双向绑定原理低配版

什么是数据模型和视图之间的双向绑定
当数据发生变化的时候,视图也就发生变化,当视图发生变化的时候,数据也会跟着同步变化;
Vue 2.0 双向数据绑定的核心其实是通过Object.defineProperty来实现数据劫持和监听。在 Vue 3.0 中则通过 Proxy来实现对整体对象的监听,对 Vue2.0 的优化
模拟双向绑定
1.编译解析
创建文件 index.html 和 vue.js

console.log(options.el) 就是 #app
获取这个dom 节点那么就是
this.$el =document.querySelector(options.el)
console.log(this.$el)![]()
向index.html 中id= "app"创建一个节点并添加data
<body>
<div id="app">
{{name}}
<h1>{{name}}</h1>
</div>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
name:'猴子'
}
})
</script>
</body>接下来开始编译解析
vue.js 中
获取index.html中的data和节点
constructor(options){
this.$el =document.querySelector(options.el)
this.$data = options.data;
console.log(options)
console.log(this.$el)
this.compile(this.$el)
}
解析
compile(node){
console.log(node,node.childNodes)
node.childNodes.forEach(item => {
console.log(item,item.nodeType)
// 元素节点
if (item.nodeType == 1){
this.compile(item)
}
// 判断文本节点
if(item.nodeType == 3){
// 正则匹配 {{}}
let reg = /\{\{(.*?)\}\}/g;
let text = item.textContent;
item.textContent = text.replace(reg,(match,vmKey)=>{
console.log(match,vmKey)
// 去掉空格
vmKey = vmKey.trim()
return this.$data[vmKey]
})
}
});
}结果

获取事件
全部代码
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{name}}
<h1>{{name}}</h1>
<button @click="handleClick">click</button>
<button @change = "handleChange">change</button>
</div>
<script src="vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
name:'猴子'
},
methods:{
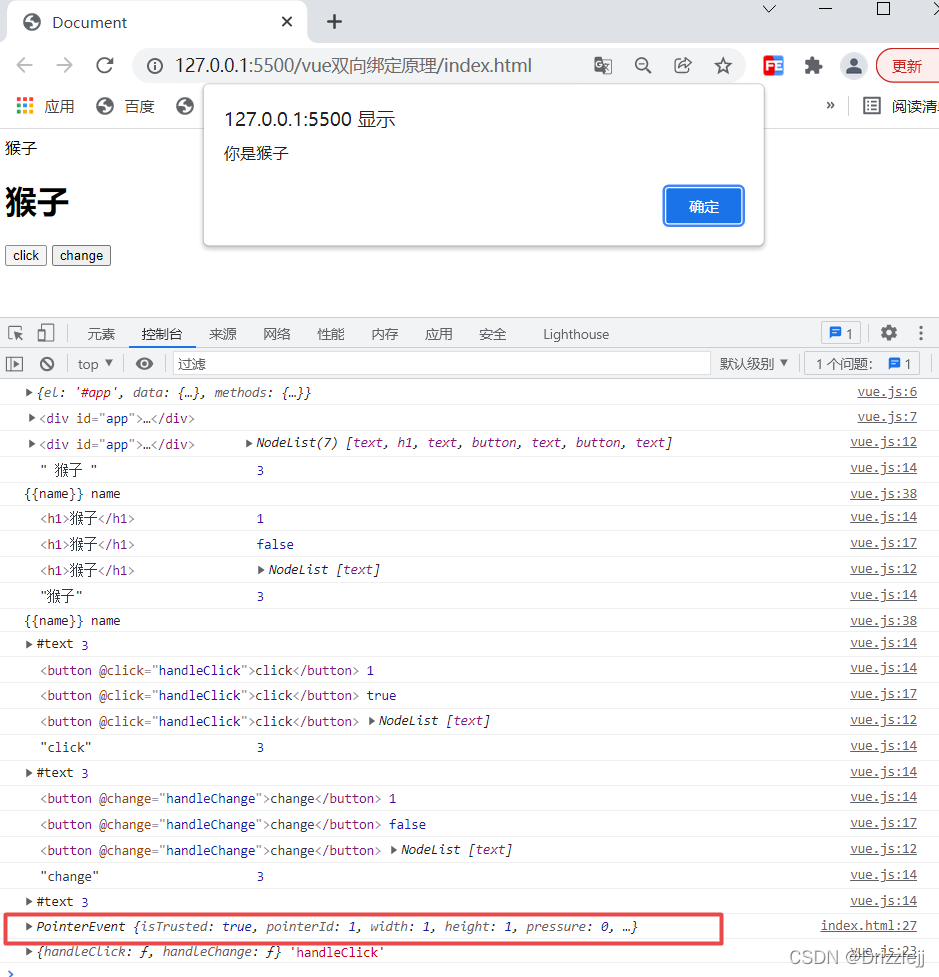
handleClick(e){
alert('你是猴子')
console.log(e)
},
handleChange(){
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>vue.js
class Vue{
constructor(options){
this.$el =document.querySelector(options.el)
this.$data = options.data;
this.$method = options.methods
console.log(options)
console.log(this.$el)
this.compile(this.$el)
}
// 编译解析
compile(node){
console.log(node,node.childNodes)
node.childNodes.forEach(item => {
console.log(item,item.nodeType)
// 元素节点
if (item.nodeType == 1){
console.log(item,item.hasAttribute("@click"))
if(item.hasAttribute("@click")){
let vmKey = item.getAttribute("@click").trim()
item.addEventListener('click',(event)=>{
this.eventFn = this.$method[vmKey].bind(this)
this.eventFn(event)
console.log(this.$method,vmKey)
this.$method[vmKey]()
})
}
if(item.childNodes.length > 0){
this.compile(item)
}
}
// 判断文本节点
if(item.nodeType == 3){
// 正则匹配 {{}}
let reg = /\{\{(.*?)\}\}/g;
let text = item.textContent;
item.textContent = text.replace(reg,(match,vmKey)=>{
console.log(match,vmKey)
// 去掉空格
vmKey = vmKey.trim()
return this.$data[vmKey]
})
}
});
}
} 
劫持
在handleclick 方法中 尝试直接访问 data 中的name
console.log(this.name,this)

可以看到是不能直接访问到 name的,name 位于 $data中,如果想要通过 this.name 直接访问
那么需要把 $data 中的内容劫持到 this 这个大对象中。在vue.js ,constructor 中创建一个 proxyDate 方法
然后利用 Object.defineProperty(属性对象,属性名称,描述)
// 劫持data 中的属性,并且给大对象赋值
proxyData(){
for (let key in this.$data){
console.log(key)
Object.defineProperty(this,key,{
get(){
return this.$data[key]
},
set(val){
this.$data[key] = val
}
})
}
}再次点击click 方法

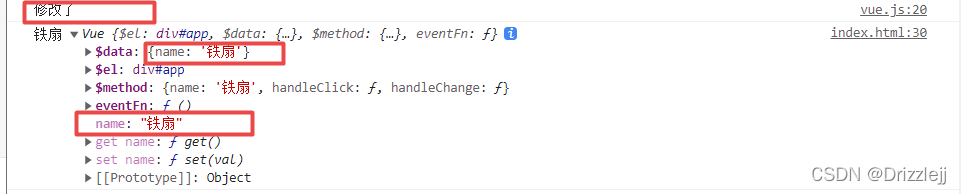
现在我们通过点击更改 data 中的 name,在index.html handleClick 方法中
this.name = '铁扇'为了更好的观察,我们在vue.js 中 proxyData()----- set(val) 打印一句话

我们可以看到,$data 中的name 随着大对象 this 中的name 一起被修改了,这是因为我们劫持了。
但是在DOM中却没有发生变化

通知DOM 更新
1.创建一个v-model
html 中
<input type="text" v-model="name">在vue.js 中判断 是否有属性 v-model,这里与判断点击事件 @click 相同
// 判断 v-model
if(item.hasAttribute("v-model")){
let vmKey = item.getAttribute("v-model").trim()
item.addEventListener('input',(event)=>{
console.log(item.value)
})
}现在我们在输入框输入就能够在控制台打印我们输入的内容。但是Dom 仍然没有发生变化

我们给输入框加入一个初始值

现在可以看到输入框有一个初始值了,我们在输入框输入并打印 this 这个大对象,发现输入框中的值改变了,但是 this 这个大对象中的 数据却没有发生变化。

2.修改对象中的数据
于是我们把输入的值赋值给这个大对象


3.如果数据发生更改了,通知DOM 触发更新
3.1 在 constructor 中 创建一个空对象,用来保存 data 中的数据
this.$WatchEvent = {}3.2定义一个类
class Watch{
constructor(vm,key,node,attr){
// Vue 对象
this.vm = vm
// 就是 data 的数据
this.key = key
// 节点
this.node = node
// textContent
this.attr = attr
}
// 数据发生改变,来更新dom
updata(){
// this.node (文本节点)
// this.attr (相当于 textContent)
// this.vm (就相当于上面的 name)
this.node[this.attr] = this.vm[this.key]
}
}3.3 如果为文本节点,把修改了哪些内容的数据放到 $WatchEvent 中
if(item.nodeType == 3){
// 正则匹配 {{}}
let reg = /\{\{(.*?)\}\}/g;
let text = item.textContent;
item.textContent = text.replace(reg,(match,vmKey)=>{
console.log(match,vmKey)
// 去掉空格
vmKey = vmKey.trim()
console.log(this.$WatchEvent)
if(this.hasOwnProperty(vmKey)){
let watcher = new Watch(this,vmKey,item,'textContent')
if (this.$WatchEvent[vmKey]){
this.$WatchEvent[vmKey].push(watcher)
}else{
this.$WatchEvent[vmKey] = []
this.$WatchEvent[vmKey].push(watcher)
}
}
return this.$data[vmKey]
})
}3.4
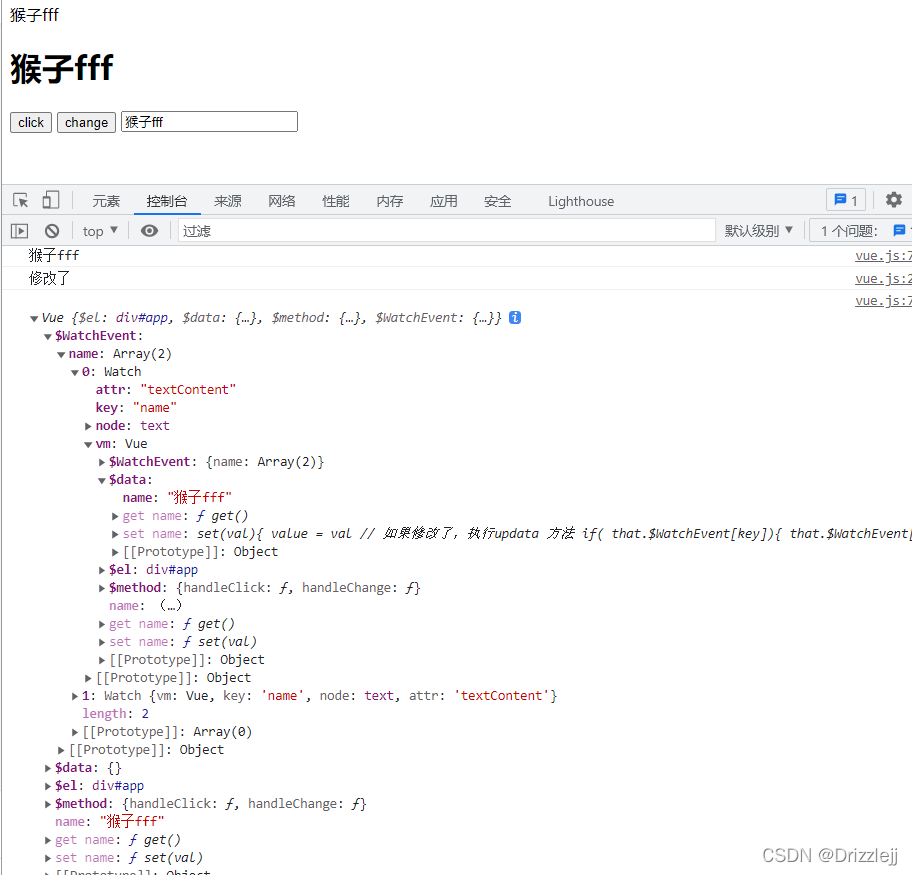
全部 vue.js
class Vue{
constructor(options){
this.$el =document.querySelector(options.el)
this.$data = options.data;
this.$method = options.methods
this.$WatchEvent = {}
console.log(options)
console.log(this.$el)
this.proxyData();
this.observe()
this.compile(this.$el)
}
// 劫持data 中的属性,并且给大对象赋值
proxyData(){
for (let key in this.$data){
console.log(key)
Object.defineProperty(this,key,{
get(){
return this.$data[key]
},
set(val){
console.log('修改了')
this.$data[key] = val
}
})
}
}
// 劫持数据变化,进行更新DOM
observe(){
for(let key in this.$data){
let value = this.$data[key]
let that = this
Object.defineProperty(this.$data,key,{
get(){
return value
},
set(val){
value = val
// 如果修改了,执行updata 方法
if( that.$WatchEvent[key]){
that.$WatchEvent[key].forEach((item,index)=>{
item.updata()
})
}
}
})
}
}
// 编译解析
compile(node){
console.log(node,node.childNodes)
node.childNodes.forEach(item => {
console.log(item,item.nodeType)
// 元素节点
if (item.nodeType == 1){
console.log(item,item.hasAttribute("@click"))
// 判断点击事件
if(item.hasAttribute("@click")){
let vmKey = item.getAttribute("@click").trim()
item.addEventListener('click',(event)=>{
this.eventFn = this.$method[vmKey].bind(this)
this.eventFn(event)
console.log(this.$method,vmKey)
this.$method[vmKey]()
})
}
// 判断 v-model
if(item.hasAttribute("v-model")){
let vmKey = item.getAttribute("v-model").trim()
// 给input 增加一个初始值
item.value = this[vmKey]
item.addEventListener('input',(event)=>{
console.log(item.value)
this[vmKey] = item.value
console.log(this)
})
}
if(item.childNodes.length > 0){
this.compile(item)
}
}
// 判断文本节点
if(item.nodeType == 3){
// 正则匹配 {{}}
let reg = /\{\{(.*?)\}\}/g;
let text = item.textContent;
item.textContent = text.replace(reg,(match,vmKey)=>{
console.log(match,vmKey)
// 去掉空格
vmKey = vmKey.trim()
console.log(this.$WatchEvent)
if(this.hasOwnProperty(vmKey)){
let watcher = new Watch(this,vmKey,item,'textContent')
if (this.$WatchEvent[vmKey]){
this.$WatchEvent[vmKey].push(watcher)
}else{
this.$WatchEvent[vmKey] = []
this.$WatchEvent[vmKey].push(watcher)
}
}
return this.$data[vmKey]
})
}
});
}
}
// 更新dom
class Watch{
constructor(vm,key,node,attr){
// Vue 对象
this.vm = vm
// 就是 data 的数据
this.key = key
// 节点
this.node = node
// textContent
this.attr = attr
}
// 数据发生改变,来更新dom
updata(){
// this.node (文本节点)
// this.attr (相当于 textContent)
// this.vm (就相当于上面的 name)
this.node[this.attr] = this.vm[this.key]
}
}扩展:react 中的双向绑定
和vue 相比 react 并没有提供向 v-model 这样的指令来实现文本框的数据流双向绑定,因为react的设计思路就是单向数据流,所以我们需要借助 onChange 和 setState 来实现一个双向的数据流。
数据影响视图
使用 setState({ }) 方法修改数据。
(React内部提供的修改方法),不允许通过this.state.属性名 = 数据 的方法进行数据修改。
视图影响数据
通过 React 提供的 onChage 监听事件 实现数据的动态录入同时,使用 value 或者 defaultValue 在 input 框中呈现内容。
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








