ++h->size;
for (; x->weight < h->data[i / 2]->weight; i /= 2) {
h->data[i] = h->data[i / 2];
}
h->data[i] = x;
return true;
}
void percDown(MinHeap h, int p) {
int parent = p;
int child;
HuffmanTree x = h->data[p];
for (parent = p; parent * 2 <= h->size; parent = child) {
child = parent * 2;
if (child != h->size && h->data[child + 1]->weight < h->data[child]->weight)
child++;
if (h->data[parent]->weight < h->data[child]->weight)
break;
else
h->data[parent] = h->data[child];
}
h->data[parent] = x;
}
HuffmanTree DeleteMin(MinHeap h) {
if (h == NULL || HeapEmpty(h)) {
return NULL;
}
HuffmanTree minItem = h->data[1];
HuffmanTree x = h->data[h->size--];
int parent, child;
for (parent = 1; parent * 2 <= h->size; parent = child) {
child = parent * 2;
if (child != h->size && h->data[child + 1]->weight < h->data[child]->weight)
child++;
if (x->weight <= h->data[child]->weight)
break;
else
h->data[parent] = h->data[child];
}
h->data[parent] = x;
return minItem;
}
void initMinHeap(MinHeap h) {
for (int i = h->size / 2; i >= 1; --i) {
percDown(h, i);
}
}
HuffmanTree CreateHuffmanTree(const DataWeightPair* dfps, int n) {
int i;
HuffmanTree T;
MinHeap h = CreateMinHeap(n * 2);
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
h->data[i + 1] = (HuffmanTree)malloc(sizeof(struct HTNode));
h->data[i + 1]->data = dfps[i].data;
h->data[i + 1]->weight = dfps[i].weight;
}
h->size = n;
initMinHeap(h);
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
T = (HuffmanTree)malloc(sizeof(struct HTNode));
T->left = DeleteMin(h);
T->right = DeleteMin(h);
T->weight = T->left->weight + T->right->weight;
T->data = '\0';
Insert(h, T);
}
T = DeleteMin(h);
return T;
}
测试代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "huffmanTree.c"
void printHuffmanTree_preOrder(HuffmanTree ht) {
if (ht) {
printf("data=%c,weight=%d\n", ht->data, ht->weight);
printHuffmanTree_preOrder(ht->left);
printHuffmanTree_preOrder(ht->right);
}
}
void printHuffmanTree_inOrder(HuffmanTree ht) {
if (ht) {
printHuffmanTree_inOrder(ht->left);
printf("data=%c,weight=%d\n", ht->data, ht->weight);
printHuffmanTree_inOrder(ht->right);
}
}
void printHuffmanTreeLeaves(HuffmanTree ht) {
if (ht) {
if (ht->left == NULL && ht->right == NULL) {
printf("data=%c,weight=%d\n", ht->data, ht->weight);
}
printHuffmanTreeLeaves(ht->left);
printHuffmanTreeLeaves(ht->right);
}
}
void test_huffmanTree() {
DataWeightPair dfps[7] = {
{'a', 10},
{'e', 15},
{'i', 12},
{'s', 3},
{'t', 4},
{'p', 13},
{'l', 1}
};
HuffmanTree ht = CreateHuffmanTree(dfps, 7);
printf("\npreOrder\n");
printHuffmanTree_preOrder(ht);
printf("\ninOrder\n");
printHuffmanTree_inOrder(ht);
printf("\nleaves\n");
printHuffmanTreeLeaves(ht);
return;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
test_huffmanTree();
return 0;
}
并查集
提供的主要操作集有:
- 普通查找算法和路径压缩查找算法
- 普通并集算法和按秩归并的并集算法
代码实现
#define MAXSETSIZE 1024
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int SetElemType;
typedef int SetName;
typedef SetElemType* SetType;
//沿着父节点指针向上查,直到找到根节点
SetName Find(SetType S, SetElemType X) {
while (S[X] >= 0)
X = S[X];
return X;
}
SetName Find_PathCompression(SetType S, SetElemType X) {
if (S[X] < 0)
return X;
else
return S[X] = Find(S, S[X]);
}
void Union_tssn(SetType S, SetName Root1, SetName Root2) {
//默认Root1和Root2是两个不同集合的根节点
S[Root2] = Root1;
}
void Union_mergeByHeight(SetType S, SetName Root1, SetName Root2) {
if (S[Root2] < S[Root1]) {
//如果集合2比较高,集合1并入集合2
S[Root1] = Root2;
} else {
//否则
if (S[Root1] == S[Root2])
S[Root1]--;
S[Root2] = Root1;
}
}
void Union_mergeBySize(SetType S, SetName Root1, SetName Root2) {
if (S[Root2] < S[Root1]) {
//如果集合2比较大
S[Root2] += S[Root1];
//集合1并入集合2
S[Root1] = Root2;
} else {
//否则集合1比较大
S[Root1] += S[Root2];
//集合2并入集合1
S[Root2] = Root1;
}
}
测试代码
无





















 2302
2302











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








