**本次学习Java ,所采用的的IDE是JetBrains公司开发的IDEA
下面是我安装并配置IDEA的流程,有需要的小伙伴可以参考。
链接: [link]()
如果IDEA获取有困难的,可以使用免费的eclipse IDE ,也很方便的。**
一个简单的java应用程序
第一步
在下拉的菜单中选择新建,然后点击项目,既可以创建一个Java Project

第二步
名称是用户自己定义,最好是与项目相关,尽量用英文,不要使用中文(可能后续编译时会产生不必要的麻烦),然后是这个项目的位置,根据你的爱好而定,接着JDK ,则是编译和调试你程序的,第一次使用时,IDEA会自动监测,如果你没事先安装的话,IDEA会提醒你在IDEA内下载,最后点击创建。
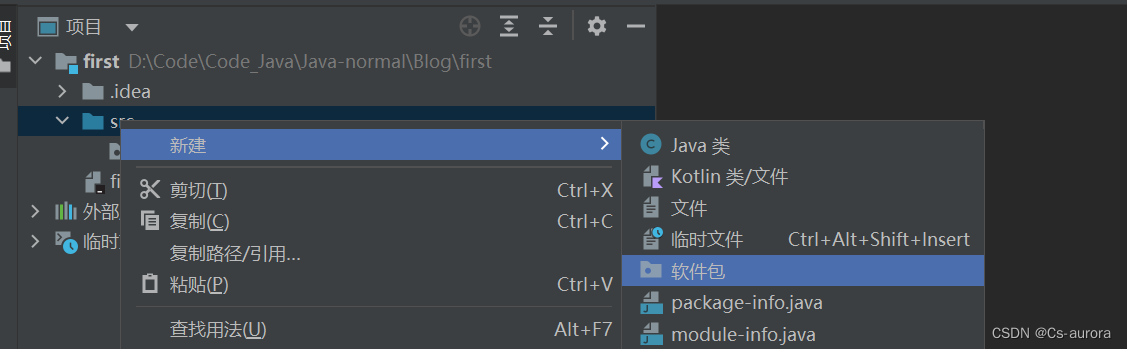
我们是在项目的src目录中写代码,下面一次右键src ,找到软件包,这是java的包文件;
在包中,右键包,然后找到java的类,即class

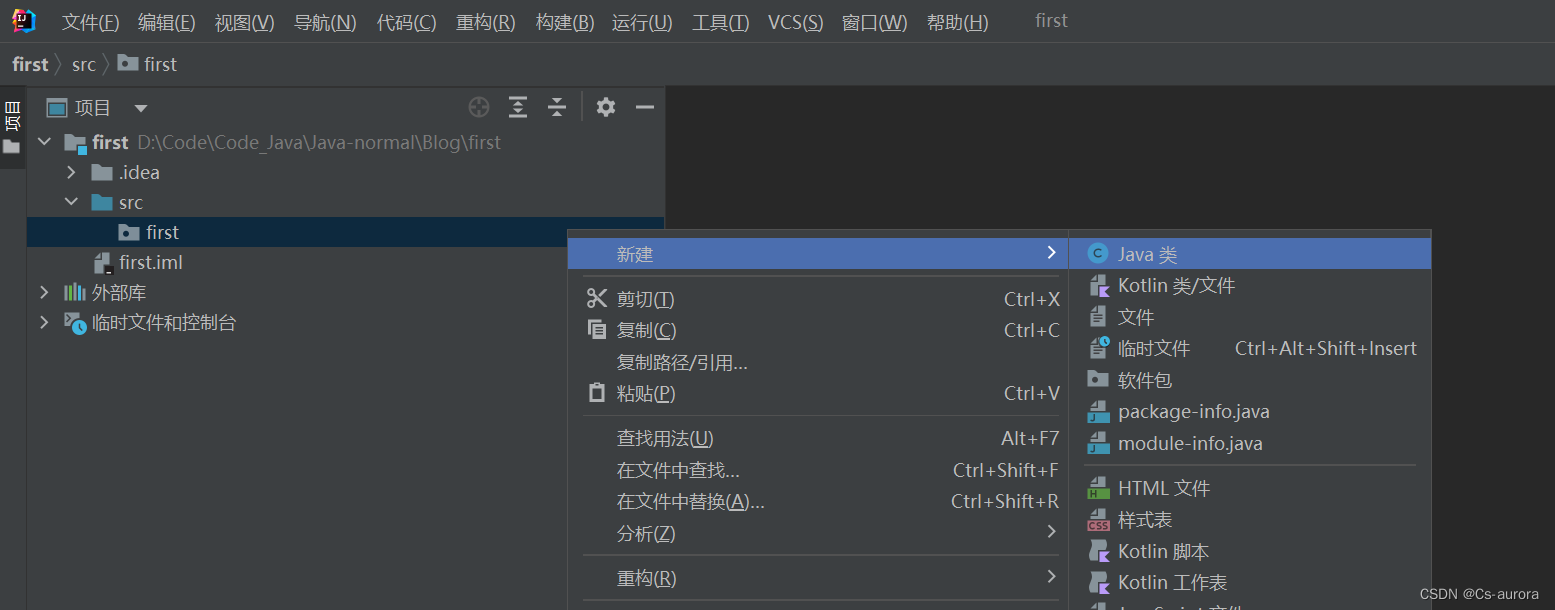
第三步
在java的main函数内,输入我们的第一个程序“ we will not use ‘hello world’“”
第四步
我们可以点击右上角的朝右的三角形,如果此图标是灰色的,别着急,我们可以看向界面的左下角。最左边下面有一个“结构” ,我们点击。然后找到我们的类名,右键点开,找到调试词条,就可以运了。
注释
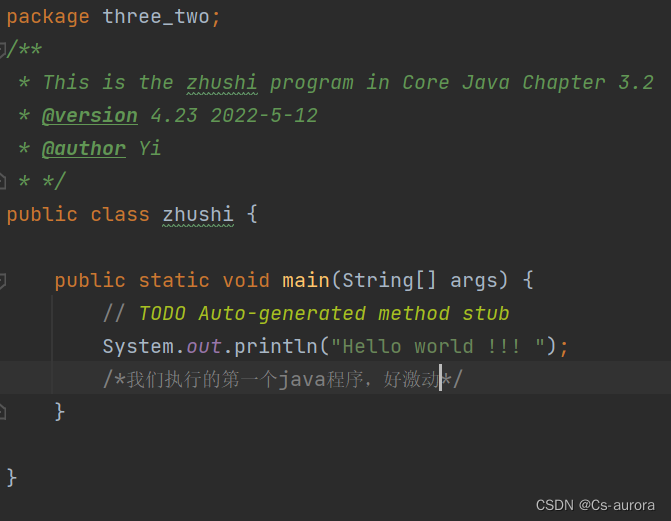
Java中有3中注释方式(Java核心技术卷(第十一版)一 P29 提及),注释以及注释的代码不会出现在可执行程序中,所以可以放心添加任意多的注释(虽然是一个好习惯,但是我觉得大部分人觉得还是比较麻烦! haha !!!)
如图
/** 开始 */结束的注释,可以用来自动生成文档,我们可以在settings中设置
// 注释一行 ,从//开始,知道这一行末尾
/**/ 用来注释更长的内容 ,以/开始 , 以/结束
数据类型
Java是一种强类型语言 , 即每一个变量必须声明一种类型。Java中,一共有8种基本类型。其中4种整型,2种浮点类型,1种字符类型和表示真值的boolean类型
下面我以代码的形式,来深入理解一下java这8种数据类型,其中boolean特殊。boolean类型有两个值:false 和 true 。用来判定逻辑条件。注意:整型值与布尔值之间不能进行相互转换。
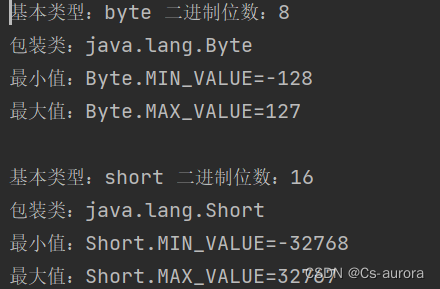
// byte
System.out.println("基本类型:byte 二进制位数:" + Byte.SIZE);
System.out.println("包装类:java.lang.Byte");
System.out.println("最小值:Byte.MIN_VALUE=" + Byte.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("最大值:Byte.MAX_VALUE=" + Byte.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println();
// short
System.out.println("基本类型:short 二进制位数:" + Short.SIZE);
System.out.println("包装类:java.lang.Short");
System.out.println("最小值:Short.MIN_VALUE=" + Short.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("最大值:Short.MAX_VALUE=" + Short.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println();
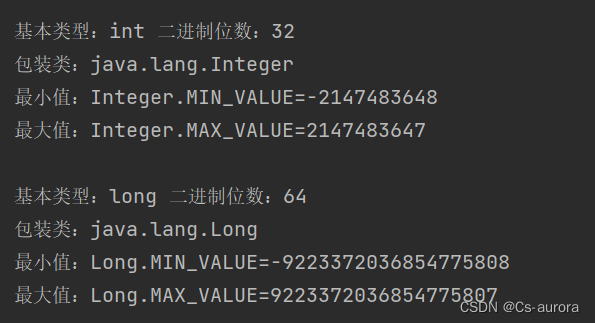
// int
System.out.println("基本类型:int 二进制位数:" + Integer.SIZE);
System.out.println("包装类:java.lang.Integer");
System.out.println("最小值:Integer.MIN_VALUE=" + Integer.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("最大值:Integer.MAX_VALUE=" + Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println();
// long
System.out.println("基本类型:long 二进制位数:" + Long.SIZE);
System.out.println("包装类:java.lang.Long");
System.out.println("最小值:Long.MIN_VALUE=" + Long.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("最大值:Long.MAX_VALUE=" + Long.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println();
// float
System.out.println("基本类型:float 二进制位数:" + Float.SIZE);
System.out.println("包装类:java.lang.Float");
System.out.println("最小值:Float.MIN_VALUE=" + Float.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("最大值:Float.MAX_VALUE=" + Float.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println();
// double
System.out.println("基本类型:double 二进制位数:" + Double.SIZE);
System.out.println("包装类:java.lang.Double");
System.out.println("最小值:Double.MIN_VALUE=" + Double.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("最大值:Double.MAX_VALUE=" + Double.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println();
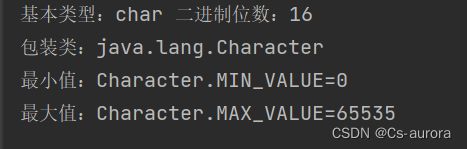
// char
System.out.println("基本类型:char 二进制位数:" + Character.SIZE);
System.out.println("包装类:java.lang.Character");
System.out.println("最小值:Character.MIN_VALUE="
+ (int) Character.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println("最大值:Character.MAX_VALUE="
+ (int) Character.MAX_VALUE);

变量与常量
Java使用变量存储值。而常量就是值不会变的变量。
变量
Java中 , 每一个变量都有一个类型(type)。声明变量时,先指定变量的类型,然后是变量名称。以下是例子
double Salary ;
int vacationDays ;
long earthPopulation ;
boolean done ;
Java中变量分为成员变量与局部变量
成员变量 :类方法外的变量 ,又分为了静态(类)变量和实例变量
局部变量 :类方法内的变量
public class Member_variable {
public static int num = 9;// 类变量
public static String Name = "类变量(类中直接引用,其他类:类名.类变量)";
public int count ; //实例变量
public String name ;
public Member_variable()
{
count = 6 ;
name = "实例变量(对象.实例变量)";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Member_variable test = new Member_variable();
System.out.println(test.name + ":"+ test.count);
System.out.println(Name+num);
}
}
通过代码发现 类变量与实例变量主要的区别就是 static关键字
static 关键字标识的就是 类变量 ,没有就是实例变量
实例变量 :
*实例变量声明在一个类中,但在方法、构造方法和语句块之外;
*实例变量可以声明在使用前或者使用后;
*实例变量在对象创建的时候创建,在对象被销毁的时候销毁;
*实例变量具有默认值。数值型变量的默认值是0,布尔型变量的默认值是false,引用类型变量的默认值是null。变量的值可以在声明时指定,也可以在构造方法中指定;
*当一个对象被实例化之后,每个实例变量的值就跟着确定;
*实例变量的值应该至少被一个方法、构造方法或者语句块引用,使得外部能够通过这些方式获取实例变量信息;
*访问修饰符可以修饰实例变量;
*实例变量对于类中的方法、构造方法或者语句块是可见的。一般情况下应该把实例变量设为私有。通过使用访问修饰符可以使实例变量对子类可见;
*实例变量可以直接通过变量名访问。但在静态方法以及其他类中,就应该使用完全限定名:ObjectReference.VariableName。
以下是例子
public class Instance_variable {
// 这个实例变量对子类可见
public String name ;
// 私有变量 , 仅在该类可见
private double salary ;
// 在构造器中对name赋值
public Instance_variable (String empName)
{
name = empName ;
}
// 设定salary的值
public void setSalary(double empSal)
{
salary = empSal ;
}
// 打印信息
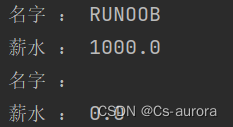
public void printEmp()
{
System.out.println("名字 : " + name) ;
System.out.println("薪水 : " + salary) ;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
/*我们给对象赋初值*/
Instance_variable empOne = new Instance_variable("RUNOOB");
empOne.setSalary(1000.0);
empOne.printEmp();
/*我们直接创建一个对象,但不赋值*/
Instance_variable none = new Instance_variable("") ;
none.printEmp();
}
}
结果
类变量 :
*类变量也称为静态变量,在类中以 static 关键字声明,但必须在方法之外。
*无论一个类创建了多少个对象,类只拥有类变量的一份拷贝。
*类变量的优先级大于实例变量
*静态变量除了被声明为常量外很少使用,静态变量是指声明为 public/private,final 和 static 类型的变量。静态变量初始化后不可改变。
*静态变量储存在静态存储区。经常被声明为常量,很少单独使用 static 声明变量。
*静态变量在第一次被访问时创建,在程序结束时销毁。
*与实例变量具有相似的可见性。但为了对类的使用者可见,大多数静态变量声明为 public 类型。
*默认值和实例变量相似。数值型变量默认值是 0,布尔型默认值是 false,引用类型默认值是 null。变量的值可以在声明的时候指定,也可以在构造方法中指定。此外,静态变量还可以在静态语句块中初始化。
*静态变量可以通过:ClassName.VariableName的方式访问。
*类变量被声明为 public static final 类型时,类变量名称一般建议使用大写字母。如果静态变量不是 public 和 final 类型,其命名方式与实例变量以及局部变量的命名方式一致。
例子
public class Static_variable {
//salary是静态的私有变量
private static double salary;
// DEPARTMENT是一个常量
public static final String DEPARTMENT = "开发人员";
public static void main(String[] args){
Static_variable.salary = 10000 ;
salary = 10000;
System.out.println(DEPARTMENT+"平均工资:"+salary);
}
}
结果
常量
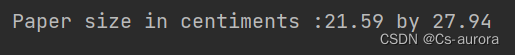
//Constant
final double CM_PER_INCH = 2.54 ;
final double paperWidth = 8.5 ;
final double paperHeight = 11 ;
System.out.println("Paper size in centiments :" + paperWidth * CM_PER_INCH + " by " + paperHeight * CM_PER_INCH);
结果
常量也分为局部常量 和 成员常量
在变量声明上加上final字段 ,即可实现常量
运算符
算术运算
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 25;
int d = 25;
System.out.println("a + b = " + (a + b) );
System.out.println("a - b = " + (a - b) );
System.out.println("a * b = " + (a * b) );
System.out.println("b / a = " + (b / a) );
System.out.println("b % a = " + (b % a) );
System.out.println("c % a = " + (c % a) );
System.out.println("a++ = " + (a++) );
System.out.println("a-- = " + (a--) );
关系运算
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
public void print2()
{
System.out.println("a == b = " + (a == b) );
System.out.println("a != b = " + (a != b) );
System.out.println("a > b = " + (a > b) );
System.out.println("a < b = " + (a < b) );
System.out.println("b >= a = " + (b >= a) );
System.out.println("b <= a = " + (b <= a) );
}
位运算
int a = 60 ; // 60 = 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0011 1100 ;
int b = 13 ; // 13 = 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1101 ;
int c = 0 ;
public void print3() // 注释只显示后8位
{
//与运算,对应位进行与处理
c = a & b ; // 12 = 0000 1100 ;
System.out.println("a & b = " + c);
//或运算,对应位或处理
c = a | b ; // 61 = 0011 1101 ;
System.out.println("a | b = " + c);
c = a ^ b ; // 49 = 0011 0001 ;
System.out.println("a ^ b = " + c);
c = ~a ; // -61 = 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1100 0011 ;
System.out.println("~a = " + c );
c = a >> 2 ; // 15 = 0000 1111
System.out.println("a >> 2 = "+ c);
c = a << 2 ; // 1111 0000 = 240
System.out.println("a << 2 = " + c);
c = a >>> 2 ; // 15 = 0000 1111
System.out.println("a >>> 2 = " + c) ;
}
逻辑运算
boolean a = true;
boolean b = false;
int c = 5 ;
boolean d = ( c <4 ) && ( c++ < 10) ;
public void print4()
{
System.out.println("a && b = " + (a&&b));
System.out.println("a || b = " + (a||b) );
System.out.println("!(a && b) = " + !(a && b));
//短路逻辑运算符 即利用性质,只需判断一个即可知道结果,另一个式子无法影响整体的结果
System.out.println("使用短路逻辑运算符的结果为" + d);
System.out.println(c);
}
赋值运算
int a = 10 ;
int b = 20 ;
int c ;
public void print5()
{
c = a + b;
System.out.println("c = a + b = " + c );
c += a ;
System.out.println("c += a = " + c );
c -= a ;
System.out.println("c -= a = " + c );
c *= a ;
System.out.println("c *= a = " + c );
a = 10;
c = 15;
c /= a ;
System.out.println("c /= a = " + c );
a = 10;
c = 15;
c %= a ;
System.out.println("c %= a = " + c );
c <<= 2 ;
System.out.println("c <<= 2 = " + c );
c >>= 2 ;
System.out.println("c >>= 2 = " + c );
c >>= 2 ;
System.out.println("c >>= 2 = " + c );
c &= a ;
System.out.println("c &= a = " + c );
c ^= a ;
System.out.println("c ^= a = " + c );
c |= a ;
System.out.println("c |= a = " + c );
}
条件运算
int a = 10 ;
int b = (a ==1) ? 20 : 30 ;
public void print6()
{
System.out.println("Value of b is " + b);
b = (a == 10) ? 20 : 30 ;
System.out.println("Value of b is " + b) ;
}
数学函数
Java中,有一个Math类,其中包含了许多静态方法,
Math类 , 其中的函数,可以帮助我们更快捷地编写程序
public class Main {
public static void main(String [] args)
{
//计算平方根
double sq = Math.sqrt(10) ;
System.out.println("10的开方为 : " + sq) ;
//幂运算
double y = Math.pow(1.5 , 2) ;
System.out.println("1.5的2次方为 : " + y);
//提供类一些三角函数
double sin = Math.sin(Math.PI * 0.5) ;
System.out.println("此三角函数的sin值为 : "+ sin) ;
sin = Math.cos(Math.PI * 0.5) ;
System.out.println("cos的值为" + sin );
//Math类定义了两个常量的接近值
System.out.println(Math.PI);
System.out.println(Math.E) ;
}
}
jieguo
强制类型转换
double i = 5.555 ;
int m ;
m = (int ) i;
System.out.println(m) ;
自增、自减运算
System.out.println("自增运算符前缀运算后a="+a+",x="+x);
System.out.println("自增运算符后缀运算后b="+b+",y="+y);
运算符
如果不使用圆括号,就按照给出的运算符优先级次序进行计算。同一个级别的运算符按照从左到右的赐福以此计算。(摘录Core Java Volume I)
| 类型 | 操作符 | 结合性 |
|---|---|---|
| 后缀 | () [] . (点操作符) | 左到右 |
| 一元 | expr++ expr– | 从左到右 |
| 一元 | ++expr --expr + - ~ ! | 从右到左 |
| 乘性 | * /% | 左到右 |
| 加性 | + - | 左到右 |
| 移位 | >> >>> << | 左到右 |
| 关系 | > >= < <= | 左到右 |
| 相等 | == != | 左到右 |
| 按位与 | & | 左到右 |
| 按位异或 | ^ | 左到右 |
| 按位或 | | | 左到右 |
| 逻辑与 | && | 左到右 |
| 逻辑或 | || | 左到右 |
| 条件 | ?: | 从右到左 |
| 赋值 | = + = - = * = / =%= >> = << =&= ^ = | = |
| 逗号 | , | 左到右 |
字符串
在Java中,String是一个字符串类,也就是代表String不是对象。在标准Java的类库中定义的。
每一个用“”双引号括起来的都是String类。
在这里介绍String类中的几个常用的函数和 常见的误区。
创建字符串
String str ;//声明一个String 类的对象
String str1 = "hello world" ; //声明并赋值
String str2 = "" ;// 声明并赋值为空串
产生子串
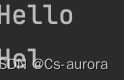
String greeting = "Hello" ;
String s = greeting.substring(0, 3) ;
System.out.println(greeting) ;
System.out.println(s);
结果
拼接的用法
//Java中 +号可以拼接
String expletive = "Expletive" ;
String PG13 = "deleted" ;
String message = expletive + PG13 ;
System.out.println("两个字符串拼接的结果 : " + message) ;
//Java中,一个字符串与一个非字符串相连接,后者会转换为字符串
int age =13 ;
String rating = "PG" + age ;
System.out.println(rating) ;
//Java中,需要将多个字符串连接,且用界定符隔开
String all = String.join("/", "S" , "M" , "L" , "XL");
System.out.println(all) ;
//Java中,重复多个字符串
String s0 = "Java" ;
String repeated = "Java".repeat(3) ;
String repeateding = s0.repeat(4) ;
System.out.println(repeated);
System.out.println(repeateding) ;
//Java中没有提供修改字符串中某个字符的方法
greeting = greeting.substring(0 , 3) + "p!" ;
System.out.println(greeting) ;
空串和null
//空串和null串
String greet = "hello" ;
String g = "" ;
int n = greet.length();
相等
//Java中的字符串相等
String s1 = "Hello" ;
String s2 = "Hello" ;
boolean e = (s2 == s1);
System.out.println(e) ;
String s3 = new String("abc");
String s4 = new String("abc");
boolean f = (s3 == s4) ;
System.out.println(f);
码点和代码单元
//Java中的码点和代码单元
String zf = "🍷代码";
int p = zf.length();
int q = zf.codePointCount(0,zf.length());
System.out.println(p) ;
System.out.println(q);
输入与输出I/O
前面这么多例子,我们都没有接触到从控制台输入,都是直接在程序里面对变量进行赋初值,然后进行操作,那么从这里开始我们后面程序基本上都有输入。
Java的io包中基本包含了所有情况的输入和输出
这回涉及到后面Java面对对象的部分知识,所以这里介绍最基本的输入输出。
//........
import java.util.Scanner ;
//.......
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in) ;
// ......
}
这样定义后,我们就可以程序中输入我们想输入的数据了。如下图,可以读取一行字符串,一个单词,一个整数。其实还有很多输入等等
System.out.println("What's your name ?");
//读取一行
String name = in.nextLine() ;
//读取一个单词
String firstName = in.next();
//读取一个整数
System.out.println("How old are you ?");
int age = in.nextInt();
控制流程
控制流程结构是用条件语句和循环语句来确定。与C/C++的大致一样,但也有细微的区别。
块作用域(Block)
public class Block {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int n = 9 ;
{
int k ;
k = 10 ;
System.out.println(k);
}
System.out.println(n);
}
}
块(即复合语句)是指由若干条Java语句组成的语句,并用一对大括号括起来。块确定了变量(常量是特殊的变量)的作用域
一个块可以嵌套在另一个块中 , 比如在main方法块中嵌套一个块,如上图。
不能在嵌套的两个块中声明同名的变量。
在块中声明的变量,只能在块中有定义,在块外或者其他地方是不能有作用。
条件语句
public class Condition_sentence {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Condition test1 = new Condition();
test1.print1();
Condition_2 test2 = new Condition_2();
test2.print2();
Condition_3 test3= new Condition_3();
test3.print3();
Condition_4 test4 = new Condition_4();
test4.print4();
}
}
class Condition{
int x = 10 ;
public void print1(){
if( x < 20 )
{
System.out.println("这是 if 语句");
}
}
}
class Condition_2{
int x = 30;
public void print2()
{
if(x < 20)
{
System.out.println("这是 if 语句");
}
else {
System.out.println("这是 else 语句");
}
}
}
class Condition_3{
int x = 30 ;
public void print3() {
if( x == 10 ){
System.out.println("Value of X is 10");
}else if( x == 20 ){
System.out.println("Value of X is 20");
}else if( x == 30 ){
System.out.println("Value of X is 30");
}else{
System.out.println("这是 else 语句");
}
}
}
class Condition_4{
int x = 30 ;
int y = 10 ;
public void print4() {
if( x== 30)
{
if( y == 10)
{
System.out.println("X = 30 and Y = 10") ;
}
}
}
}
循环语句
public class Loop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
loop_1 one = new loop_1() ;
one.print1();
loop_2 two = new loop_2();
two.print2(); ;
loop_3 three = new loop_3();
three.print3();
}
}
class loop_1{
int x = 10;
public void print1()
{
while( x < 20 )
{
System.out.print("value of x : " + x );
x++;
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
class loop_2{
int x= 10 ;
public void print2()
{
do{
System.out.print("value of x : " + x );
x++;
System.out.print("\n");
}while( x < 20 );
}
}
class loop_3{
public void print3()
{
for(int x = 10; x < 20; x = x+1)
{
System.out.print("value of x : " + x );
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
break语句
public class Break_statement {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//不带标签的break
int years = 50 ;
int balance = 1000 ;
int goal = 10000 ;
int Rate = 2 ;
while(years <= 100)
{
balance = balance + years * Rate ;
if(balance >= goal)
{
break ;
}
years ++ ;
}
//代标签的break语句
}
}
/*
* break语句主要用作于循环语句或者switch语句
*/
continue 语句
package three_eight;
public class Continue_statement {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int [] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
for(int x : numbers ) {
if( x == 30 ) {
continue;
}
System.out.print( x );
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
/*
continue 适用于任何循环控制结构中。作用是让程序立刻跳转到下一次循环的迭代。
在 for 循环中,continue 语句使程序立即跳转到更新语句。
在 while 或者 do…while 循环中,程序立即跳转到布尔表达式的判断语句。
*/
多路选择语句——switch语句
public class Multiple_sele {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//char grade = args[0].charAt(0);
char grade = 'C';
switch(grade)
{
case 'A' :
System.out.println("优秀");
break;
case 'B' :
System.out.println("不错");
break ;
case 'C' :
System.out.println("良好");
break;
case 'D' :
System.out.println("及格");
break;
case 'F' :
System.out.println("你需要再努力努力");
break;
default :
System.out.println("未知等级");
}
System.out.println("你的等级是 " + grade);
//无break 语句
int i = 5 ;
switch(i)
{
case 0:
System.out.println(0);
case 1 :
System.out.println(1);
case 2 :
System.out.println(2);
case 3 :
System.out.println(3);
case 4 :
System.out.println(4) ;
default :
System.out.println("default");
}
int j = 1 ;
switch(j)
{
case 0:
System.out.println("0");
case 1:
System.out.println("1");
case 2:
System.out.println("2");
default:
System.out.println("default");
}
int k = 1 ;
switch(k)
{
case 0 :
System.out.println("0");
case 1 :
System.out.println("1");
case 2 :
System.out.println("2");
break ;
case 3 :
System.out.println("3");
break ;
default :
System.out.println("default");
break ;
}
}
}
/*
* char类型为char 、byte 、 short 或 int 的常量表达式
* 枚举常量
* 从Java 7开始 , case标签还可以是字符串字面量
*
**/

























 2484
2484











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










