Convolutional Layer
low-level features-- 边缘特征;high--level features-- complex
increasing the depth :
spatial dimension: output size = (N-F) / stride + 1; 
Pooling Layer:
only on spatial, the depth doesn't change;filter_size; no overlap
Activation Functions:
1. Sigmoid :range[0,1]; Saturated nuerons kill the gradient
2. tanh(x) : range[-1, 1]; still kill gradient when saturated
3.ReLU : No saturated, computationally efficient, actually more biologically plausible than sigmoid. dead ReLU, will never activate and update
4. Leaky ReLU : f(x) = max(0.01x, x); no saturated, computationally efficient
5. Exponential Linear Units(ELU)
6. Maxout "Neuron" : Linear Regime, no saturated, no die
In practice:
1. Use ReLU. Be carefu with your learning rates.
2. Try out Leaky ReLU/ Maxout/ELU
3. Try out tanh but don't expect much
4. Don't use Sigmoid.
Date processing:

- Substract the mean image(e.g. AlexNet)
(mean image = [32, 32, 3] array
- Substract per-channel mean (e.g. VGGNet)\
(mean along each channel = 3 numbers)
Weight Initializing :
Batch Normalization:

1. Compute the empirical mean and variance independently for each dimension
2. Normalize
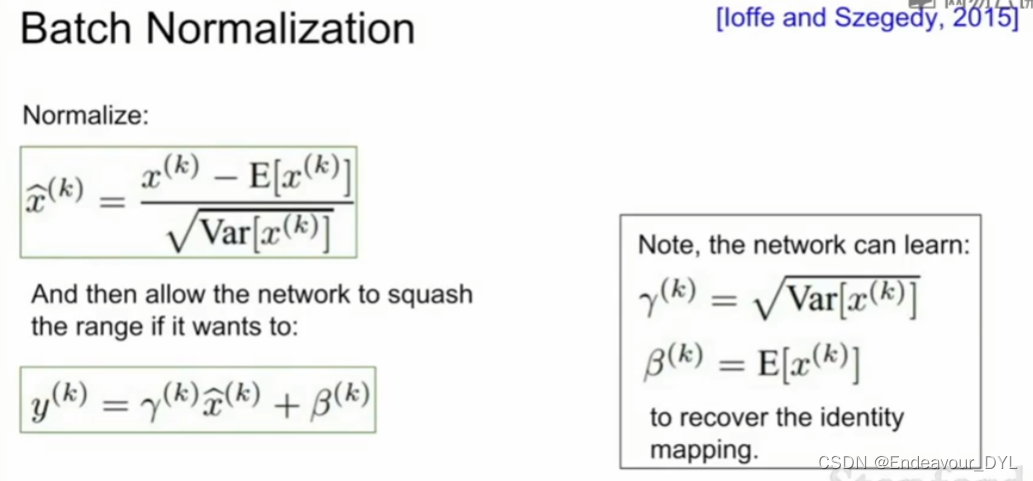
 Batcth Normalization is more likely to use in standard convolutional neural networks
Batcth Normalization is more likely to use in standard convolutional neural networks
Situation 1: loss 几乎不变, accuracy提升很多;虽然这里的分布依然很分散,损失项因此很接近,分布在向正确的方向移动,权重参数也在朝正确的方向改变,accuracy此时可能jump
Rough range for learning rate : [1e-3, ..., 1e-5]
Cross-validation strategy:
交叉验证是在训练集上训练,在验证集验证,观察超参数的效果
First Stage : obly a few epochs to get rough idea of what params work
Second stage : longer ruuning time finer search
CNN 框架:
pooling layer没有需要训练的参数, 其只是在观察池化区域
VGGNet:
Why use smaller filters? : deeper, more non-linearities, fewer parameters
输出尺寸与输入尺寸保持一致:使用零填充。
ResNet:
residual connection : 更深的网络不一定具有更好的效果
F(x) is the residual , sue layers to fit residual F(x)=H(x) - x instead of H(x) directly
RNN Network:
input: video, sentence, variably length, 可变序列数据

读取输入,更新隐藏状态,生成输出
Notice: the same function and the same set pf parameters are used at evey time step
Vanilla Recurent Neural Network:

tanh 将结果映射到[-1, 1]

Re-use the same weight matrix at evey time-step
Semantic Segmentation :
sliding window -- computational cost
fully convolutional -- 保持原尺寸; the training dataset is obtained by labeling each pixel
downsample -- pooling, strided convolution
uosample -- unpooling

 Learnable Upsampling :Transpose Convolution
Learnable Upsampling :Transpose Convolution



卷积与转置卷积操作不是可逆的, 对于同一个卷积核,经过转置卷积并不能恢复原来的值,只能保持原来的形状。
Generative Models:
Unsupervied Learning
data : x ; just data, no labels
goal : learn some underlying hidden structure of the data
examples : clustering, dimensionality reduction, feature learnin, densit estimation, etc
supervised learning
data : (x, y), x is data, y is label;
goal : learn a function to map x->y
examples : classification, regression, object detection, semantic segmentation, image captioning,etc..

Why Generative Models ?
从数据分布中创造出我们想要的真是样本






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








