1. css的介绍
1.1 W3C的介绍
其实就是
World Wide Web Consortium
的缩写,中文是
W3C
组织或者万维网联盟,
W3C
这个组织
是做什么的呢?简单的说,就是出网页标准的。那么又
W3C
组织推出的标准就被称为
W3C
标准或
web标准
大家所看到的
W3C
的文档,其实就是万维网联盟提出的标准
W3C
标准或者叫
web
标准
web
标准是一系列的标准
结构层
:
HTML
用于描述网页的
展示结构
表现层
:
CSS
用于修饰装饰网页的
美观度
行为层
: JavaScript
用于完成页面的
组件
(按钮,动画 事件 或者窗口等一些
动态效果
)
1.2 什么是CSS
CSS
是
Cascading Style Sheets
(
层叠样式
表单)的简称。
CSS
是一种用来表现
HTML
或
XML等文件样式的计算机语言。
CSS不仅可以
静态地
修饰网页,还可以配合各种脚本语言
动态地
对网页各元素进行格式化。
2. css层叠样式表
2.1 css引入方式
四种
行内样式
内嵌样式
外链样式
导入样式
2.1.1行内样式
行内样式又叫做
标签样式
,它是在标签里面加上
style属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>css样式</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2 style="color:red;text-align:center">这是一个标题</h2>
</body>
</html>2.1.2 内嵌样式
样式写在style标签里面(style标签在head标签内)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>css样式</title>
<style type="text/css"> h2{
color: blue;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>这是一个标题</h2>
</body>
</html>2.1.3 外链样式
第一步:新建一个
.css
的文件,专门写
css
样式
第二步:
head
标签内写入
link
标签
(link
标签可以存在在
body
标签内,但是
不推荐使用
)
第三步:
link
里
href
属性 将
css
文件引入 (路径(绝对路径和相对路径))
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>css样式</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="1.css">
</head>
<body>
<h2>这是一个标题</h2>
</body>
</html>2.1.4 导入样式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>css样式</title>
<style type="text/css"> @import url("1.css");
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>这是一个标题</h2>
</body>
</html>
注意:就近原则,修饰的样式距离标签越近优先级越高
3. 选择器
3.1基本选择器
1
、标签选择器
2
、
ID
选择器
3
、类选择器
4
、通用选择器(通配符选择器)
注意:id > 类 > 标签 > 通配符
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
/*注释 标签选择器*/
h2{
color: red;
}
/*id选择器*/
#one{
color: blue;
}
/*类选择器*/
.two{
color: green;
}
/*通配符选择器*/
*{
color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>这是一个标题</h2>
<p id="one">这是一段话</p>
<div class="two">这是一个div</div>
<div>这是第二个div</div>
<p>这是第二个段落</p>
</body>
</html>3.2 包含选择器
1
、子代选择器
------
获取的某个标签的
第一级子标签
2
、后代选择器
-----
获取某个标签内的
所有子标签
3
、分组选择器(也叫做
逗号选择器
,可以给多个标签加上样式,通过,隔开)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>选择器优先级</title>
<style type="text/css">
/* 子代选择器 */
/* .list>ul{
color: green;
}*/
/* 后代选择器 */
/* .list li{
color: red;
}*/
/* 分组选择器 */
h2,.list,#list{
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>这是一个标签</h2>
<p id="list">这是一个段落</p>
<div class="list">
<ul>
<li>这是列表1</li>
<li>这是列表2</li>
<li>这是列表3</li>
<li>这是列表4</li>
<li>这是列表5</li>
</ul>
<li>这是列表6</li>
<li>这是列表7</li>
<li>这是列表8</li>
<li>这是列表9</li>
</div>
</body>
</html>3.3 属性选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>属性选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
/* 选中某个标签的某个属性 */
div[title]{
color: red;
}
/* 确切的等于 */
input[type="text"]
{
background: pink;
}
/* 某个属性含有某个值 */
input[type*="e"]
{
background: red;
}
/* 某个属性以什么开始 */
input[type^="e"]{
background: green;
}
/* 某个属性以什么结束 */
input[type$="rl"]{
background: blue;
}
/* 表示下一个标签 */
.msg + {
color: red;
}
/* 属性名称等于某个值 */
[title="这是一个标题"]{
color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div title="one">这是一个div</div>
<p class="two">这是一个段落</p>
<input type="text" id="" class="" value="张三">
<input type="url" id="" class="" value="李四">
<input type="email" id="" class="" value="王五">
<div class="msg">这是第二个div</div>
<div title="这是一个标题">这是第三个div</div>
<p id="msg1">这是第二个段落</p>
</body>
</html>3.4 伪类选择器
同一个标签,根据不同的状态,有不同的样式,这就叫做伪类,使用的是
冒号表示
的。
:link --------
超链接
点击之前
的样式
:visited --------
链接被
访问之后
:hover ------
悬停,
鼠标放到
标签上的样式
:active --------
被激活的时候,
鼠标点击
的时候,
但是不松手
的时候
:focus --------
某个标签
获得焦点
的时候
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伪类选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
/* 让超链接点击之前是红色 */
a:link{
color: red;
}
/* 让超链接点击之后是绿色 */
a:visited{
color: green;
}
/* 让鼠标悬停的时,放到标签上变成粉色 */
a:hover{
color: pink;
}
/* 让鼠标点击链接不松手的时候橙色 */
a:active{
color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="https://www.baidu.com/">点击我</a>
</body>
</html>注意:顺序是一定的,不可以改变,他们的顺序 :link :visited :hover :active
3.5 伪元素选择器
:after ------- CSS2
提供的
:before
::after ----- CSS3
提供
::before
注意:如果要使用before和after,一定要加上content(内容)属性
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伪元素选择器</title>
<style type="text/css">
p::before{
content: "zhangsan";
color: red;
}
p::after{
content: "lisi";
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>这是一个段落</p>
</body>
</html>
4. CSS常见样式
4.1 Css样式的基本语法
选择器
{
属性:属性值;
}
4.2 常见样式
4.2.1 控制字体
设置字号
------ font-size:12px
设置颜色
------ color:#rrggbb
设置字体
------- font-family:"
宋体
"
设置行高
------ line-height:150% 1.5em
设置字体的粗细
------- font-weight:normal(
正常,默认值
) blod(
粗体
)
<style type="text/css">
#one{
font-size: 12px;
color: #0000ff;
font-family: "宋体";
line-height: 300%;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>4.2.2 样式特点
1
、继承性
2
、层叠性
4.2.3 控制文本
设置文本的缩进
------text-indent
:
2em (
可以取负值
)
文本对齐方式
------ text-align : left center right
对象中的空白处理
-------white-space:normal pre nowrap
文本大小写的控制
-------text-transform:none (
按照原文本大小写显示
)capitalize(
每个单词首字母
大写
)uppercase(
将小写转换大写
)lowercase(
将大写转换为小写
)
vertical-align
导航栏案例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>导航栏</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin: 0; padding: 0;
}
a{
color: white;
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bolder;
text-decoration: none;
}
ul{
list-style: none;
}
.nav
{ width: 900px;
height: 65px;
/*border: 1px solid black;*/
background-image: url(bg.jpg);
background-repeat: repeat-x;
}
.nav ul{
width: 900px;
height: 65px;
text-align: center;
}
.nav>ul>li{
width: 100px; height: 65px; float: left; line-height: 64px;
}
.nav>ul>li:hover{
background-color: red; cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="nav">
<ul>
<li><a href="#">游戏1</a></li>
<li><a href="#">游戏2</a></li>
<li><a href="#">游戏3</a></li>
<li><a href="#">游戏4</a></li>
<li><a href="#">游戏5</a></li>
<li><a href="#">游戏6</a></li>
<li><a href="#">游戏7</a></li>
<li><a href="#">游戏8</a></li>
<li><a href="#">游戏9</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
商品展示页面:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>商品展示</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
a{
color: #999999;
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bolder;
text-decoration: none;
}
.goods{
width: 250px;
height: 400px;
float: left;
margin: 10px;
border: 1px solid white;
}
.goods:hover{
border: 1px solid red;
}
.goods>img{
width: 250px;
height: 251px;
}
.goods>.prices{
width: 250px;
height: 30px;
/* border: 1px solid black;
*/ line-height: 30px;
}
.goods>.prices>.price
{
color: red;
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
font-family: "仿宋";
}
.goods>p{
margin: 5px;
}
.goods>p>a{
font-size: 12px;
}
.goods>p>a:hover{
text-decoration: underline;
color: red;
}
.counts{
font-size: 14px;
float: right;
color: #666;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.shop_name{
font-size: 14px;
color: #999999;
float: left;
}
.container{
width: 1200px;
height: 2000px;
/* border: 1px solid black; */ m
argin:0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="goods">
<img src="哆啦A梦.jpg">
<div class="prices">
<span class="price">¥78</span>
<span class="counts">2000人付款</span>
</div>
<p><a href="#">哆啦A梦玩偶 重庆直邮</a></p>
<div class="prices"> <a class="shop_name">XXX玩偶旗舰店</a>
<span class="counts">重庆 永川</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="goods">
<img src="哆啦A梦.jpg">
<div class="prices">
<span class="price">¥78</span>
<span class="counts">2000人付款</span>
</div>
<p>
<a href="#">哆啦A梦玩偶 重庆直邮</a>
</p>
<div class="prices">
<a class="shop_name">XXX玩偶旗舰店</a>
<span class="counts">重庆 永川</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="goods">
<img src="哆啦A梦.jpg">
<div class="prices">
<span class="price">¥78</span>
<span class="counts">2000人付款</span>
</div>
<p><a href="#">哆啦A梦玩偶 重庆直邮</a></p>
<div class="prices">
<a class="shop_name">XXX玩偶旗舰店</a>
<span class="counts">重庆 永川</span> </div> </div> <div class="goods"> <img src="哆啦A梦.jpg">
<div class="prices">
<span class="price">¥78</span>
<span class="counts">2000人付款</span>
</div> <p><a href="#">哆啦A梦玩偶 重庆直邮</a>
</p>
<div class="prices">
<a class="shop_name">XXX玩偶旗舰店</a>
<span class="counts">重庆 永川</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="goods"> <img src="哆啦A梦.jpg">
<div class="prices"> <span class="price">¥78</span>
<span class="counts">2000人付款</span>
</div>
<p><a href="#">哆啦A梦玩偶 重庆直邮</a>
</p>
<div class="prices">
<a class="shop_name">XXX玩偶旗舰店</a>
<span class="counts">重庆 永川</span>
</div> </div> <div class="goods">
<img src="哆啦A梦.jpg"> <div class="prices">
<span class="price">¥78</span>
<span class="counts">2000人付款</span>
</div> <p><a href="#">哆啦A梦玩偶 重庆直邮</a></p>
<div class="prices"> <a class="shop_name">XXX玩偶旗舰店</a>
<span class="counts">重庆 永川</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="goods">
<img src="哆啦A梦.jpg"> <div class="prices">
<span class="price">¥78</span> <span class="counts">2000人付款</span>
</div>
<p><a href="#">哆啦A梦玩偶 重庆直邮</a></p>
<div class="prices"> <a class="shop_name">XXX玩偶旗舰店</a>
<span class="counts">重庆 永川</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="goods"> <img src="哆啦A梦.jpg">
<div class="prices">
<span class="price">¥78</span>
<span class="counts">2000人付款</span>
</div>
<p><a href="#">哆啦A梦玩偶 重庆直邮</a>
</p>
<div class="prices"> <a class="shop_name">XXX玩偶旗舰店</a>
<span class="counts">重庆 永川</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>5. 布局
5.1 盒子布局

border:

padding
margin
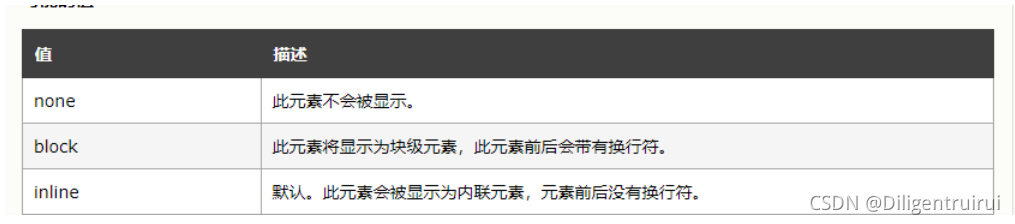
5.2 元素分类
块级元素
独占一行,可以设置宽和高
div p hn
等
内联元素
不会自动换行,设置宽和高的时候是不起作用的
span a
等
块级元素和内联元素可以进行相互转换:
display
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>块级元素和内联元素</title>
<style type="text/css">
.box{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid black;
background-color: blue;
display: inline;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid black;
background-color: red;
}
.box2{width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid black;
background-color: yellow;
}
a{ width: 200px;
height: 200px;
display: block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">这是第一个div</div>
<div class="box1">这是第二个div</div>
<div class="box2">这是第三个div</div>
<a href="#">这是一个a标签
</a>
<a href="#">这是一个a标签</a>
<a href="#">这是一个a标签</a>
</body>
</html>
注意:
css
隐藏元素的方式:
display:none;
width:0 height:0
5.3 浮动布局
通过设置
float
属性进行布局
none -----
不浮动
left --------
对象向左浮动,而后面的内容会流向对象的右侧
right---------------
对象向右浮动,而后面的内容会流向对象的左侧
清除浮动:
clear

5.4 定位布局
属性
:position --------
定位方式
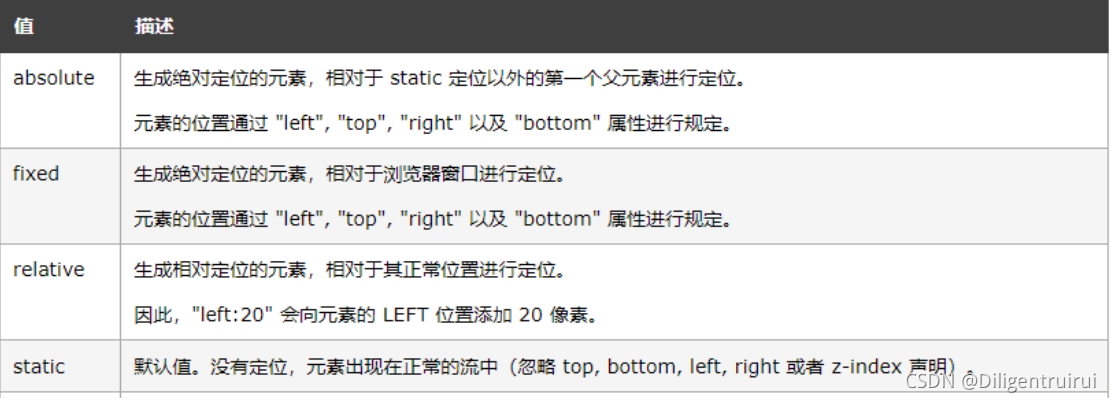
static :
默认值
absolute:
绝对定位,会将对象从文档流中分离出来,通过设置
Left right top bottom
四个方向上的
值相较于父级元素的绝对定位,如果不存在这样的父级元素,相较于
body
relative:
相对定位,不会将对象从文档流中分离出来,通过设置
Left right top bottom
四个方向上
的值进行相对定位
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>定位</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{ padding: 0; margin: 0; }
.main{width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border:1px solid black;
margin: 200px;
position: relative;
}
.one{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
left: 200px;
}
.two{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
}
.three{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="main">
<div class="one">这是第一个div</div>
<div class="two">这是第一个div</div>
<div class="three">这是第一个div</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>5.5 其他的属性
5.5.1 overflow

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>overflow</title>
<style type="text/css">
#main{
height: 400px;
width: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
overflow: scroll;
}
</style>
</head>
<body><div id="main">
<img src="哆啦A梦.jpg">
</div>
</body>
</html>
3
种隐藏元素的方式:
1
、
display:none
2
、
width:0 height:0
3
、
overflow:hidden
5.5.2 zoom
对图片进行放大和缩小的一个属性,一般取
1
或者
100%
的时候是按照原比例显示的
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>overflow</title>
<style type="text/css">
#main{
height: 1000px;
width: 1000px;
/*border: 1px solid black;
overflow: scroll;*/
}
img{
zoom:0.5;
}
</style>
</head>
<body><div id="main">
<img src="哆啦A梦.jpg">
</div>
</body>
</html>5.6 css3 弹性盒子
display:flex; ---------
弹性盒子
主要的属性:
flex-direction:
弹性盒子中子元素的排列方式
flex-wrap:
设置子元素超过父元素后是否自动换行
flex-flow:flex-direction
和
flex-wrap
的简写
align-items
:设置弹性盒子在侧轴(纵轴)上的对齐方式
align-content:
对
flex-wrap
的一个修改,和
align-items
相似,但不是设置对齐方式
justify-content:
设置弹性盒子在横轴(主轴)上的对齐方式
5.6.1 flex-direction

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>弹性盒子</title>
<style type="text/css">
.flex-container{
width: 400px;
height: 250px;
background-color: lightgrey;
display: flex;
flex-direction:column-reverse;
}
.flex-item{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin: 10px;
} </style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子1</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子2</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>5.6.2 flex-wrap

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>弹性盒子</title>
<style type="text/css">
.flex-container{
width: 400px;
height: 250px;
background-color: lightgrey;
display: flex; flex-wrap:wrap-reverse;
/* margin-top: 400px;*/
}
.flex-item{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子1</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子2</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子3</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子4</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子5</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子6</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子7</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子8</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子9</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>5.6.3 flex-flow
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>弹性盒子</title>
<style type="text/css">
.flex-container{
width: 400px;
height: 250px;
background-color: lightgrey;
display: flex;
/* flex-direction:row-reverse;
flex-wrap:wrap; */
flex-flow:row-reverse wrap;
/* margin-top: 400px;*/
}
.flex-item{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="flex-container">
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子1</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子2</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子3</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子4</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子5</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子6</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子7</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子8</div>
<div class="flex-item">弹性盒子9</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>5.6.4 align-items

5.6.5 align-content

5.6.6 justify-content

扩展:
order------
可以改变子元素的顺序
flex - grow :
规定在相同的容器中,项目相对于其余弹性项目的增长量
flex-shrink :
固定在相同的容器中,项目相对于其余弹性项目的收缩量
flex-basis :
规定弹性项目的初始长度
flex:flex - grow
、
flex-shrink
、
flex-basis
align-self
:指定弹性容器内所选项目的对齐方式





















 96
96

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








