- 文章:

借鉴:https://blog.csdn.net/woodcorpse/article/details/133820294
Article, 2023-10-10, Cancer Cell, [IF 50.3]
DOI:10.1016/j.ccell.2022.09.009
原文链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S153561082200438X
第一作者:Bassel Ghaddar, Antara Biswas
通讯作者:Martin J. Blaser, Subhajyoti De
合作作者:Chris Harris, M. Bishr Omary, Darren R. Carpizo
主要单位:
罗格斯大学新泽西州罗格斯肿瘤研究所系统与计算生物学中心(Center for Systems and Computational Biology, Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey, Rutgers University)
罗切斯特大学医学中心外科系(Department of Surgery, University of Rochester Medical Center)
罗格斯大学高级生物技术与医学中心(Center for Advanced Biotechnology and Medicine, Rutgers University)
RESULTS:
1. 检测和验证单细胞RNA测序(scRNA-seq)数据中的宏基因组读序
Detection and validation of metagenomic reads in scRNA-seq data
这部分主要概括了SAHMI的流程结构。
F1A
(1)读入微生物和测序的结果,并进行映射(映射什么?)
(2)Denoise降噪:kCT & CLQT
K_mer 相关性检验 :
Cell line quantile test:
(3)把微生物信息定位到细胞上
(4)分子关联
(5)临床关联
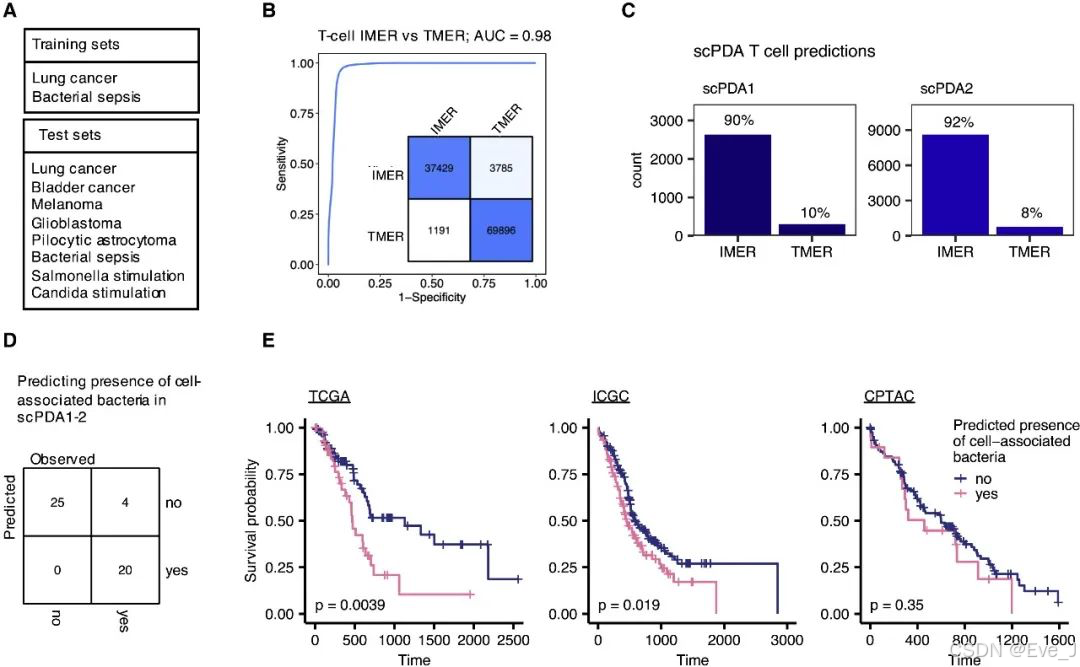
B图 :scRNA-seq和WGS,以及16S-rRNA和RNA-seq在微生物检测上的相关性。说明方法在微生物检测方面的可靠性。
C图:SAHMI对样品分类
D图:所有检测到的物种的kCT(k-mer相关性测试)散点图。每个点代表一个物种。说明SAHMI的结果是真实的
E图:scPDA样本的微生物种计数与正常样本的对比。发现污染物没有明显更多,说明降噪去除污染物是有效的。
F图:scPDA样本各物种水平的读取在其各自基因组中的映射位置的叠加直方图。(不懂)
G图:微生物技术与整体计数的对比,说明SAHMI富集了非人类序列,也就是可以有效抓取微生物信息。
H图:把SAHMI的结果用mBodyMap(人工矫正过的人类微生物数据库)计算了scPDA属的体部位富集分数。
I图:scRNA-seq和其他技术之间存在显著的一致性(前面都说过了吧)
J图:比较scPDA1和scPDA2与其他胰腺癌研究(绿色)或其他组织类型和疾病(蓝色)的细菌属的重叠系数的箱形图。结果验证了SAHMI识别出正确的组织存在的分类单元的能力。
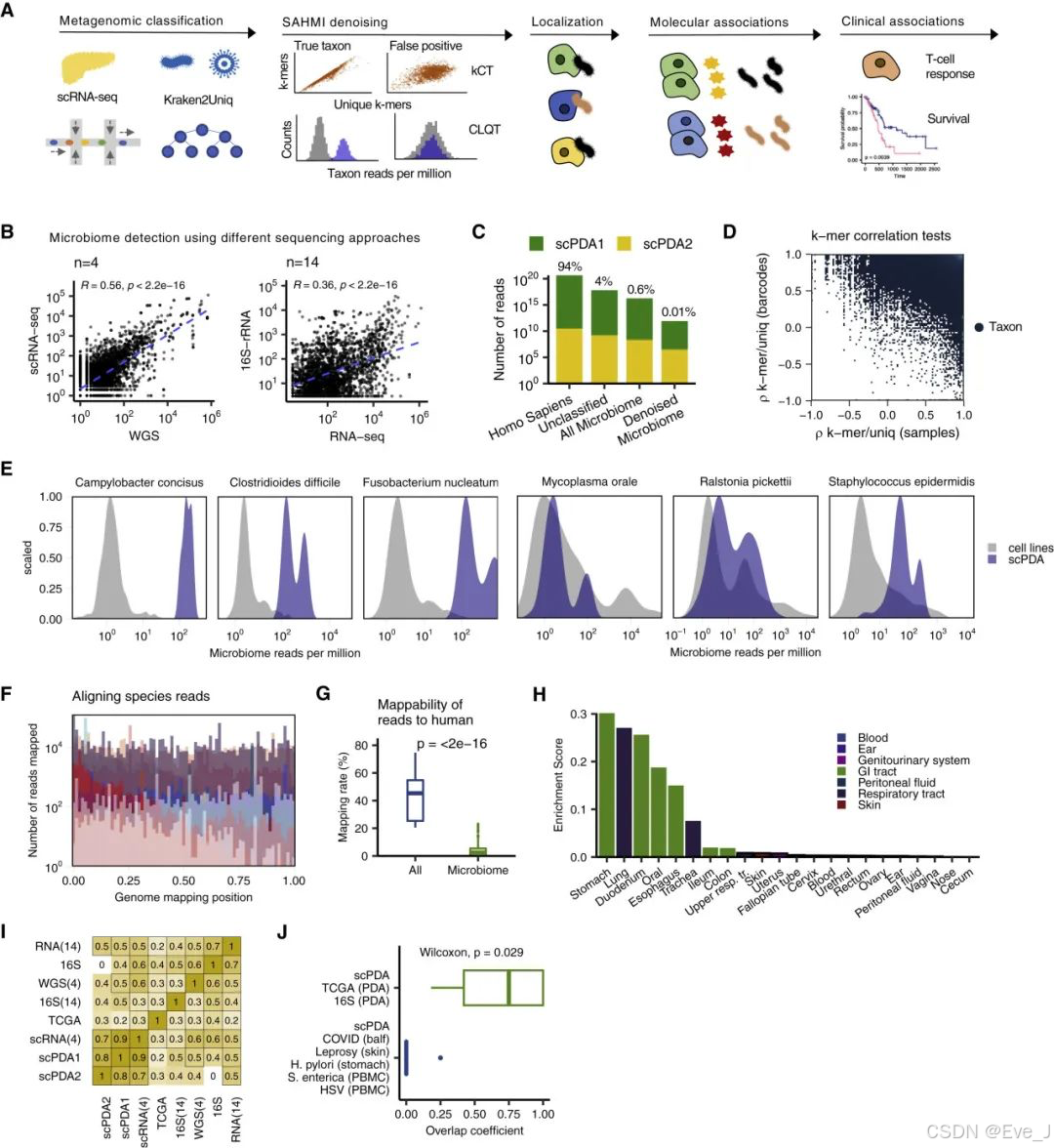
总结:F1主要就是介绍SAHMI这个方法的流程(A),然后从各个角度证明该方法的可信度。
2. 细胞相关的细菌存在于部分胰腺肿瘤中
Cell-associated bacteria are present in a subset of pancreatic tumors
(1)87%的样本中检测到微生物,共19种
(2)肿瘤样本比正常样本有更多的微生物,并且微生物与宿主有共定位(共用barcode)
(3)细菌与大多数细胞类型共定位,但主要集中在肿瘤细胞中,且其存在与癌症相关的细胞类型特异性过程(如细胞迁移、细胞外基质相互作用和PD-1信号传导)相关联。
A:箱线图显示在scPDA1和scPDA2中检测到的每个属分配的独特k-mer数量。
B:比较T(肿瘤)样本与N(正常)样本中每个样本的细菌计数总数。
C:在scPDA1和scPDA2中的细胞相关细菌计数表。堆叠条形图显示每个样本的计数和属组成。K表示千。
D:UMAP 微生物共享barcode的细胞被标记为黄色/绿色
E:在scPDA1和scPDA2中,每个细胞类型与细菌相关的细菌计数的条形图。
F:使用Wilcoxon测试识别在单条形码水平上显著的细菌细胞类型富集,并在scPDA1和scPDA2中共享的Circos图。tumor关联最强
G:箱形图显示了在每种细胞类型中,与细菌共定位的细胞与未共定位细胞的转录多样性比较的调整后的Wilcoxon p值。
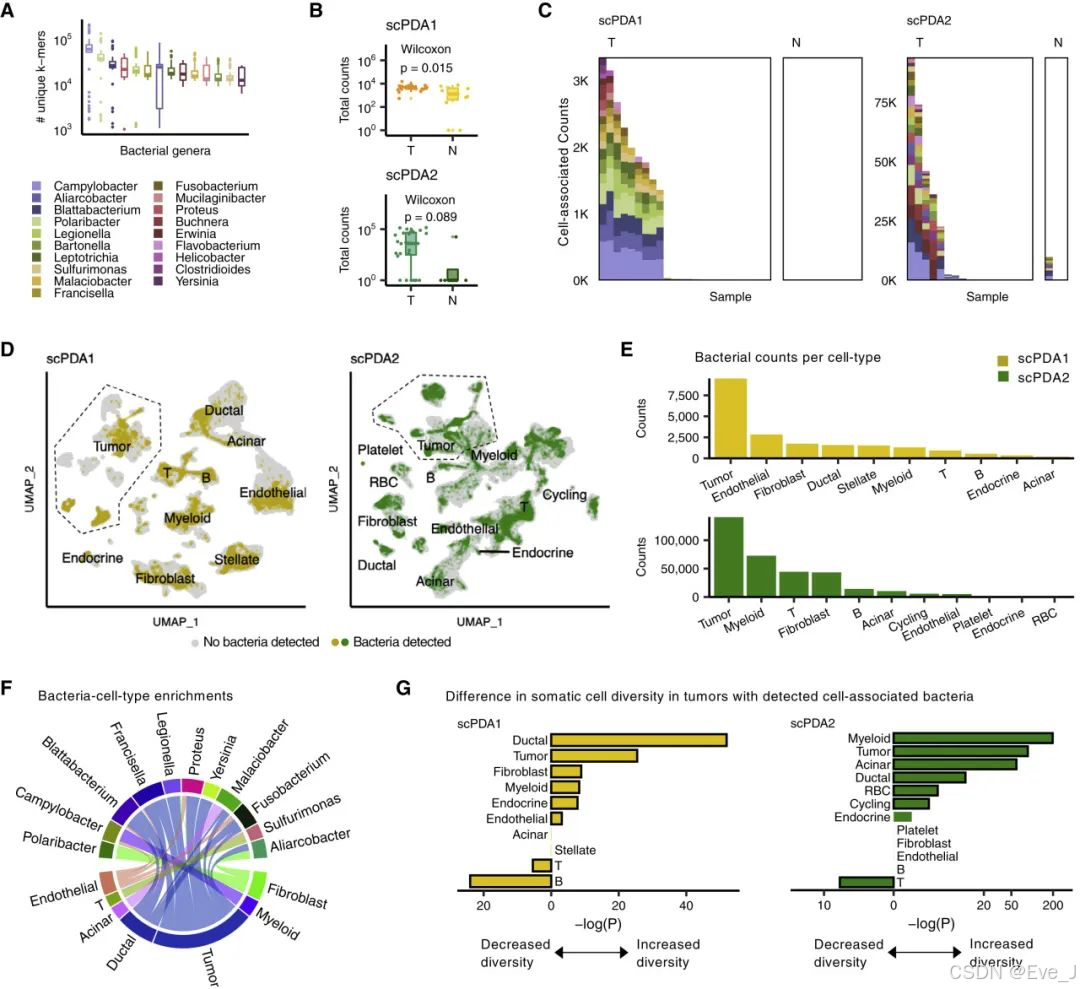
3. 细菌与细胞类型特异性的多样性和活动相关
Bacteria are associated with cell-type-specific diversity and activities
(1)细胞多样性:
- 肿瘤和髓样细胞:在细菌共定位的肿瘤和髓样细胞中,转录多样性显著增加。
- T细胞:在细菌共定位的T细胞中,转录多样性显著降低。
(2)基因表达:
肿瘤细胞与细菌共定位时,表现出最多的差异表达基因
方法上,需要把细菌与宿主细胞条形码配对,从而识别细菌共定位细胞中特异性差异表达的基因。
(3)关键基因的研究&通路分析
A:横横轴表示在与细菌共定位的细胞中与未共定位的细胞相比的基因表达的平均log2倍数变化,纵轴表示Wilcoxon测试的假发现率(FDR)校正p值。发现细菌是否共定位与宿主细胞的基因差异表达没有关系
B:柱状图显示了scPDA1和scPDA2中显著的基因-细菌对的数量。肿瘤细胞有最多的不同表达基因
C:散点图显示了每个显著基因在不同细菌或细胞类型中的差异表达次数。所有细胞类型和细菌中,最常受影响的基因包括角蛋白、粘蛋白和三叶草蛋白基因。
D:箱形图比较了与特定细菌属共定位的细胞与未共定位的细胞中的基因表达值。如:Clostridioides difficile共定位的肿瘤细胞中,EDIL3基因的表达显著增加,然后查看EDIL3在共定位/没有共定位的细胞中的表达水平。
E:点图显示了由DEGs共享的Reactome通路的富集情况。
F:(没看明白)
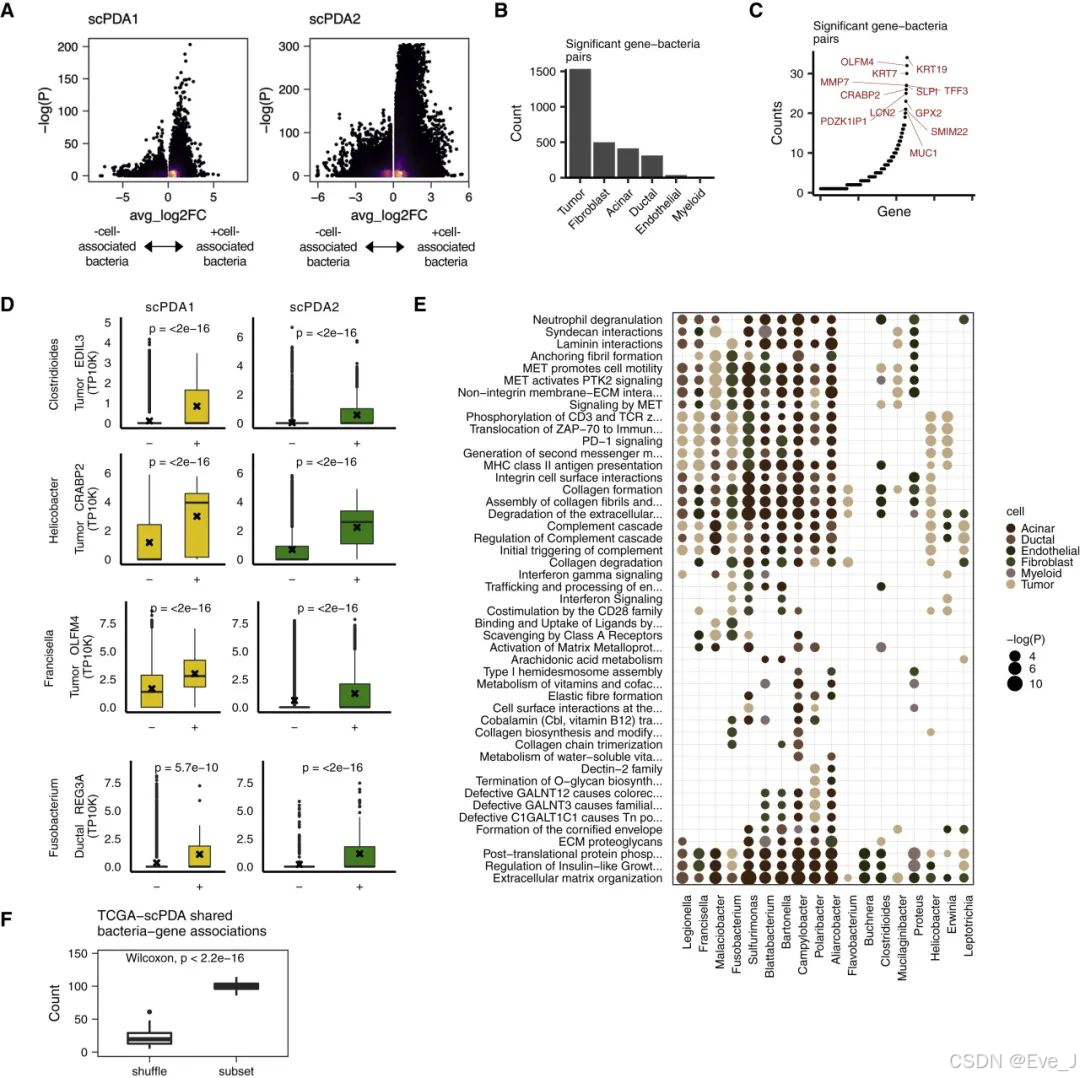
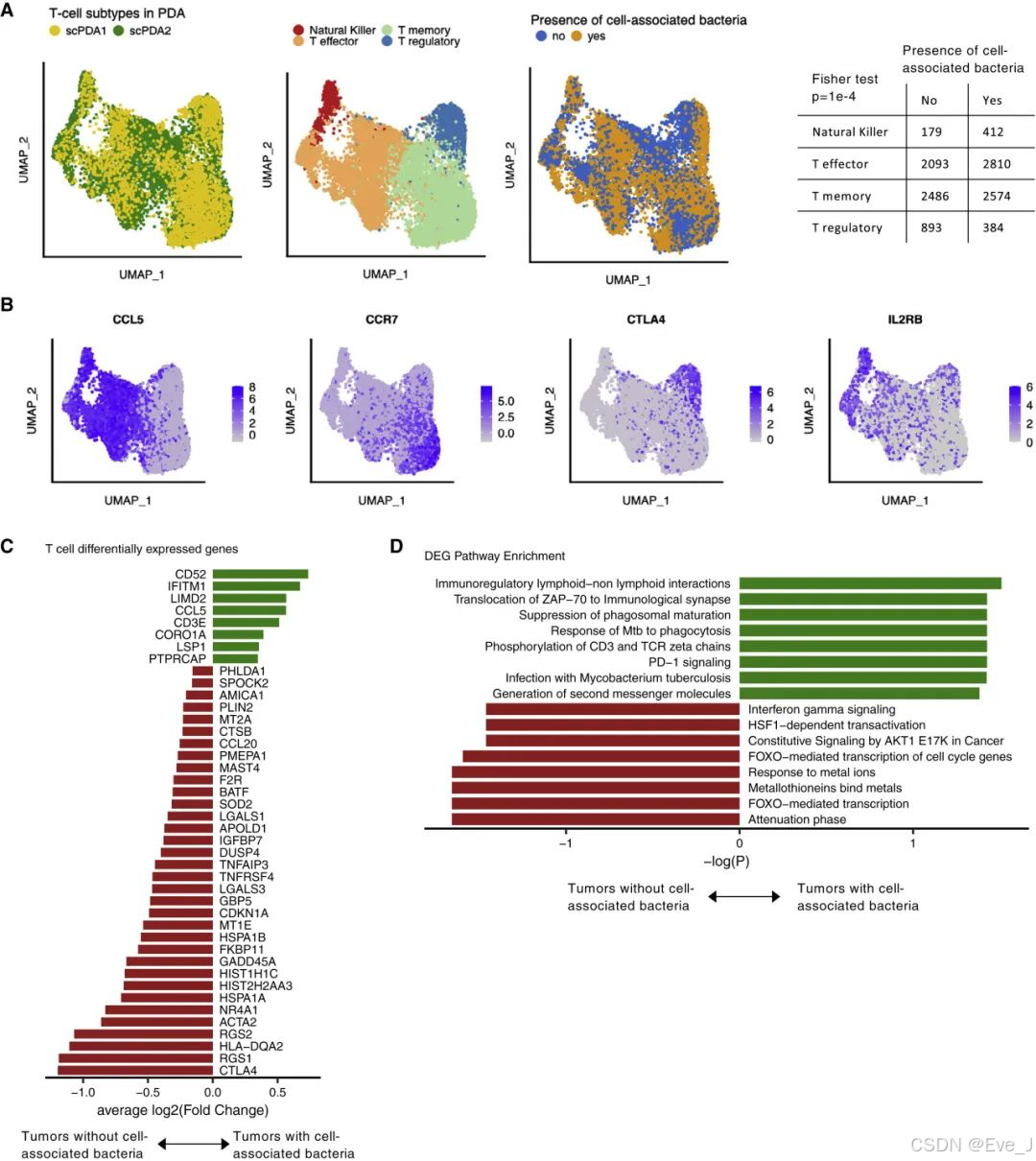
4. 携带细菌的肿瘤中的T细胞被激活
Tumors with cell-associated bacteria have activated T cells
带有细胞相关细菌的肿瘤中的T细胞亚型与没有细菌的肿瘤不同
(1)T细胞亚型分析:
- 研究者整合了来自scPDA1和scPDA2的数据,基于经典的亚型标志物识别了调节性T细胞、记忆T细胞、效应T细胞和自然杀伤T细胞(NK T cells)。
- 带有细胞相关细菌的肿瘤中的T细胞更可能呈现活化表型(如NK T细胞、效应T细胞),而不太可能是调节性表型(Fisher's检验,p = 1e-4)。
(2)差异表达基因(DEGs):
- 比较带有和不带有细胞相关细菌的肿瘤中的T细胞,发现多个差异表达基因在两个scPDA队列中共享。
- 上调的通路包括PD-1信号传导和对细胞内感染的响应,表明这些肿瘤细胞与细菌共定位时PD-1信号传导增加。
(3)通路富集分析:
- 下调的通路包括FOXO介导的转录和干扰素γ信号传导,这与这些肿瘤中相对较少的调节性T细胞一致。
A:UMAP
左:按样本。中:按主要的T细胞亚型。右:按是否存在微生物共定位。
与没有细胞相关细菌的肿瘤相比,携带细胞相关细菌的肿瘤中的T细胞更有可能具有激活的表型(即自然杀伤性T细胞、效应性T细胞),而不太可能具有调节性表型(我没看出来啊)
B:经过批次校正的scPDA1和scPDA2中的T细胞数据的UMAP图,根据选择的T细胞亚型标记物的标准化表达着色
C:是否有微生物共定位的T细胞的共有显著差异表达基因DEGs
D:DEGs的Reactome通路富集结果
5. 大多数胰腺导管腺癌(PDA)的T细胞被预测为具有与感染相关的转录谱
The majority of PDA T cells are predicted to have infection-related transcriptional profiles
大多数胰腺导管腺癌(PDA)中的T细胞表现出与感染相关的转录特征。研究者通过构建一个随机森林模型来区分T细胞是响应已知的感染还是响应其他微生物负荷较低的肿瘤,从而进行分类。
结果表明,胰腺癌中的T细胞在转录上更类似于感染相关的微环境中的T细胞
6. 微生物组特征对存活率分层
Microbiome characteristics stratify survival
肿瘤内微生物特征与整体生存率的关联。由于当前没有包含生存数据的大型单细胞PDA队列,研究者开发了一个模型,该模型基于总RNA表达数据分类肿瘤中是否存在细胞相关细菌,然后用该模型预测TCGA、ICGC和CPTAC中的胰腺肿瘤的感染状态,并测试其与生存率的关系。
工具:SAHMI/README.md at main · sjdlabgroup/SAHMI · GitHub
SAHMI 单细胞宿主-微生物互作分析代码实战-腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云
## Introduction
SAHMI enables the systematic recovery and denoising of microbial signals from genomic sequencing of host tissues. The pipeline consists of R command line functions that implement the following main steps which are further described below.1. Taxonomic classification (recommended with Kraken2Uniq)
2. Extract microbiome reads
3. Single-cell k-mer analysis
4. Barcode level signal denoising (barcode k-mer correlation test)
5. Sample-level signal denoising (sample k-mer correlation tests)
6. Identifying contaminants and false positives (cell line quantile test)
7. Quantitation of microbes and creating the barcode-metagenome counts matrix
8. Joint analysis of host and microbial data
-
不需要下载SAHMI,主要的脚本是:
run_kraken.r -
The following R packages must be installed prior to running some SAHMI functions:
optparse, stringr, tidyverse, dplyr, ShortRead, data.table -
需要安装kraken2 -
-
工具流程:
-
1、分类学分类:
- 使用Kraken2Uniq进行分类,生成分类报告和原始测序文件。
-
2、提取微生物读取:
- 从分类后的fastq文件中提取微生物读取。
-
3、单细胞k-mer分析:
- 对每个条形码进行k-mer统计,过滤掉宿主相关的k-mers。
-
4、条形码级别信号去噪:
- 通过k-mer相关性测试过滤条形码信号。
-
5、样本级别信号去噪:
- 进行样本级别的k-mer相关性测试,识别真实的微生物信号。
-
6、识别污染物和假阳性:
- 通过rpmm分布和分位数测试(CLQT)识别并去除污染物和假阳性。
-
rpmm(reads per million microbiome reads)
-
7、微生物定量和计数矩阵创建:
- 创建条形码-元基因组计数矩阵,用于定量分析。
-
8、联合分析:
- 结合宿主和微生物数据,进行联合分析和可视化。
(1)Taxonomic classification (recommended with Kraken2Uniq)
The required outputs from this step are: a Kraken summary report with
sample level metagenomic counts,
a Kraken output file with read and k-mer level taxonomic classifications,
an MPA-style report,
and raw sequencing fastq files with taxonomic classification for each read.
- 工具:Kraken2Uniqkraken2/docs/MANUAL.markdown at master · DerrickWood/kraken2 · GitHub
- 目的:对单细胞RNA测序的fastq文件进行分类,生成分类报告、读取和k-mer级别的分类数据,以及MPA(Metagenomic Phylogenetic Analysis)的报告。
- 输入:
--samplesample name
--fq1path to fastq 1 file
--fq2path to fastq 2 file
--out_pathoutput directory path
--ncbi_blast_pathpath to ncbi-blast (see Kraken documentation for details)
--Kraken2Uniq_pathpath to Kraken2 main 'kraken2' function
--kraken_database_pathpath to kraken database
--kreport2mpa_pathpath to kreport2mpa.py function (included in SAHMI/functions)
--pairedare fastq files paired end (T) or single-end/unpaired (F). Default is T.
- 输出:生成分类报告、Kraken输出文件和带分类信息的fastq文件。
#MPA reports sample
D:Bacteria;P:Proteobacteria;C:Gammaproteobacteria;O:Enterobacterales;F:Enterobacteriaceae;G:Escherichia;S:Escherichia coli 1000
D:Bacteria;P:Firmicutes;C:Bacilli;O:Lactobacillales;F:Lactobacillaceae;G:Lactobacillus;S:Lactobacillus reuteri 500
#第一行表示Escherichia coli的读取数为1000。
#第二行表示Lactobacillus reuteri的读取数为500。(2)Extract microbiome reads
提取微生物的读数
- 输入
extract_microbiome_reads.r
--sample_namesample name--fqpath to classified fastq file (sample_1.fq/sample_2.fq) (if paired end reads this function must be once for each read)kraken_reportpath to kraken2uniq report (sample.kraken.report.txt)mpa_reportpath to mpa style report (sample.kraken.report.mpa.txt)out_pathoutput pathextract_microbiome_output.r
--sample_namesample name--output_filepath to kraken output file (sample.output.txtkraken_reportpath to kraken2uniq report (sample.kraken.report.txt)mpa_reportpath to mpa style report (sample.kraken.report.mpa.txt)out_pathoutput path
- 输出:fasta files for microbiome reads; microbiome output file.
(3)Single-cell k-mer analysis
- 输入:
sckmer.r
--sample_namesample name--fa1path to microbiome fasta 1 file (sample_1.fa)--fa2path to microbiome fasta 2 file (sample_2.fa)--microbiome_output_filepath to microbiome output file (sample.microbiome.output.txt)kraken_reportpath to kraken2uniq report (sample.kraken.report.txt)mpa_reportpath to mpa style report (sample.kraken.report.mpa.txt)out_pathoutput pathcb_lennucleotide length of cell barcodesumi_lennucleotide length of unique molecular identifiers (UMI)rankstaxa ranks to analyze. more than one value allowed (e.g. c('G', 'S')). See Kraken report for more detailhosthost taxonomy ID to excludemin_fracminimum fraction of k-mers directly assigned to taxon ID or its lineage to use read.nsamplemax number of barcodes to sample per taxon ID
暂缓待续//0715//






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








