转载:杨尚川
地址:http://yangshangchuan.iteye.com/blog/2031813
内容有修改
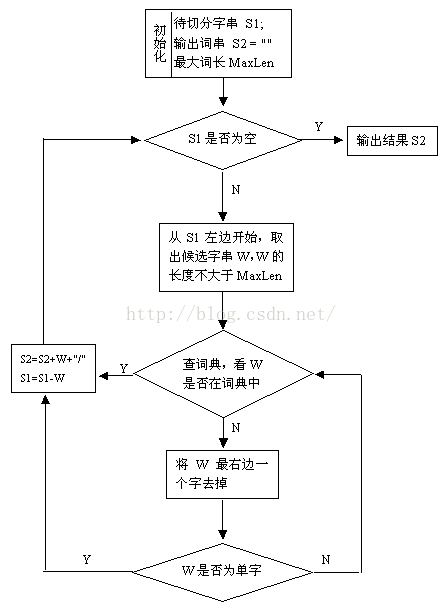
基于词典的正向最大匹配算法(最长词优先匹配),算法会根据词典文件自动调整最大长度,分词的好坏完全取决于词典。
算法流程图如下:
Java实现代码如下:
| package nlp.segmentation; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.nio.file.Files; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * 基于词典的正向最大匹配算法 */ public class FMMSeg { private static final List<String> DIC = new ArrayList<String>(); private static int MAX_LENGTH = 0; static{ //手动添加try-catch try { System.out.println("开始初始化词典"); int count = 0; int max = 1; //java8读取文件方式 List<String> lines = Files.readAllLines(Paths.get("C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/robot/笔记/dic.txt"), StandardCharsets.UTF_8); for (String line : lines) { DIC.add(line); count ++; if(max < line.length()){ max = line.length(); } } MAX_LENGTH = max; System.out.println("完成初始化词典,词数目:" + count); System.out.println("最大分词长度:" + MAX_LENGTH); } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("词典装载失败:" + e.getMessage()); } } public static List<String> seg(String text){ List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>(); while(text.length() > 0){ int len = MAX_LENGTH; if(text.length() < len){ len = text.length(); } //只取词典中最长分词的长度的子串进行匹配 String tryWord = text.substring(0, 0 + len); while(!DIC.contains(tryWord)){ //如果长度为一且在词典中未找到匹配,则按长度为一切分 if(tryWord.length() == 1){ break; } tryWord = tryWord.substring(0, tryWord.length() - 1); } result.add(tryWord); tryWord = tryWord.substring(tryWord.length()); } return result; } public static void main(String[] args){ String text = "杨尚川是APDPlat应用级产品开发平台的作者"; System.out.println(seg(text)); } } |
运行效果:
开始初始化词典
完成初始化词典,词数目:427452
最大分词长度:16
分析:text为"杨尚川是APDPlat应用级产品开发平台的作者"
-
取最大分词长度tryword为"杨尚川是APDPlat应用级产品"——无匹配
tryword长度减一为"杨尚川是APDPlat应用级产"——无匹配
……
tryword长度减一为"杨尚川"——匹配
-
去除已匹配,取最大分词长度tryword为"是APDPlat应用级产品开发平"——无匹配
……
tryword长度减一为"是"——匹配
-
去除已匹配,取最大分词长度tryword为"APDPlat应用级产品开发平台"——无匹配
……
tryword长度减一为"APDPlat"——匹配
-
去除已匹配,取最大分词长度tryword为"应用级产品开发平台的作者"——无匹配
……
tryword长度减一为"应用"——匹配
-
去除已匹配,取最大分词长度tryword为"应用级产品开发平台的作者"——无匹配
……
tryword长度减一为"应用"——匹配
-
去除已匹配,取最大分词长度tryword为"级产品开发平台的作者"——无匹配
……
tryword长度减一为"级"——匹配
-
去除已匹配,取最大分词长度tryword为"产品开发平台的作者"——无匹配
……
tryword长度减一为"产品开发"——匹配
-
去除已匹配,取最大分词长度tryword为"平台的作者"——无匹配
……
tryword长度减一为"平台"——匹配
-
去除已匹配,取最大分词长度tryword为"的作者"——无匹配
……
tryword长度减一为"的"——匹配
-
去除已匹配,取最大分词长度tryword为"作者"——匹配
打印:[杨尚川, 是, APDPlat, 应用, 级, 产品开发, 平台, 的, 作者]
词典文件下载地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1i37gKLZ。
上面的代码是利用了JDK的Collection接口的contains方法来判断一个词是否在词典中,而这个方法的不同实现,其性能差异极大,上面的初始版本是用了ArrayList:List<String> DIC = new ArrayList<>()。通常来说,对于查找算法,在有序列表中查找比在无序列表中查找更快,分区查找比全局遍历要快。
通过查看ArrayList、LinkedList、HashSet的contains方法的源代码,发现ArrayList和LinkedList采用全局遍历的方式且未利用有序列表的优势,HashSet使用了分区查找,如果hash分布均匀冲突少,则需要遍历的列表就很少甚至不需要。
测试代码如下:
| package nlp.test; import java.io.IOException; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.nio.file.Files; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Random; /** * 比较词典查询算法的性能 */ public class SearchTest { //为了生成随机查询的词列表 private static final List<String> DIC_FOR_TEST = new ArrayList<>(); //通过更改这里DIC的实现来比较不同实现之间的性能 //private static final List<String> DIC = new ArrayList<>(); //private static final List<String> DIC = new LinkedList<>(); private static final HashSet<String> DIC = new HashSet<String>(); static{ try { System.out.println("开始初始化词典"); int count=0; List<String> lines = Files.readAllLines(Paths.get("C:/dic.txt"), StandardCharsets.UTF_8); for(String line : lines){ DIC.add(line); DIC_FOR_TEST.add(line); count++; } System.out.println("完成初始化词典,词数目:"+count); } catch (IOException ex) { System.err.println("词典装载失败:"+ex.getMessage()); } } public static void main(String[] args){ //选取随机值 List<String> words = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i=0;i<100000;i++){ words.add(DIC_FOR_TEST.get(new Random(System.nanoTime()+i).nextInt(427452))); } long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(String word : words){ DIC.contains(word); } long cost = System.currentTimeMillis()-start; System.out.println("cost time:"+cost+" ms"); } } |
HashSet性能最好,比LinkedList和ArrayList快约3个数量级! LinkedList要比ArrayList慢一些,虽然他们都是全局遍历,但是LinkedList需要操作下一个数据的引用,所以会多一些操作,LinkedList因为需要保存前驱和后继引用,占用的内存也要高一些。
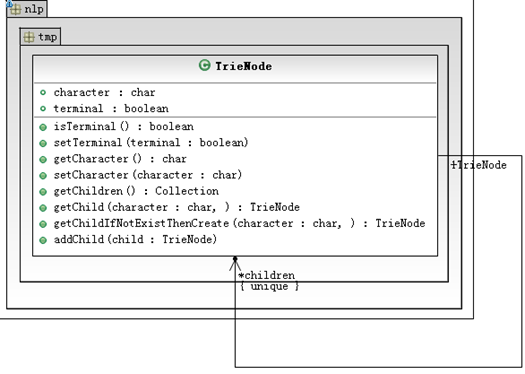
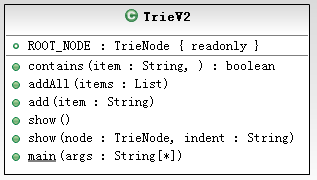
前缀树(Trie)与HashSet效率接近,内存更低。自己实现一个Trie的数据结构,用ConcurrentHashMap和HashMap实现内存较高,采用数组实现,代码如下:
| package nlp.test; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.List; public class TrieV2 { private final TrieNode ROOT_NODE = new TrieNode('/'); public boolean contains(String item){ //去掉首尾空白字符 item=item.trim(); int len = item.length(); if(len < 1){ return false; } //从根节点开始查找 TrieNode node = ROOT_NODE; for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ char character = item.charAt(i); TrieNode child = node.getChild(character); if(child == null){ //未找到匹配节点 return false; }else{ //找到节点,继续往下找 node = child; } } if(node.isTerminal()){ return true; } return false; } public void addAll(List<String> items){ for(String item : items){ add(item); } } public void add(String item){ //去掉首尾空白字符 item=item.trim(); int len = item.length(); if(len < 1){ //长度小于1则忽略 return; } //从根节点开始添加 TrieNode node = ROOT_NODE; for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ char character = item.charAt(i); TrieNode child = node.getChildIfNotExistThenCreate(character); //改变顶级节点 node = child; } //设置终结字符,表示从根节点遍历到此是一个合法的词 node.setTerminal(true); } private static class TrieNode{ private char character; private boolean terminal; private TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[0]; public TrieNode(char character){ this.character = character; } public boolean isTerminal() { return terminal; } public void setTerminal(boolean terminal) { this.terminal = terminal; } public char getCharacter() { return character; } public void setCharacter(char character) { this.character = character; } public Collection<TrieNode> getChildren() { return Arrays.asList(children); } public TrieNode getChild(char character) { for(TrieNode child : children){ if(child.getCharacter() == character){ return child; } } return null; } public TrieNode getChildIfNotExistThenCreate(char character) { TrieNode child = getChild(character); if(child == null){ child = new TrieNode(character); addChild(child); } return child; } public void addChild(TrieNode child) { children = Arrays.copyOf(children, children.length+1); this.children[children.length-1]=child; } }
public void show(){ show(ROOT_NODE,""); } private void show(TrieNode node, String indent){ if(node.isTerminal()){ System.out.println(indent+node.getCharacter()+"(T)"); }else{ System.out.println(indent+node.getCharacter()); } for(TrieNode item : node.getChildren()){ show(item,indent+"\t"); } } public static void main(String[] args){ TrieV2 trie = new TrieV2(); trie.add("APDPlat"); trie.add("APP"); trie.add("APD"); trie.add("杨尚川"); trie.add("杨尚昆"); trie.add("杨尚喜"); trie.add("中华人民共和国"); trie.add("中华人民打太极"); trie.add("中华"); trie.add("中心思想"); trie.add("杨家将"); trie.show(); } } |
TrieV2实现了节省内存的目标,节省了约70%,但是速度也慢了,慢了约10倍,可以对TrieV2做进一步优化,TrieNode的数组children采用有序数组,采用二分查找来加速。
使用了一个新的方法insert来加入数组元素,从无到有构建有序数组,把新的元素插入到已有的有序数组中,insert的代码如下:
| /** * 将一个字符追加到有序数组 * @param array 有序数组 * @param element 字符 * @return 新的有序数字 */ private TrieNode[] insert(TrieNode[] array, TrieNode element){ int length = array.length; if(length == 0){ array = new TrieNode[1]; array[0] = element; return array; } TrieNode[] newArray = new TrieNode[length+1]; boolean insert=false; for(int i=0; i<length; i++){ if(element.getCharacter() <= array[i].getCharacter()){ //新元素找到合适的插入位置 newArray[i]=element; //将array中剩下的元素依次加入newArray即可退出比较操作 System.arraycopy(array, i, newArray, i+1, length-i); insert=true; break; }else{ newArray[i]=array[i]; } } if(!insert){ //将新元素追加到尾部 newArray[length]=element; } return newArray; } |
有了有序数组,在搜索的时候就可以利用有序数组的优势,重构搜索方法getChild:
数组中的元素是TrieNode,所以需要自定义TrieNode的比较方法:
时间:#分别运行10次测试,然后取平均值
LinkedList 10000次查询 cost time:48812 ms
ArrayList 10000次查询 cost time:40219 ms
HashSet 10000次查询 cost time:8 ms
HashSet 1000000次查询 cost time:258 ms
HashSet 100000000次查询 cost time:28575 ms
Trie 10000次查询 cost time:15 ms
Trie 1000000次查询 cost time:1024 ms
Trie 100000000次查询 cost time:104635
TrieV1 10000次查询 cost time:16 ms
TrieV1 1000000次查询 cost time:780 ms
TrieV1 100000000次查询 cost time:90949 ms
TrieV2 10000次查询 cost time:50 ms
TrieV2 1000000次查询 cost time:4361 ms
TrieV2 100000000次查询 cost time:483398
TrieV3 10000次查询 cost time:21 ms
TrieV3 1000000次查询 cost time:1264 ms
TrieV3 100000000次查询 cost time:121740 ms
TrieV3待优化:text.substring(0, 0+len);会导致产生大量的新的字符串的产生,消耗CPU的同时还会促发垃圾回收频繁发生导致性能下降。
解决方案:见《逆向最大匹配算法》
结论:经过优化后TrieV3仍然比HashSet慢4倍,也不影响它在分词算法中的作用,从上面的数据可以看到,TrieV3的整体分词性能领先HashSet十五个百分点(15%),而且内存占用只有HashSet的80%。
| TrieV2-UML |
| TrieNode类图 TrieV2类图
|

























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








