本期内容:
1 Scala中的类、object实战详解
2 Scala中的抽象类、接口实战详解
3 综合案例及Spark源码解析
重点内容
(1)Scala单例对象
单例对象,不能带参数,因为不能用new来实例化,而每个单例对象都是被实例化的虚构类,且在第一次被访问的时候才会被实例化;单例对象不能定义静态成员,所以更加面向对象。Scala单例对象是十分重要的,没有像在Java一样,有静态类、静态成员、静态方法,但是Scala提供了object对象,这个object对象类似于Java的静态类,它的成员、它的方法都默认是静态的。如果object的静态成员要被外界访问,则该成员不能被private修饰
与Java另一个不一样的是,如果是静态类的静态变量、静态方法,类加载就会执行,但是Scala只有在第一次使用object的静态变量,静态方法才会生效。object也有一个隐形的无参的构造器。
(2)抽象类、抽象字段、抽象方法
申明抽象类使用abstract,在scala中,抽象类和物质中的方法、字段和类型都可以是抽象的。抽象字段和抽象方法都是只有字段或者方法的定义,而没有字段或者方法的具体实现。
抽象字段:具体类中给字段申明的时候不给字段赋值,该字段变为抽象字段,抽象字段没有值,定义的时候必须申明返回类型,否则编译器会报错
val name :Int
var number:Int=_
//非抽象类,申明字段必须赋值(具体值或者用占位符_代替,且使用占位符的时候必须为var)
抽象方法:抽象方法不需要(也不允许)有abstract修饰符,一个方法只要是没有实现(没有等号或没有方法体),它就是抽象的,在子类中覆写或者覆写Trait中的非抽象方法(方法有具体实现)要使用override关键字。
抽象类型:scala中的类型成员也可以是抽象的。
Final 后子类没法继承和覆盖,类同样有final不能被访问。
super是在调用父类同名的非抽象方法时使用。
抽象的属性:定义时没有具体的值。
(3)Scala中类的继承,超类的重载等
1、与Java语言一样,Scala语言也是使用extends关键字实现子类对父类的继承。
2、子类中的方法和字段可以使用 override 关键字实现对它的超类(父类)中同名的方法或字段进行覆写(重写)。Override使用两种作用:
类调用父类的非抽象方法,必须使用override,并且使用override可以检查代码的错误;
3、当子类使用主构造器进行实例化时,与父类的主构造器中同名的参数也会直接传递具体的参数值给父类使用。抽象字段没有值,定义的时候必须申明返回类型,否则编译器会报错。
//与类名放一起的构造器是默认构造器,调用默认构造器时候,会执行没有放在方法或者代码块中的代码。
class Person{
val name =”Flink”
val age =10
def update(newName:String){
println(“Hi”)
}
def this(name:String){
//重载构造器,调用主构造器,所以必须写this
this
this.name =name
}
def this (name:String,age:Int){
//重载构造器,加入成员age
this(name)
this.age =age
}
}
val p = new Person(“Spark”,22)
p.name //这边是构造器的重载,调用默认构造器
(4)Apply方法
我们采用object对象的apply方式的好处是,例如我们构建一个数组,数组里面有很多元素或其它的集合,我们不需要new 一个对象,直接以object传递参数就好。
我们new一个伴生类的对象,调用它的方法,如果我们要调用类的apply方法,用类构建的实例对象加个(),在object伴生对象中通过apply方法来构造相应类的实例。
(5)Trait(特质)
在trait中实现抽象类的抽象方法,Scala中的trait类型于Java中的interface,但比interface强大的多,trait支持部分实现,也就是说可以在scala的trait中可以实现部分方法。Scala语言中trait的定义和使用:
1、与Java语言中的接口(interface)中只含有抽象方法不同,Scala语言中的特质(trait)可以包含抽象字段、抽象方法或者实现了方法体的方法。
2、在使用Scala语言构建对象时,可以为该对象添加特质。
(6)伴生对象、伴生类
伴生对象中创建的private的成员可以被伴生类通过import的方式调用,伴生对象中定义的protected无法被访问。伴生类、伴生对象(内部成员全是静态的),必须在同一文件中定义,伴生对象的apply方法:当前类的对象的工厂方法。
object Person{
println(“Scala”)
val salary = 0.0
def getSalary =salary
} (7)Scala中的包
包可以嵌套,同一个包可以定义在多个文件当中,也不需要将源文件的目录和包之间对应起来。包可以包含类、对象和特质,但不能包含函数或变量的定义,这是JVM的局限。将工具函数或常量添加到包,而不是某个Utils对象,更为合理。
package com.horstmann.impatient
package object people {
val defaultName = "John Q. Public"
}
package people {
class Person {
val name = defaultName
}
}//每个包可以有一个包对象,需要在父包中定义,名称与子包一样。
而Scala则是“公共可见”的。如果要想让成员在某个包内可见,可以使用类似于对象私有字段的语法来指定:
private[package-name] …
即package-name包中的所有类和对象都可以访问private后面的成员。
import java.awt.{Color, Font}
// 重命名成员
import java.util.{HashMap => JavaHashMap}
// 隐藏成员
import java.util.{HashMap => _, _} // 引入了util包的所有成员,但是HashMap被隐藏了 (8)私有val和val生成getter和setter解析
字段所生成的公有getter和setter的编写
class person {
var myName =”Hadoop” //生成公有的getter和setter方法,外部可以调用
def name =this.myName
def name_=(newName:String){
//设置name的setter,再访问的时候可以重新赋值
myName = newName
println(“hi:” + myName)
}
}
val rocky = new person
rocky.name //访问的是生成公有的getter和setter方法
rocky.name =”Spark”
//给name赋值,调用了name的自定义getter、setter方法
//下面是对默认的getter和setter的编写,只想暴露getter方法
class person {
private var myName =”Hadoop”
def name =this.myName
def update(newName:String){
//设置name的setter,再访问的时候可以重新赋值
myName = newName
println(“hi:” + myName)
}
}
val rocky = new person
rocky.name
rocky.name = “Flink” //会报错,找不到
rocky.update(“Scala”) 仅暴露getter的两种方法(控制外部对内容的改变:
1、使用private val的方式定义变量;
2、使用var的方式 ,采用其他setter的实现,使用update覆写控制外界对于 getter和setter的访问。
class person {
private var myName = "Hadoop"
def name =this.myName //getter获取到name
def update(newName:String){
myName =newName
println("Hi:" + myName)
}
def talk(p:person) ={
println("Hello"+p.name)
}
}
//申明两个Person的实例p1,p2
val p1 = new person
val p2 = new person
p1.talk //报错,类中没有talk方法的访问参数
p2.update("Flume") //Hi:Flume
p1.talk(p2) //HelloFlume
//Private[this]在类私有的基础上,类对象也私有。
Private[this] val name =”FLink”
//对象私有,不容许其他对象进行访问,该类的对象的方法亦不可访问也不容许访问,例如上面talk方法中p.name不容许访问 第二部分:作业
分析Spark核心类:SparkContent,RDD,读懂70%代码并提交微博
(仅从scala语法方面解读)以下只是象征性的列出一些方法或者代码块,旨在以Spark实例的角度强化对scala语言语法的理解和掌握,不足之处请指出,方便相互学习,也为了对Spark有一个更加深入的理解。
一、RDD(弹性分布式数据集)
import scala.reflect.{classTag, ClassTag} //引用{}中的两个包
import org.apache.spark.Partitioner._ //引用Partitioner下所有包内容
/*
* 定义抽象类RDD,主构造器中带一个参数T,为泛型classTag
* 语法:
* 1、抽象:抽象RDD,因为有为实现的变量_sc、deps等申明,以及方法
* 2、私有字段定义:使用private关键字定义var 变量,生成了私有的setter和getter方法
* 3、继承:使用extends关键字,继承自Serializble类
* 4、Trait(特质):RDD使用with关键字包含特质logging
* 5、泛型:ClassTag:RDD参数T类型为ClassTag
* 6、序列:Seq
*/
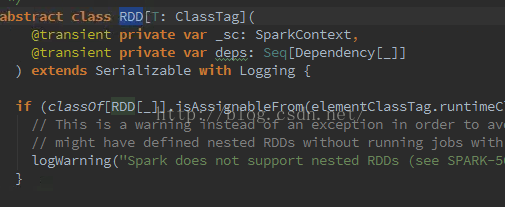
abstract class RDD[T: ClassTag](
@transient private var _sc: SparkContext,
@transient private var deps: Seq[Dependency[_]]
) extends Serializable with Logging {
if (classOf[RDD[_]].isAssignableFrom(elementClassTag.runtimeClass)) {
// This is a warning instead of an exception in order to avoid breaking user programs that
// might have defined nested RDDs without running jobs with them.
logWarning("Spark does not support nested RDDs (see SPARK-5063)")
}
/*
* 定义方法sc,返回类型为SparkContext的对象
* 语法:
* 1、抛出异常,若变量_sc==null,抛出异常
*/
private def sc: SparkContext = {
if (_sc == null) {
throw new SparkException(
"RDD transformations and actions can only be invoked by the driver, not inside of other " +
"transformations; for example, rdd1.map(x => rdd2.values.count() * x) is invalid because " +
"the values transformation and count action cannot be performed inside of the rdd1.map " +
"transformation. For more information, see SPARK-5063.")
}
_sc
}
/*
* 定义this附属构造器调用注构造器(默认构造器)
* 语法:
* 1、附属构造器调用RDD注构造器,类型RDD[_]对象
*/
/** Construct an RDD with just a one-to-one dependency on one parent */
def this(@transient oneParent: RDD[_]) =
this(oneParent.context , List(new OneToOneDependency(oneParent)))
/*
* 定义私有方法conf
* 语法:
* 1、private[spark]:在spark包中该方法可以被其他对象及实例访问
*/
private[spark] def conf = sc.conf
* 定义抽象方法getPartitions
* 语法:
* 1、抽象方法:getPartitions返回一个数组类型,数组中为Partition对象
*/
protected def getPartitions: Array[Partition]
/*
* 定义一个protected级别的方法getPartitions
* 定义方法setName,返回当前对象实例的类型
* 语法:
* 1、this:指向当前执行方法被调用的对象实例
*/
protected def getPartitions: Array[Partition]
def setName(_name: String): this.type = {
name = _name
this
}
* 定义方法iterator,传入2个参数,返回一个Iterator迭代器
* 语法:
* 1、自指向this指代iterator本身
* 2、使用final:final关键字指定义的方法不能被继承后访问
*/
final def iterator(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = {
if (storageLevel != StorageLevel.NONE) {
SparkEnv.get.cacheManager.getOrCompute(this, split, context, storageLevel)
} else {
computeOrReadCheckpoint(split, context)
}
/*
* 定义方法distinct
* 语法:
* 1、implicit隐式转化
*/
/**
* Return a new RDD containing the distinct elements in this RDD.
*/
def distinct(numPartitions: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T] = withScope {
map(x => (x, null)).reduceByKey((x, y) => x, numPartitions).map(_._1)
}
}
/*
* 定义方法takeSample,包含3个字段,返回一个数组
* 语法:
* 1、require:使用先决条件
*/
def takeSample(
withReplacement: Boolean,
num: Int,
seed: Long = Utils.random.nextLong): Array[T] = withScope {
val numStDev = 10.0
require(num >= 0, "Negative number of elements requested")
require(num <= (Int.MaxValue - (numStDev * math.sqrt(Int.MaxValue)).toInt),
"Cannot support a sample size > Int.MaxValue - " +
s"$numStDev * math.sqrt(Int.MaxValue)") 二、SparkContext(应用上下文,控制应用的生命周期)
/*
* 定义类SparkContext,主构造器中带一个参数config,继承了logging的Trait并混入另一个Trait:ExecutorAllocationClient
* 语法:
* 1、私有字段定义:使用private关键字定义val常量,生成了私有的setter和getter方法
* 2、函数:函数getCallSite作为一等公民赋值给creationSite
* 3、继承:使用extends关键字,继承病混入了两个Trait
* 4、Trait(特质):RDD使用with关键字混入logging
* 5、getBoolean:allowMultipleContexts返回Boolean类型,封装了getOrElse
*/
class SparkContext(config: SparkConf) extends Logging with ExecutorAllocationClient {
// The call site where this SparkContext was constructed.
private val creationSite: CallSite = Utils.getCallSite()
// If true, log warnings instead of throwing exceptions when multiple SparkContexts are active
private val allowMultipleContexts: Boolean =
config.getBoolean("spark.driver.allowMultipleContexts", false)
/*
* 调用方法markPartiallyConstructed,创建注构造器的时候执行方法。
* this:指代SparkContext对象实例本身
* private[spark]:stopped字段可以被spark下的成员访问
* 过程化:定义private方法 assertNotStopped,只能被当下使用,返回值为Unit表示方法为过程化
*/
SparkContext.markPartiallyConstructed(this, allowMultipleContexts)
val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
private[spark] val stopped: AtomicBoolean = new AtomicBoolean(false)
private def assertNotStopped(): Unit = {
if (stopped.get()) {
val activeContext = SparkContext.activeContext.get()
val activeCreationSite =
if (activeContext == null) {
"(No active SparkContext.)"
} else {
activeContext.creationSite.longForm
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
s"""Cannot call methods on a stopped SparkContext.
|This stopped SparkContext was created at:
|
|${creationSite.longForm}
|
|The currently active SparkContext was created at:
|
|$activeCreationSite
""".stripMargin)
}
}
/*
* 使用@deprecated:注解,不希望被使用的
* 重载构造器调用主构造器,添加新字段preferredNodeLocationData,类型为Map
* this(config)调用SparkContext默认的主构造器
*/
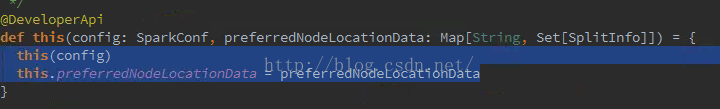
@deprecated("Passing in preferred locations has no effect at all, see SPARK-8949", "1.5.0")
@DeveloperApi
def this(config: SparkConf, preferredNodeLocationData: Map[String, Set[SplitInfo]]) = {
this(config)
logWarning("Passing in preferred locations has no effect at all, see SPARK-8949")
}
/*
* 使用@deprecated:注解,不希望被使用的
* 重载构造器调用主构造器,添加新字段master, appName, sparkHome, jars, environment
* this(...)调用SparkContext默认的主构造器
* 使用new SparkConf创建对象,非object是因为,SparkConf是被框架构造的,且只能构造一次
*/
@deprecated("Passing in preferred locations has no effect at all, see SPARK-10921", "1.6.0")
def this(
master: String,
appName: String,
sparkHome: String = null,
jars: Seq[String] = Nil,
environment: Map[String, String] = Map(),
preferredNodeLocationData: Map[String, Set[SplitInfo]] = Map()) =
{
this(SparkContext.updatedConf(new SparkConf(), master, appName, sparkHome, jars, environment))
if (preferredNodeLocationData.nonEmpty) {
logWarning("Passing in preferred locations has no effect at all, see SPARK-8949")
}
}
/*
* 对私有变量的定义
* 该变量会在执行主构造器时候被执行,生成private的getter和setter方法,不能被外部所调用
*/
private var _conf: SparkConf = _
private var _eventLogDir: Option[URI] = None
private var _eventLogCodec: Option[String] = None
private var _env: SparkEnv = _
private var _metadataCleaner: MetadataClea
/*
* 定义字段protected localProperties,只在spark包下被访问
* 使用override关键字覆写父类的方法,带一个参数parent
* 通过类的伴生对象的apply方法创建对象
*/
// Thread Local variable that can be used by users to pass information down the stack
protected[spark] val localProperties = new InheritableThreadLocal[Properties] {
override protected def childValue(parent: Properties): Properties = {
// Note: make a clone such that changes in the parent properties aren't reflected in
// the those of the children threads, which has confusing semantics (SPARK-10563).
SerializationUtils.clone(parent).asInstanceOf[Properties]
}
override protected def initialValue(): Properties = new Properties()
}
/*
* 对私有的成员变量_conf调用方法
* 对_jars、_files进行赋值,使用了map、filter操作
* 通过类的伴生对象的apply方法创建对象
*/
// Set Spark driver host and port system properties
_conf.setIfMissing("spark.driver.host", Utils.localHostName())
_conf.setIfMissing("spark.driver.port", "0")
_conf.set("spark.executor.id", SparkContext.DRIVER_IDENTIFIER)
_jars = _conf.getOption("spark.jars").map(_.split(",")).map(_.filter(_.size != 0)).toSeq.flatten
_files = _conf.getOption("spark.files").map(_.split(",")).map(_.filter(_.size != 0))
.toSeq.flatten
/*
* 创建SparkContext的伴生对象
* 伴生对象中创建的private的成员可以被伴生类SparkContext通过import的方式调用
* 伴生对象SparkContext中定义的protected无法被访问
*/
object SparkContext extends Logging {
/**
* Lock that guards access to global variables that track SparkContext construction.
*/
private val SPARK_CONTEXT_CONSTRUCTOR_LOCK = new Object()
/**
* The active, fully-constructed SparkContext. If no SparkContext is active, then this is `null`.
*
* Access to this field is guarded by SPARK_CONTEXT_CONSTRUCTOR_LOCK.
*/
private val activeContext: AtomicReference[SparkContext] =
new AtomicReference[SparkContext](null)
/*
* 定义单例对象DoubleAccumulatorParam
* 单例对象继承自AccumulatorParam
* 单例对象不能带参数,每个单例对象会被实现为虚构类的实例
* 在第一次被访问的时候实例化
*/
object DoubleAccumulatorParam extends AccumulatorParam[Double] {
def addInPlace(t1: Double, t2: Double): Double = t1 + t2
def zero(initialValue: Double): Double = 0.0
}
@deprecated("Replaced by implicit objects in AccumulatorParam. This is kept here only for " +
"backward compatibility.", "1.3.0")
object IntAccumulatorParam extends AccumulatorParam[Int] {
def addInPlace(t1: Int, t2: Int): Int = t1 + t2
def zero(initialValue: Int): Int = 0
}
/*
* 使用泛型
* implicit隐式转化
* 类型的上界约束
*/
def newAPIHadoopFile[K, V, F <: NewInputFormat[K, V]]
(path: String)
(implicit km: ClassTag[K], vm: ClassTag[V], fm: ClassTag[F]): RDD[(K, V)] = withScope {
newAPIHadoopFile(
path,
fm.runtimeClass.asInstanceOf[Class[F]],
km.runtimeClass.asInstanceOf[Class[K]],
vm.runtimeClass.asInstanceOf[Class[V]])
} 





















 5429
5429

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








