上一篇文章当中已经推导出了整个频域上的表达式,这个表达式叫做蝶形运算,下面就借由蝶形运算实现FFT算法。
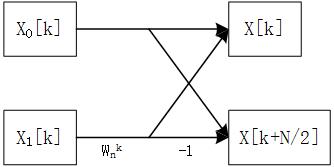
那么首先就要先说说蝶形运算。蝶形运算听着挺高大上的,但可以有一种简单方便的图形表示方法,为方便起见我这里再贴一次公式:
X
[
k
]
=
X
0
[
k
]
+
W
N
k
X
1
[
k
]
X[k]=X_0[k]+W_N^{k}X_1[k]
X[k]=X0[k]+WNkX1[k]
X
[
k
+
N
2
]
=
X
0
[
k
]
−
W
N
k
X
1
[
k
]
X[k+\frac N2]=X_0[k]-W_N^{k}X_1[k]
X[k+2N]=X0[k]−WNkX1[k]
那么这个蝶形运算可以用图形表示为
当然,可以看出一次蝶形运算虽然简化了运算,但仍然需要知道 X 0 [ k ] X_0[k] X0[k] 和 X 1 [ k ] X_1[k] X1[k] ,就是说在进行蝶形运算之前我们仍需对 x 0 [ n ] x_0[n] x0[n] 和 x 1 [ n ] x_1[n] x1[n] 进行DFT得到 X 0 [ k ] X_0[k] X0[k] 和 X 1 [ k ] X_1[k] X1[k] 然后才能得到完整的 X [ k ] X[k] X[k] ,我们知道DFT运算起来是很麻烦的,但是注意到,这里DFT的运算量已经减少了一半,也就是每次只对 N 2 \large \frac N2 2N个点进行DFT,那么可以由此得到启示,能不能像得到 X [ k ] X[k] X[k] 一样通过蝶形运算来得到 X 0 [ k ] X_0[k] X0[k] 和 X 1 [ k ] X_1[k] X1[k] 呢?这是可以的,对于 X 0 [ k ] X_0[k] X0[k] 只需将其分为奇偶两组,然后再通过一次蝶形运算即可得到 X 0 [ k ] X_0[k] X0[k] ,这时单次DFT的运算量为 N 4 \large \frac N4 4N,重复以上过程,直到DFT的运算量为1,此时就会出现一个有趣的事情:
X [ 0 ] = ∑ n = 0 0 x [ n ] e − i 2 π ∗ 0 N n = x [ 0 ] X[0]=\sum\limits_{n=0}^{0} x[n]e^{-i\frac{2\pi *0}{N}n}=x[0] X[0]=n=0∑0x[n]e−iN2π∗0n=x[0]
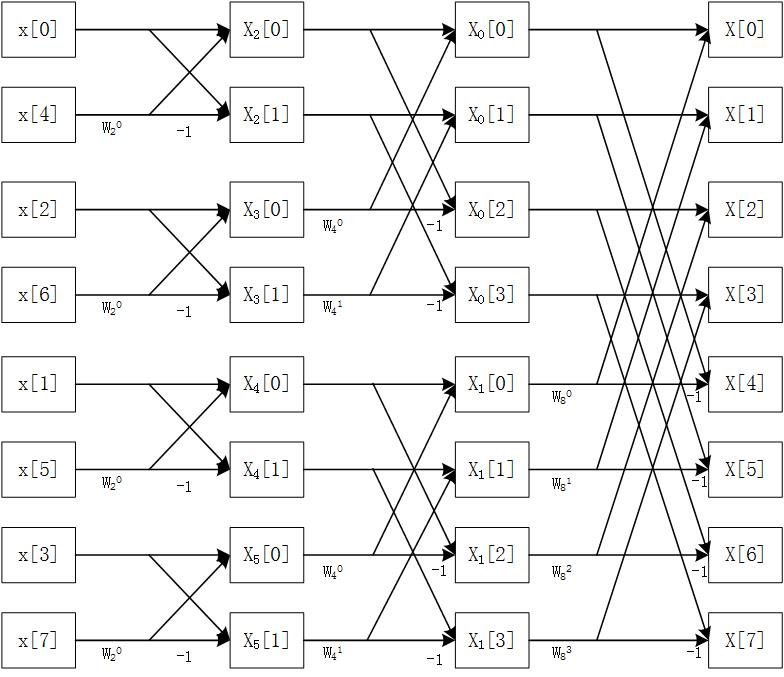
此时就不需进行DFT了,直接进行蝶形运算就可以了,这就是FFT算法。以上的说明可能比较抽象,下面举一个8点FFT的例子,假设使用 x [ 0 ] x[0] x[0]$x[7]$表示要进行FFT的8个点,用$X[0]$ X [ 7 ] X[7] X[7]表示对应频域上的点,那么根据以上思路,需先将0~7分为奇偶两组,即:{0,2,4,6}和{1,3,5,7},然后继续分组:{0,4}和{2,6}、{1,5}和{3,7},最后一次分组:{0}和{4}、{2}和{6}、{1}和{5}、{3}和{7}。经过三次分组后发现DFT的运算量已经是1了,这时再进行蝶形运算,如下图:
按照这个图我们只需要用程序实现这个图,就可以得到FFT的结果。但是在此之前还有一件事,就是分组问题,可以看到我们首先需要将01234567的顺序换为04261537的顺序,这个顺序有什么规律呢?将其转换为二进制可以看到:000、100、010、110、001、101、011、111。其实就是逆向的二进制加法,最左边为最低位,最右边为最高位,从低位开始加1,然后向高位进位。
所以要完成一个FFT分两步,第一步先将拿到的数组进行逆序,第二步进行蝶形运算。第二步的是最复杂的,但总的可以将其看成两个for循环来实现,以上图为例,8点的FFT需要进行3次蝶形运算,每一次蝶形运算又分为几个单次的蝶形运算,如第1次蝶形运算就分为4个小的单次蝶形运算。
先给出C语言版本(话说啥时候用结构体重构一下。。。)
/* linux下gcc编译 */
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <time.h>
#define FFTN 32 //fft的点数
#define PWE 5 //2^PWE=NFFT
#define LEN FFTN*2
#define FRE 2000 //采样频率
#define RS 62.5 //分辨率=FRE/FFTN
//由于一个点是复数,因此用偶数脚标表示实部,奇数脚标表示虚部
float fft_input[LEN] = {0,0,1,0,2,0,3,0,4,0,5,0,6,0,7,0,
8,0,9,0,10,0,11,0,12,0,13,0,14,0,15,0,
16,0,17,0,18,0,19,0,20,0,21,0,22,0,23,0,
24,0,25,0,26,0,27,0,28,0,29,0,30,0,31,0};
/*
float fft_input[LEN] = {31,0,30,0,29,0,28,0,27,0,26,0,25,0,24,0,
23,0,22,0,21,0,20,0,19,0,18,0,17,0,16,0,
15,0,14,0,13,0,12,0,11,0,10,0,9,0,8,0,
7,0,6,0,5,0,4,0,3,0,2,0,1,0,0,0};
*/
float fft_output[LEN];
float MAX[2]; //保存最后得出的结果
int ReverseArrange(void);
int Redix2FFT(void);
void IntegrateData(void);
void main(void)
{
int i;
clock_t begin, end;
begin = clock();
ReverseArrange(); //倒序
Redix2FFT(); //FFT变换
end = clock();
printf("%lfs\n",(double)(end-begin)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}
/*倒序函数,将fft_input进行逆向排序
* 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
倒序前脚标: 0-1 2-3 4-5 6-7 8-9 10-11 12-13 14-15
0 4 2 6 1 5 3 7
倒序后脚标: 0-1 8-9 4-5 12-13 2-3 10-11 6-7 14-15
*/
//其中:2^PWE=NFFT,PWE表示次幂,即脚标由几位二进制组成
int ReverseArrange(void)
{
int8_t i,j;
int8_t tmp = 0x00; //用来表示脚标
//先给第一个复数赋值
fft_output[0] = fft_input[0];
fft_output[1] = fft_input[1];
//对剩下的数进行倒序
for(i=0;i<(FFTN-1)*2;i+=2){
j = PWE-1; //得出需要左移的位数
//逆向二进制加法
while((tmp & (1<<j)) != 0){
tmp &= ~(1<<j); //把第j位置零
j--;
}
tmp |= (1<<j); //这里最后得出的是:0 4 2 6 1 5 3 7
fft_output[i+2] = fft_input[tmp*2]; //按照新的顺序给输出赋值
fft_output[i+3] = fft_input[tmp*2+1];
}
return 1;
}
/*基2fft运算,需先将fft_input倒序输入到fft_out中*/
int Redix2FFT(void)
{
int8_t layer; //表示FFT的层数
int8_t pmul; //= 2^(PWE - layer),表示当前层中需要进行几次小FFT,FFTN/pmul表示当前小FFT的点数
int8_t i; //表示正在进行第几次小FFT
int8_t j; //= 2^(layer - 1),表示当前层小FFT中蝶形运算的次数
int8_t k; //每次小FFT中,正在进行第几次蝶形运算
int8_t currentBase; //表示当前层的小FFT中,第一个元素的脚标
int8_t current; //=currentBase + k,表示当前需要进行蝶形运算的元素的脚标
int8_t another; //=current + j,表示当前需要进行蝶形运算的元素的脚标
int8_t m;
float Re,Im; //实部、虚部的暂存区
float TPOA; //=2 * pi / FFTN,FFT旋转因子WNK的w值
float TPOATP;//=TPOA * pmul,表示小FFT中WNK的w值
float reFactor,imFactor; //=cos(TPOATP * k),=-sin(TPOATP * k),表示WNK的实部和虚部
//下面的注释假设FFTN=8
TPOA = 2 * M_PI / FFTN; //TPOA = PI/4
for(layer=1;layer<=PWE;layer++){ //layer = 1,2,3
j = 0x01<<(layer-1); //使用math中的pow()会出现bug,使用左移运算减轻计算量
pmul = 0x01<<(PWE - layer);
for(i=0;i<pmul;i++){ //pmul=4时,i = 0,1,2,3
currentBase = i * 4 *j; //j = 1时,currentBase = 0,4,8,12
TPOATP = TPOA * pmul; //pmul=4时,TPOATP = PI
for(k=0;k<j;k++){ //j=1时,k=0
current = currentBase + k*2; //current = 0,4,8,12;
another = current + j*2; //another = 2,6,10,14;
//准备WNK
reFactor = cos(TPOATP * k); //1
imFactor = -sin(TPOATP * k);//0
//乘上WNK
Re = fft_output[another]; //备份实部
fft_output[another] = fft_output[another] * reFactor
- fft_output[another+1] * imFactor; //fft_output[2] = 8
fft_output[another+1] = fft_output[another+1] * reFactor
+ Re * imFactor; //fft_output[3] = 0
//蝶形加法
Re = fft_output[current]; //Re=0
Im = fft_output[current+1]; //Im=0
fft_output[current] += fft_output[another]; //fft_output[0] = 8;
fft_output[current+1] += fft_output[another+1]; //fft_output[1] = 0
fft_output[another] = Re - fft_output[another]; //fft[2] = -8
fft_output[another+1] = Im - fft_output[another+1]; //fft[3] = 0
}
}
}
for(m = 0; m < LEN; m += 2) {
printf("[%d]: %f+%fi\n", m/2, fft_output[m], fft_output[m+1]);
}
}
/* 输出整合,计算出每个频率的幅值,取出幅值最大的点
*/
void IntegrateData(void)
{
//计算复数的模,注意,所有的模都存到偶数项中
//fft_output[0] = sqrt(fft_output[0]*fft_output[0]+fft_output[1]*fft_output[1])/FFTN;
fft_output[LEN-2] = sqrt(fft_output[LEN-2]*fft_output[LEN-2]+fft_output[LEN-1]*fft_output[LEN-1])/FFTN;
for(uint8_t i=2;i<(LEN-2);i+=2){ //最后一个点和第一个点已单独处理
fft_output[i] = 2*sqrt(fft_output[i]*fft_output[i]+fft_output[i+1]*fft_output[i+1])/FFTN;
}
//找出其中模长最大的值,记录脚标和模长
MAX[0] = 2; //脚标
MAX[1] = fft_output[2]; //模长
for(uint8_t i=4;i<LEN;i+=2){
if(MAX[1]<fft_output[i]){ //替换
MAX[0] = i;
MAX[1] = fft_output[i];
}
}
}
下面将这个算法在Arduino上实现,注释已经写得很完善了,这里就不多加说明。
/*从ADC读取数值后,使用FFT对波形进行分析,得出其中所含频率和对应幅度*/
/* FFTN fft时间(ms) 求最值时间(ms)
* 8 4
* 16 10
* 32 25 2
*/
#include <math.h>
#define FFTN 32 //fft的点数
#define PWE 5 //2^PWE=NFFT
#define LEN FFTN*2
#define FRE 2000 //采样频率
#define RS 62.5 //分辨率=FRE/FFTN
//由于一个点是复数,因此用偶数脚标表示实部,奇数脚标表示虚部
float fft_input[LEN] = {0,0,1,0,2,0,3,0,4,0,5,0,6,0,7,0,
8,0,9,0,10,0,11,0,12,0,13,0,14,0,15,0,
16,0,17,0,18,0,19,0,20,0,21,0,22,0,23,0,
24,0,25,0,26,0,27,0,28,0,29,0,30,0,31,0};
float fft_output[LEN];
float MAX[2]; //保存最后得出的结果
unsigned long curTime,lastTime;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
ReverseArrange(); //倒序
lastTime = millis();
Redix2FFT(); //FFT变换
curTime = millis();
Serial.print("fft=");
Serial.println(curTime-lastTime);
/* 以上是fft */
//lastTime = millis();
//IntegrateData();
//curTime = millis();
//Serial.print("int=");
//Serial.println(curTime-lastTime);
}
/*倒序函数,将fft_input进行逆向排序
* 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
倒序前脚标: 0-1 2-3 4-5 6-7 8-9 10-11 12-13 14-15
0 4 2 6 1 5 3 7
倒序后脚标: 0-1 8-9 4-5 12-13 2-3 10-11 6-7 14-15
*/
//其中:2^PWE=NFFT,PWE表示次幂,即脚标由几位二进制组成
int ReverseArrange(){
int8_t i,j;
int8_t tmp = 0x00; //用来表示脚标
//先给第一个复数赋值
fft_output[0] = fft_input[0];
fft_output[1] = fft_input[1];
//对剩下的数进行倒序
for(i=0;i<(FFTN-1)*2;i+=2){
j = PWE-1; //得出需要左移的位数
//逆向二进制加法
while((tmp & (1<<j)) != 0){
tmp &= ~(1<<j); //把第j位置零
j--;
}
tmp |= (1<<j); //这里最后得出的是:0 4 2 6 1 5 3 7
fft_output[i+2] = fft_input[tmp*2]; //按照新的顺序给输出赋值
fft_output[i+3] = fft_input[tmp*2+1];
}
return 1;
}
/*基2fft运算,需先将fft_input倒序输入到fft_out中*/
int Redix2FFT(){
int8_t layer; //表示FFT的层数
int8_t pmul; //= 2^(PWE - layer),表示当前层中需要进行几次小FFT,FFTN/pmul表示当前小FFT的点数
int8_t i; //表示正在进行第几次小FFT
int8_t j; //= 2^(layer - 1),表示当前层小FFT中蝶形运算的次数
int8_t k; //每次小FFT中,正在进行第几次蝶形运算
int8_t currentBase; //表示当前层的小FFT中,第一个元素的脚标
int8_t current; //=currentBase + k,表示当前需要进行蝶形运算的元素的脚标
int8_t another; //=current + j,表示当前需要进行蝶形运算的元素的脚标
float Re,Im; //实部、虚部的暂存区
float TPOA; //=2 * pi / FFTN,FFT旋转因子WNK的w值
float TPOATP;//=TPOA * pmul,表示小FFT中WNK的w值
float reFactor,imFactor; //=cos(TPOATP * k),=-sin(TPOATP * k),表示WNK的实部和虚部
//下面的注释假设FFTN=8
TPOA = 2 * PI / FFTN; //TPOA = PI/4
for(layer=1;layer<=PWE;layer++){ //layer = 1,2,3
j = 0x01<<(layer-1); //使用math中的pow()会出现bug,使用左移运算减轻计算量
pmul = 0x01<<(PWE - layer);
for(i=0;i<pmul;i++){ //pmul=4时,i = 0,1,2,3
currentBase = i * 4 *j; //j = 1时,currentBase = 0,4,8,12
TPOATP = TPOA * pmul; //pmul=4时,TPOATP = PI
for(k=0;k<j;k++){ //j=1时,k=0
current = currentBase + k*2; //current = 0,4,8,12;
another = current + j*2; //another = 2,6,10,14;
//准备WNK
reFactor = cos(TPOATP * k); //1
imFactor = -sin(TPOATP * k);//0
//乘上WNK
Re = fft_output[another]; //备份实部
fft_output[another] = fft_output[another] * reFactor
- fft_output[another+1] * imFactor; //fft_output[2] = 8
fft_output[another+1] = fft_output[another+1] * reFactor
+ Re * imFactor; //fft_output[3] = 0
//蝶形加法
Re = fft_output[current]; //Re=0
Im = fft_output[current+1]; //Im=0
fft_output[current] += fft_output[another]; //fft_output[0] = 8;
fft_output[current+1] += fft_output[another+1]; //fft_output[1] = 0
fft_output[another] = Re - fft_output[another]; //fft[2] = -8
fft_output[another+1] = Im - fft_output[another+1]; //fft[3] = 0
}
}
}
for(int8_t m=0;m<FFTN*2;m++){
Serial.print(fft_output[m]);
Serial.print("\t");
}
Serial.println("");
}
/*输出整合,计算出每个频率的幅值,取出幅值最大的点
*/
void IntegrateData(){
//计算复数的模,注意,所有的模都存到偶数项中
//fft_output[0] = sqrt(fft_output[0]*fft_output[0]+fft_output[1]*fft_output[1])/FFTN;
fft_output[LEN-2] = sqrt(fft_output[LEN-2]*fft_output[LEN-2]+fft_output[LEN-1]*fft_output[LEN-1])/FFTN;
for(uint8_t i=2;i<(LEN-2);i+=2){ //最后一个点和第一个点已单独处理
fft_output[i] = 2*sqrt(fft_output[i]*fft_output[i]+fft_output[i+1]*fft_output[i+1])/FFTN;
}
//找出其中模长最大的值,记录脚标和模长
MAX[0] = 2; //脚标
MAX[1] = fft_output[2]; //模长
for(uint8_t i=4;i<LEN;i+=2){
if(MAX[1]<fft_output[i]){ //替换
MAX[0] = i;
MAX[1] = fft_output[i];
}
}
}
























 298
298

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








