目录
多次给小房子a赋值,小房子a中存放的将始终是最后一次赋的值:
a = a + 1的作用是把小房子a中的值在原来的基础上增加1:
让计算机计算 10 - 5与 10 + 5 的值,第一行显示差,第二行显示和:
指定两个数,输出这两个数的和、差、积和商。例如指定两个数9和3:
读入两个整数放到变量a和变量b中,并将变量a和变量b中的数互换:
第1节 编程的魔力
八皇后问题:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int queen[8] = { 0 }; //用来储存皇后的位置 即queen的值就为第i行的列
//queen[0]表示第0行
//queen[i]表示第i行
int cnt = 0; //表示摆放了几个皇后,也表示摆放皇后的行数。
int col = 0; //表示在这一列上摆放了皇后
int sum = 0; //总共有几种摆法
while (1) {
//在(cnt,col)这个坐标摆放皇后
if (cnt == 1 && queen[0] == 7 && col == 6) { //表示第一行的皇后已经到了第八列且第二行的皇后到了第六列位置,已经摆放不下皇后了就退出循环
break;
}
int isAttack = 0; //用来表示皇后们之间是否能够攻击的到,如果攻击的到就是1,否则就为0
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
if (queen[i] == col) { //表示在同一列上
isAttack = 1;
}
int div_row = cnt - i; //表示斜线上的纵坐标之差
int div_col = queen[i] - col; //表示斜线上横坐标之差
if (div_row == div_col || div_row == -div_col) { //表示在同一斜线上
isAttack = 1;
}
}
if (isAttack == 0) { //表示可以放置
queen[cnt] = col; //记录皇后当前的列数
cnt++; //开始摆放下一个皇后
col = 0; //下一个皇后从第一列开始遍历
if (cnt == 8) { //如果摆满了八个皇后就打印出他们的摆法
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
printf("%d ", queen[i] + 1);
}
printf("\n");
sum++; //并且摆放种数+1
do { //越界问题 //回朔
cnt--; //撤回正在摆放的皇后
col = queen[cnt] + 1; //往下一个列寻找摆放位置
} while (col >= 8);
}
}
else { //表示不能摆放
col++;
while (col >= 8) { //回朔
cnt--; //退一格
col = queen[cnt] + 1; //上一个皇后往后移一格
}
}
}
printf("总共有%d种摆法\n", sum);
return 0;
}调试结果:
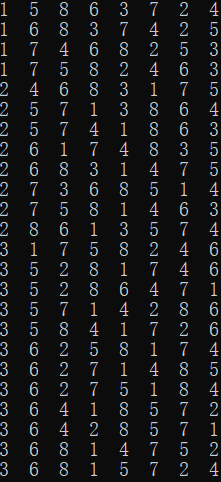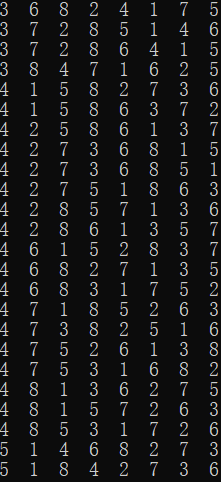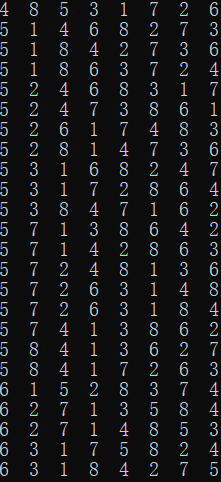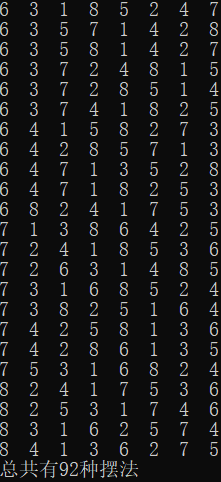
数独:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int SolveCount = 0; //! 解法计数
//! 需要求解的数独数据 0表示未知数,需要求解的值,不同的数独,修改此数组的值
int SudokuArr[9][9] =
{
{0 , 9 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 2 , 0 , 0 , 1 } ,
{0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 6 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 2 } ,
{0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 4 , 0 , 0 } ,
{6 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 8 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 } ,
{0 , 2 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 } ,
{0 , 0 , 1 , 7 , 0 , 4 , 0 , 0 , 0 } ,
{3 , 6 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 } ,
{0 , 0 , 7 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 5 , 0 , 0 } ,
{9 , 5 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 7 , 0 , 0 , 8 } ,
};
//! 打印显示数独
void Display_Sudoku(void)
{
int row, col;
for (row = 0; row < 9; ++row)
{
for (col = 0; col < 9; ++col)
printf(" %d", SudokuArr[row][col]);
printf("\n");
}
}
//! 寻找下一个需要填的空位
int Find_Next_Empty(int* pos)
{
int row, col;
for (row = 0; row < 9; ++row)
{
for (col = 0; col < 9; ++col)
{
if (SudokuArr[row][col] == 0)
{
*pos = row * 9 + col;
return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
//! 检查该位置的数字是否满足要求,1 满足 0 不满足
int Check_Sudoku(int pos, int num)
{
int row = pos / 9, col = pos % 9, i, j, x, y;
//! 判断行重复
for (i = 0; i < 9; ++i)
{
if (SudokuArr[row][i] == num) return 0;
}
//! 判断列重复
for (i = 0; i < 9; ++i)
{
if (SudokuArr[i][col] == num) return 0;
}
//! 判断小九宫格重复
x = col / 3 * 3; y = row / 3 * 3;
for (i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; ++j)
{
if (SudokuArr[y + i][x + j] == num) return 0;
}
}
return 1; //! 无重复,满足要求
}
//! 求解数独
void Solve_Sudoku(void)
{
int pos;
if (!Find_Next_Empty(&pos)) //! 判断是否填完
{
SolveCount++;
printf("Solution: %d\n", SolveCount);
Display_Sudoku();
getchar(); //! 按下Enter键获取下一个解法
}
else
{
int num = 1;
for (; num < 10; ++num)
{
if (Check_Sudoku(pos, num)) //! 判断该值是否满足要求
{
int row = pos / 9, col = pos % 9;
SudokuArr[row][col] = num;
Solve_Sudoku();
SudokuArr[row][col] = 0;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
Solve_Sudoku();
return 0;
}调试结果:

上面这个数独一共有99410种解。
第2节 让计算机开头说话
ni hao:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("ni hao");
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
![]()
ni hao(分两行展示):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("ni\nhao");
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

让计算机显示下面这些图形:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("*\n");
printf("**\n");
printf("***\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf(" *\n * *\n* *\n * *\n *\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf(" *\n *\n *\n* *\n * *\n *\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

让计算机说“早上好”:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("早上好\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
![]()
让计算机显示下面这个图形:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("A\nBC\nDEF\nGHIJ\nKLMNO\nPQRSTU\nV\nW\nX\nY\nZ\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
A
BC
DEF
GHIJ
KLMNO
PQRSTU
V
W
X
Y
Z第3节 多彩一点
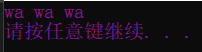
让计算机开口说话的语句(紫色文字的wawa):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
system("color 5");
printf("wa wa wa\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
让计算机在屏幕上输出绿底白字的hi:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
system("color 2f");
printf("hi\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

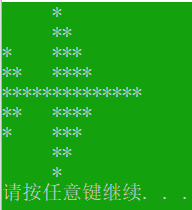
让计算机打印这个小飞机图案(绿底白字):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
system("color 27");
printf(" *\n **\n* ***\n** ****\n**************\n");
printf("** ****\n* ***\n **\n *\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
让计算机打印这个小队旗图案(白底红字):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
system("color f4");
printf("A\nI*\nI**\nI***\nI****\nI*****\nI\nI\nI\nI\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
第4节 让计算机做加法
让计算机计算1+2的和:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
a = 1;
b = 2;
c = a + b;
printf("%d\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

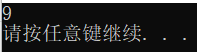
让计算机计算321-123的结果:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
a = 321;
b = 123;
c = a - b;
printf("%d\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
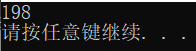
让计算机计算5+3+1=?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c, d;
a = 5;
b = 3;
c = 1;
d = a + b + c;
printf("%d\n", d);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
让计算机算出下面3个算术:
//计算 123456789 + 43214321 的值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
a = 123456789;
b = 43214321;
c = a + b;
printf("%d\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

//计算 7078 * 8712 的值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
a = 7078;
b = 8712;
c = a * b;
printf("%d\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
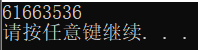
//计算 (123456 + 5432)* 321 的值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c, d;
a = 123456;
b = 54321;
c = 321;
d = (123456 + 54321) * 321;
printf("%d\n", d);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

第5节 数学的家——变量
计算机执行完上面的代码后,将会输出1还是2:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a;
a = 1;
a = 2;
printf("%d\n", a);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

多次给小房子a赋值,小房子a中存放的将始终是最后一次赋的值:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a;
a = 1;
a = 2;
a = 3;
a = 4;
a = 5;
a = 6;
a = 7;
printf("%d\n", a);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

a = a + 1的作用是把小房子a中的值在原来的基础上增加1:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a;
a = 7;
a = a + 1;
printf("%d\n", a);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
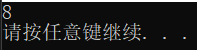
猜猜计算机最终会输出多少?:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a;
a = 10;
a = a * a;
printf("%d\n", a);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
![]()
让计算机计算1.2 * 1.5的值:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
float a, b, c;
a = 1.2;
b = 1.5;
c = a * b;
printf("%f\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

进行两个小数的加法运算,例如:5.2+3.1=?:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
float a, b, c;
a = 5.2;
b = 3.1;
c = a + b;
printf("%.1f\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

通过计算机把下面3个式子算出来吧!
//计算 1.2 + 2.3 + 3.4 + 4.5 的值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
float a, b, c, d, e;
a = 5.2;
b = 3.1;
c = 3.4;
d = 4.5;
e = a + b + c + d;
printf("%.1f\n", e);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
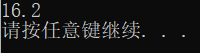
//计算 1.1 * 100的值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
float a, b, c;
a = 1.1;
b = 100;
c = a + b;
printf("%.1f\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

//计算10.1 * (10 * 10)的值
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
float a, b, c;
a = 10.1;
b = 10;
c = a * (b * b);
printf("%.1f\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

第6节 数据输出——我说咋地就咋地
将整个算术等式输出,例如:1 + 2 = 3:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
a = 1;
b = 2;
c = a + b;
printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
![]()
让计算机计算 10 - 5与 10 + 5 的值,第一行显示差,第二行显示和:
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
a = 10;
b = 5;
c = a - b;
printf("%d\n", c);
c = a + b;
printf("%d\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

指定两个数,输出这两个数的和、差、积和商。例如指定两个数9和3:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
a = 9;
b = 3;
c = a + b;
printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
c = a - b;
printf("%d - %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
c = a * b;
printf("%d * %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
c = a / b;
printf("%d / %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

第7节 数据输入——我说算啥就算啥
从键盘读入这两个数,输出这两个数的和:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
c = a + b;
printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

让“加法计算器”更加人性化——带有提示的读入和输出:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
printf("这是一个加法计算器,欢迎您使用\n");
printf("-----------------------------------\n");
printf("请输入第一个数(输入完毕后请按回车)\n");
scanf("%d", &a);
printf("请输入第二个数(输入完毕后请按回车)\n");
scanf("%d", &b);
c = a + b;
printf("它们的和是%d\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

从键盘读入两个整数,并输出他们的和:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
c = a + b;
printf("%d\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

从键盘读入两个数(整数),并输出这两个数的和、差、积和商:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
c = a + b;
printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
c = a - b;
printf("%d - %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
c = a * b;
printf("%d * %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
c = a / b;
printf("%d / %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

第8节 究竟有多少种小房子
用数据类型float和double申请小房子a的区别:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
float a;
a = 3.1415926535897932;
printf("%.15f\n", a);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
![]()
只输出你输入的第一个字母(char是用来存放字符的):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char a;
scanf("%c", &a);
printf("你刚才输入的字符是%c\n", a);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

让计算机读入一个字符并把这个字符原样输出:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char c;
scanf("%c", &c);
printf("%c\n", c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
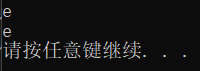
从键盘读入一个字符,输出这个字符后面一个字符:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char a;
scanf("%c", &a);
printf("后面的一个字符是%c\n", a + 1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

第9节 拨开云雾见月明
计算任意两个数的和:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
printf("%d + %d = %d", a, b, a + b);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

计算4+5的值:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", 4 + 5);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

计算4+(6-3)*7的值:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", 4 + (6 - 3) * 7);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

第10节 逻辑挑战1:交换小房子中的数
将变量a和变量b的值互换:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, t;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
printf("%d %d", a, b);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

读入两个整数放到变量a和变量b中,并将变量a和变量b中的数互换:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, t;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
printf("%d %d\n", a, b);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:
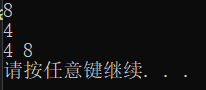
在不增加任何新变量的情况下将两个变量的值进行交换:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
a = b - a;
b = b - a;
a = b + a;
printf("%d %d", a, b);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

第11节 天啊!这怎么能看懂
有效地在代码中添加注释,可以让你的程序更具有可读性:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a;
a = 1;
//a = 2;
//a = 3;
//a = 4;
//a = 5;
printf("%d\n", a);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a;
a = 1;
/*
a = 2;
a = 3;
a = 4;
a = 5;
*/
printf("%d\n", a);
system("pause");
return 0;
}调试结果:























 4247
4247











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








