Nearest Common Ancestors
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 30606 | Accepted: 15626 |
Description
A rooted tree is a well-known data structure in computer science and engineering. An example is shown below:
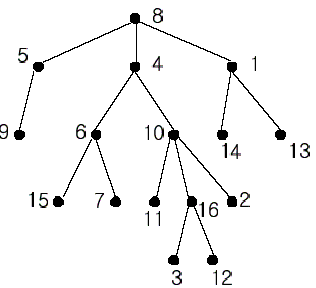
In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.

In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T) is given in the first line of the input file. Each test case starts with a line containing an integer N , the number of nodes in a tree, 2<=N<=10,000. The nodes are labeled with integers 1, 2,..., N. Each of the next N -1 lines contains a pair of integers that represent an edge --the first integer is the parent node of the second integer. Note that a tree with N nodes has exactly N - 1 edges. The last line of each test case contains two distinct integers whose nearest common ancestor is to be computed.
Output
Print exactly one line for each test case. The line should contain the integer that is the nearest common ancestor.
Sample Input
2
16
1 14
8 5
10 16
5 9
4 6
8 4
4 10
1 13
6 15
10 11
6 7
10 2
16 3
8 1
16 12
16 7
5
2 3
3 4
3 1
1 5
3 5
Sample Output
4 3先输入t为测试数据组数,然后输入一个n,表示有n个顶点
接下来n-1行,表明有n-1条边,每行包括两个顶点u,v
接下来一行是需要查询的两个顶点u,v
即求u,v的最近公共祖先。本题本组测试数据只涉及到了一条查询
maxn顶点最多个数,maxq最大查询条数.ans[i]保存第i次输入的查询的结果,i从0开始#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <algorithm> #include <string.h> using namespace std; const int maxn = 10010; //顶点数 const int maxq = 100; //最多查询次数,根据题目而定,本题中其实每组数据只有一个查询. //并查集 int f[maxn];//根节点 int find(int x) { if (f[x] == -1) { return x; } return f[x] = find(f[x]); } void unite(int u, int v) { int x = find(u); int y = find(v); if (x != y) { f[x] = y; } } //并查集结束 bool vis[maxn];//节点是否访问 int ancestor[maxn];//节点i的祖先 struct Edge { int to, next; } edge[maxn * 2]; int head[maxn], tot; void addedge(int u, int v) //邻接表头插法加边 { edge[tot].to = v; edge[tot].next = head[u]; head[u] = tot++; } struct Query { int q, next; int index;//查询编号,也就是输入的顺序 } query[maxq * 2]; int ans[maxn * 2]; //存储每次查询的结果,下表0~Q-1,其实应该开maxq大小的。 int h[maxn], tt; int Q;//题目中需要查询的次数 void addquery(int u, int v, int index) //邻接表头插法加询问 { query[tt].q = v; query[tt].next = h[u]; query[tt].index = index; h[u] = tt++; query[tt].q = u; //相当于两次查询,比如查询 3,5 和5,3结果是一样的,以3为头节点的邻接表中有5,以5为头节点的邻接表中有3 query[tt].next = h[v]; query[tt].index = index; h[v] = tt++; } void init() { tot = 0; memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); tt = 0; memset(h, -1, sizeof(h)); memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); memset(f, -1, sizeof(f)); memset(ancestor, 0, sizeof(ancestor)); } void LCA(int u) { ancestor[u] = u; vis[u] = true; for (int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next) //和顶点u相关的顶点 { int v = edge[i].to; if (vis[v]) { continue; } LCA(v); unite(u, v); ancestor[find(u)] = u; //将u的左右孩子的祖先设为u } for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = query[i].next) //看输入的查询里面有没有和u节点相关的 { int v = query[i].q; if (vis[v]) { ans[query[i].index] = ancestor[find(v)]; } } } bool flag[maxn];//用来确定根节点的 int t; int n, u, v; int main() { scanf("%d", &t); while (t--) { scanf("%d", &n); init(); memset(flag, 0, sizeof(flag)); for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &u, &v); flag[v] = true; //有入度 addedge(u, v); addedge(v, u); } Q = 1; //题目中只有一组查询 for (int i = 0; i < Q; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &u, &v); addquery(u, v, i); } int root; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (!flag[i]) { root = i; break; } } LCA(root); for (int i = 0; i < Q; i++) { printf("%d\n", ans[i]); } } return 0; }























 659
659

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








