引言
SpringBoot相信很多同学都非常了解,实际工作中也经常使用到。但是不知道大家在使用过程中有没有想过一个问题,SpringBoot内嵌tomcat到底是怎么启动的?内嵌tomcat启动服务的好处又是什么呢?本文将结合SpringBoot源码探讨下这些问题。
- SpringBoot如何启动内嵌Tomcat
- 总结
一、SpringBoot如何启动内嵌Tomcat
大致的代码流程如下所示:

下面我们来一起详细分析下内嵌Tomcat的启动过程吧。
1、构建SpringApplication实例
SpringBoot整个启动过程的起点就是在这个SpringApplication类中,所它是我们理解启动流程的关键。这边给大家一个小建议,在阅读源码之前首先看下官方的代码注释,便于我们对源码的功能有大致的感受和理解。如下图可知,SpringApplication类实际是通过main方法来启动和加载Spring应用。

SpringApplication在run方法中进行启动操作,具体代码如下所示:
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class[]{primarySource}, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return (new SpringApplication(primarySources)).run(args);
}
在上述代码中可知,通过创建SpringApplication实例之后来继续后续的步骤,在创建SpringApplication实例过程中进行了一些非常重要的初始化步骤,我们在一起深入看下。其中最重要的两个方法在代码中进行了注释。
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//设置初始化
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//设置监听器
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
2、设置初始化

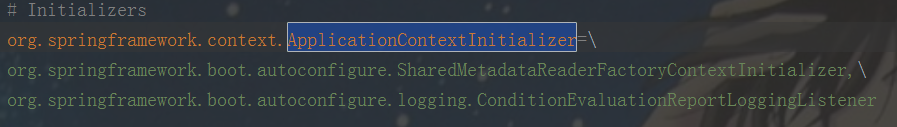
通过META-INF/spring.factories获取对应的类名,由于都是完全限定名,因此在下一步骤中根据该信息进行对应实例的创建。分别对应spring-oot jar包中的META-INF/spring.factories以及spring-boot-autoconfigure jar包中的META-INF/spring.factories中关于ApplicationContextInitializer对应的需要创建的实例。

spring-boot jar包中的META-INF/spring.factories文件中的5个类

以及spring-boot-autoconfigure jar包中的两个类。
3、设置监听器
和初始化原理一样,也是从spring-boot jar以及spring-boot-autoconfigure jar包中的META-INF/spring.factories获取需要进行设置的监听器的类信息。

4、实例构建好了,那就run起来创建应用上下文
public class SpringApplication {
...
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList();
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
Collection exceptionReporters;
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
//创建应用上下文
context = this.createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context);
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
this.refreshContext(context);
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var10);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
return context;
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
}
}
在创建应用上下文的过程中,此处根据webApplicationType属性判断来决定创建具体类型的ApplicationContext,而webApplicationType属性在第一阶段的SpringApplication实例创建的时候进行获取。SpringBoot将应用程序分为三种类型NONE(非web类型应用)、SERVLET(以嵌入web服务器启动的web应用)、REACTIVE(响应式web应用程序)。根据获取到的应用类型创建对应的ApplicationContext。
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch(this.webApplicationType) {
//创建AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext");
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext");
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName("org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", var3);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
这里获取到的应用类型为SERVLET,因此会创建AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext上下文。
而AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext类继承了ServletWebServerApplicationContext,而这个类是最终继承了AbstractApplicationContext。
5、刷新应用上下文
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
}
由下图可知,实际进行应用上下文刷新的由之前创建的ServletWebServerApplicationContext进行。

ServletWebServerApplicationContext应用上下文中完成refresh,我们可以看到refresh操作是通过实现父类AbstractApplicationContext操作来进行的。,
@Override
public final void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
try {
super.refresh();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
stopAndReleaseWebServer();
throw ex;
}
}
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
在onRefresh操作中,实际在ServletWebServerApplicationContext中进行属于该应用上下文业务相关的操作,即创建WebServer 实例

6、创建WebServer实例,启动Tomcat实例
ServletWebServerApplicationContext中定义了onRefresh操作,用以创建WebServer 实例。
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
//创建webServer实例
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
TomcatServletWebServerFactory用于实现获取WebServer 实例。
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
//创建Tomcat实例
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
//创建Tomcat工作目录
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
//创建连接对象(Connector是Tomcat重要组件,主要负责处理客户端连接,以及请求处理,这里简单解释下)
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
//准备tomcat context
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
//返回WebServer实现TomcatWebServer
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
在返回TomcatWebServer实例过程中,进行TomcatWebServer初始化操作,进而完成tomcat实例的启动流程。
public TomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart) {
Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null");
this.tomcat = tomcat;
this.autoStart = autoStart;
initialize();
}
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized (this.monitor) {
try {
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
Context context = findContext();
context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
if (context.equals(event.getSource()) && Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't
// happen when the service is started.
removeServiceConnectors();
}
});
// Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
this.tomcat.start();
// We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
try {
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader());
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
// Naming is not enabled. Continue
}
// Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
// blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
stopSilently();
destroySilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
}
}
}
至此,Springboot通过内嵌tomcat完成服务启动的流程给大家分析完了,通过这种自启动的方式减少了手动部署tomcat等web容器的步骤,提升了微服务的开发效率。
二、总结
基于以上分析,我们将整个流程用图形化的形式表现出来,帮助大家们理解内嵌Tomcat启动的流程。下图中将主要的步骤中进行了汇总,后续在系列文章结束时,将奉上比较完整的流程图,期待一下哦。
欢迎大家关注作者微信公众号,不定期更新文章,也可以和大家交流技术以及为大家提供免费的技术资料哦。

























 659
659











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










