Android学习系列之(三)Activity的使用
目前各大安卓市场上都拥有着许许多多的app,其界面丰富多彩,简单美观。那么这些漂亮的界面是怎么完成的呢?那就得学习学习Android四大组件之一的Activity了。
一、Activity的简单介绍:
- Activity是Android组件中最基本、最常见用的四大组件(Activity、Service服务、Content Provider内容提供者、BroadcastReceiver广播接收器)之一,是一个负责与用户交互的组件。
- 在一个App中,一个Activity通常就是一个单独的屏幕,它上面可以显示一些控件也可以监听并处理用户的事件做出响应。
- Activity之间通过Intent进行通信。
二、Activity的使用案例:需求说明:模拟用户登录
1. 新建一个Android项目: LoginDemo
2.
编辑res-->layout-->activity_main.xml 布局文件:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.johnnie.login.MainActivity" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_username"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:singleLine="true"
android:hint="@string/et_username"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_userpass"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:singleLine="true"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:hint="@string/et_userpass"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_login"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/btn_login"
/>
</LinearLayout>
3. 编辑 res-->values-->strings.xml 文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="app_name">LoginDemo</string>
<string name="hello_world">Hello world!</string>
<string name="action_settings">Settings</string>
<string name="et_username">用户名:</string>
<string name="et_userpass">密码:</string>
<string name="btn_login">登录</string>
</resources>

5. 编辑 MainActiviy.java 文件:
package com.johnnie.login;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
/**
* 模拟登录
* @author johnnie
*
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
// 控件的声明
private EditText et_username;
private EditText et_userpass;
private Button btn_login;
/**
* Activity 生命周期的方法之一:当 Activity 被创建时调用
*/
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); // 加载布局文件
System.out.println("onCreate...");
initViews();
initEvents();
}
/**
* 初始化控件
*/
private void initViews() {
et_username = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_username);
et_userpass = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_userpass);
btn_login = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_login);
}
/**
* 监听事件
*/
private void initEvents() {
btn_login.setOnClickListener(this); // 按钮的点击事件
}
/**
* 控件被点击时:实现 android.view.View.OnClickListener 时,必须实现的方法
*/
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_login:
login();
break;
}
}
/**
* 用户登录
*/
private void login() {
// 获取用户输入
String username = et_username.getText().toString().trim();
String userpass = et_userpass.getText().toString().trim();
// 输入校验
String msg = "登录失败!";
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(userpass) && !TextUtils.isEmpty(username)) {
msg = "登录成功!";
}
// 弹出提示
Toast.makeText(this, msg, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
/**
* 当 Activity 变成用户可见时调用
*/
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
System.out.println("onStart...");
}
/**
* 当界面获取焦点时调用
*/
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
System.out.println("onResume...");
}
/**
* 界面失去焦点时调用
*/
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
System.out.println("onPause...");
}
/**
* 界面不可见时调用
*/
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
System.out.println("onStop...");
}
/**
* Activity被销毁时调用
*/
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
System.out.println("onDestroy...");
}
}
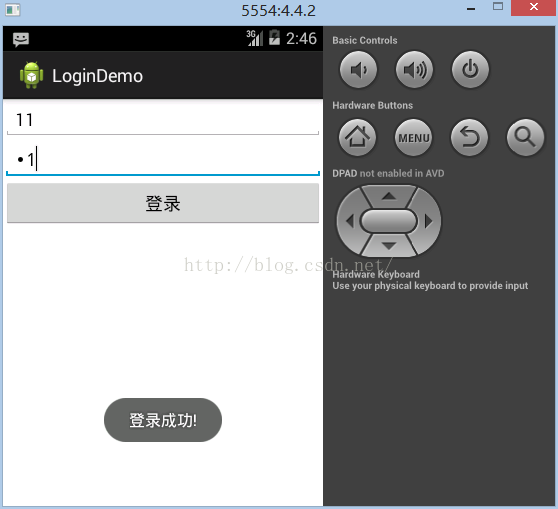
根据测试,可以看到我们的需求完成了
三、Activity 的生命周期:
当我们运行程序时,可以从LogCat中看到如下输出:onCreate、onStart、onResume、 onPause-、 onStop、 onDestory,从而可以知道 MainActivity 中函数的调用情况,也从而得知 Activity 的生命周期的情况。
总结如下:
Activity 的生命周期:
1)完整生命周期:onCreate---> onStart---> onResume---> onPause---> onStop---> onDestory
2)可视生命周期:onStart---> onResume---> onPause---> onStop
3)前台生命周期:onResume---> onPause
1)完整生命周期:onCreate---> onStart---> onResume---> onPause---> onStop---> onDestory
2)可视生命周期:onStart---> onResume---> onPause---> onStop
3)前台生命周期:onResume---> onPause
至此,Activity 的基本使用,大概都清楚了。其他知识,留待下回分解!

























 1025
1025

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








