In a directed graph, we start at some node and every turn, walk along a directed edge of the graph. If we reach a node that is terminal (that is, it has no outgoing directed edges), we stop.
Now, say our starting node is eventually safe if and only if we must eventually walk to a terminal node. More specifically, there exists a natural number K so that for any choice of where to walk, we must have stopped at a terminal node in less than K steps.
Which nodes are eventually safe? Return them as an array in sorted order.
The directed graph has N nodes with labels 0, 1, ..., N-1, where N is the length of graph. The graph is given in the following form: graph[i] is a list of labels jsuch that (i, j) is a directed edge of the graph.
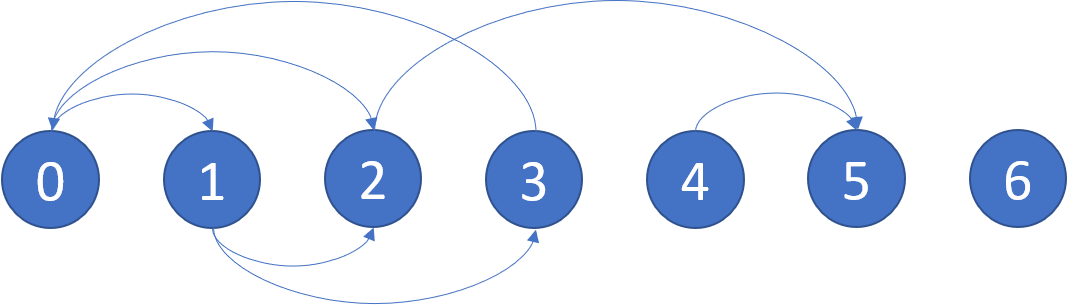
Example: Input: graph = [[1,2],[2,3],[5],[0],[5],[],[]] Output: [2,4,5,6] Here is a diagram of the above graph.
Note:
graphwill have length at most10000.- The number of edges in the graph will not exceed
32000. - Each
graph[i]will be a sorted list of different integers, chosen within the range[0, graph.length - 1].
分析
这道题我看到别人用递归加cache来做。但是没看太明白算法。我这里介绍一个队列的算法。
要想找到所有安全的点,有一个前提:这个点所有的路径到达出度为0的点。那么先寻找出度为0的点,压入队列中,然后遍历队列,将所有指向该点的路径删除,如果有新的出度为0的点的话,那么说明该点的所有的路径都是指向之前已经遍历的安全点,那么就把新的点压入队列,直到队列为空。
我们使用了map保存指向该点的点,这样在删除路径的时候就可以比较方便的查找。
Code
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> eventualSafeNodes(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
int n = graph.size();
map<int, set<int>> grid;
vector<int> count(n, 0);
queue<int> q;
vector<int> res;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
count[i] = graph[i].size();
for (int j = 0; j < graph[i].size(); j ++)
{
int end = graph[i][j];
if (grid.find(end) == grid.end())
{
grid[end] = set<int>();
}
grid[end].insert(i);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
if (count[i] == 0)
q.push(i);
}
while (!q.empty())
{
int end = q.front();
res.push_back(end);
q.pop();
set<int>::iterator it = grid[end].begin();
for (; it != grid[end].end(); it ++)
{
count[*it] --;
if (count[*it] == 0)
q.push(*it);
}
}
sort(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
};运行效率
Runtime: 428 ms, faster than 12.30% of C++ online submissions for Find Eventual Safe States.
Memory Usage: 72.5 MB, less than 14.38% of C++ online submissions forFind Eventual Safe States.





















 161
161











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








