文章目录
面向对象三大特性:封装、继承、多态
STL:standard Template Library(标准模板库)
分类:
广义:容器、算法、迭代器
容器和算法之间通过迭代器进行无缝连接
STL几乎所有代码都采用了类模板或者函数模板
细分:
六大类
- 容器:各种数据结构,vector、list、deque、set、map等
- 算法:各种常用的算法,如sort、find、copy、fpr_each
- 迭代器:扮演了容器与算法之间的胶合剂
- 仿函数:行为类似函数,可以作为算法的某种策略
- 适配器:一种用来修饰容器或者仿函数或迭代器接口的东西
- 空间配置器:负责空间 的配置与管理
STL中容器、算法、迭代器
容器:放东西的地方
STL容器就是将运用最广泛的一些数据结构实现出来
常用的数据结构:数组、链表、树、栈、队列、集合、映射表等
分类:
序列式容器:强调值的排序,序列式容器中的每个元素均有固定的位置
关联式容器:二叉树结构。各元素之间没有严格的物理上的顺序关系
算法:问题的解决方法
有限的步骤、解决逻辑或数学上的问题
质变算法:运算过程中会更改区间内的元素的内容、例如copy、instead、delete等
非质变算法:运算过程中不会更改区间内的元素内容,例如,查找、技术、遍历、寻找极值等
迭代器:容器和算法之间的粘合剂
提供一种方法,是指能够依序寻访某个容器所含的各个元素,而又无序暴露该容器的内部表示方式
每个容器都有自己专属的迭代器
迭代器使用非常类似于指针
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5OYoeTw4-1673535814364)(https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/secure.notion-static.com/34fbf0a3-70d0-4162-986f-bd2286f1cf7e/Untitled.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5b20108286ab492a8082051e2a637814.png)
vector
使用时需要包含头文件
#include<vector>
向容器中插入数据
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
}
通过迭代器访问容器中的数据
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print(int a)
{
cout << a << endl;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
//第一种遍历方式
//vector<int>::iterator v_begin = v.begin();
//vector<int>::iterator v_end = v.end();
//while (v_begin != v_end)
//{
// cout << *v_begin++ << endl;
//}
//第二种遍历方式
// for (vector<int>::iterator arr = v.begin();arr!=v.end();arr++)
// {
// cout << *arr << endl;
// }
//第三种遍历方式 直接使用STL提供的算法,需要添加头文件#include<algorithm>
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(),print);
}
自定义数据类型的使用(添加到vector容器)
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age,double height)
{
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
this->height = height;
}
string name;
int age;
double height;
};
int main()
{
vector<Person> v;
Person p3("小陈", 18, 1.83);
Person p4("小李", 18,1.78);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
for (vector<Person>::iterator a = v.begin(); a != v.end(); a++)
{
cout << "姓名:"<<(*a).name <<' ' << "年龄:" << (*a).age<<"身高:" <<(*a).height<< endl;
}
}
指针类型的使用方法
vector<Person*>v;
Person p1("小王", 20, 1.80);
Person p2("小孙", 20, 1.80);
Person p3("小陈", 20, 1.83);
Person p4("小李", 20, 1.83);
Person p5("小贾", 20, 1.83);
v.push_back(&p1);
v.push_back(&p2);
v.push_back(&p3);
v.push_back(&p4);
v.push_back(&p5);
for (vector<Person*>::iterator a = v.begin(); a != v.end(); a++)
{
cout << "姓名:"<<(*a)->name << ' ' << "年龄:" << (*a)->age << "身高:" << (*a)->height << endl;
}
/***************************************************************/
//另一种
vector<Person*>v;
Person *p1 = new Person("小王", 20, 1.80);
Person *p2 = new Person("小孙", 20, 1.80);
Person *p3 = new Person("小陈", 20, 1.83);
Person *p4 = new Person("小李", 20, 1.83);
Person *p5 = new Person("小贾", 20, 1.83);
v.push_back( p1);
v.push_back( p2);
v.push_back( p3);
v.push_back( p4);
v.push_back( p5);
for (vector<Person*>::iterator a = v.begin(); a != v.end(); a++)
{
cout << "姓名:"<<(*a)->name << ' ' << "年龄:" << (*a)->age << "身高:" << (*a)->height << endl;
}
容器嵌套容器
//容器中嵌套容器
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void test()
{
//创建大容器对象
vector<vector<int>>v;
//创建小容器对象
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
vector<int>v3;
vector<int>v4;
//添加小容器数据
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i + 1);
v2.push_back(i + 2);
v3.push_back(i + 3);
v4.push_back(i + 4);
}
//小容器添加到大容器
v.push_back(v1);
v.push_back(v2);
v.push_back(v3);
v.push_back(v4);
//输出数据
for (vector<vector<int>>::iterator a = v.begin(); a != v.end(); a++)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator b = a->begin(); b != a->end(); b++)
{
cout << *b << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test();
}
string
string基本概念
本质:string本质上是一个类
string和char*的区别
- char*是一个指针
- string是一个类,类内封装了char*,管理这个字符串,是一个char*型的容器
特点
string类内部封装了很多成员方法
例如:查找find,copy,delete,replace,insert
string 构造函数
注意:使用字符串时要添加头文件
#include<string>
void test01()
{
string s1; //默认无参构造
string s2("abc"); //创建对象时初始化字符串
string s3(s2); //创建字符串时用另一个字符串初始化新的字符串
string s4(5,'c'); //用5个c初始化字符串s4;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s4 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
}
string 的赋值操作
- 直接使用“ = ”赋值
- 使用”assign”赋值
//赋值操作
void test02()
{
//1.直接赋值
string s1;
s1 = "hello world!";
cout << s1 << endl;
//2.传入一个对象
string s2;
s2 = s1;
cout << s2 << endl;
//3.赋值单个字符
string s3;
s3 = 'a';
cout << s3 << endl;
//4.使用assign直接赋值
string s4;
s4.assign("hello C (^_^) ");
cout << s4 << endl;
//5.使用assign传入一个对象
string s5;
s5.assign(s4);
cout << s5 << endl;
//6.获取另一个字符串的前n个字符
string s6;
s6.assign("hello C++", 5);
cout << s6 << endl;
//7.给一个字符串赋值为n个为某某某的字符
string s7;
s7.assign(10, 'H');
cout << s7 << endl;
}
int main()
{
//test01();
test02();
}
字符串拼接
- 一种是直接使用“+=”拼接
- 一种是使用“append”拼接
//字符串拼接
void test03()
{
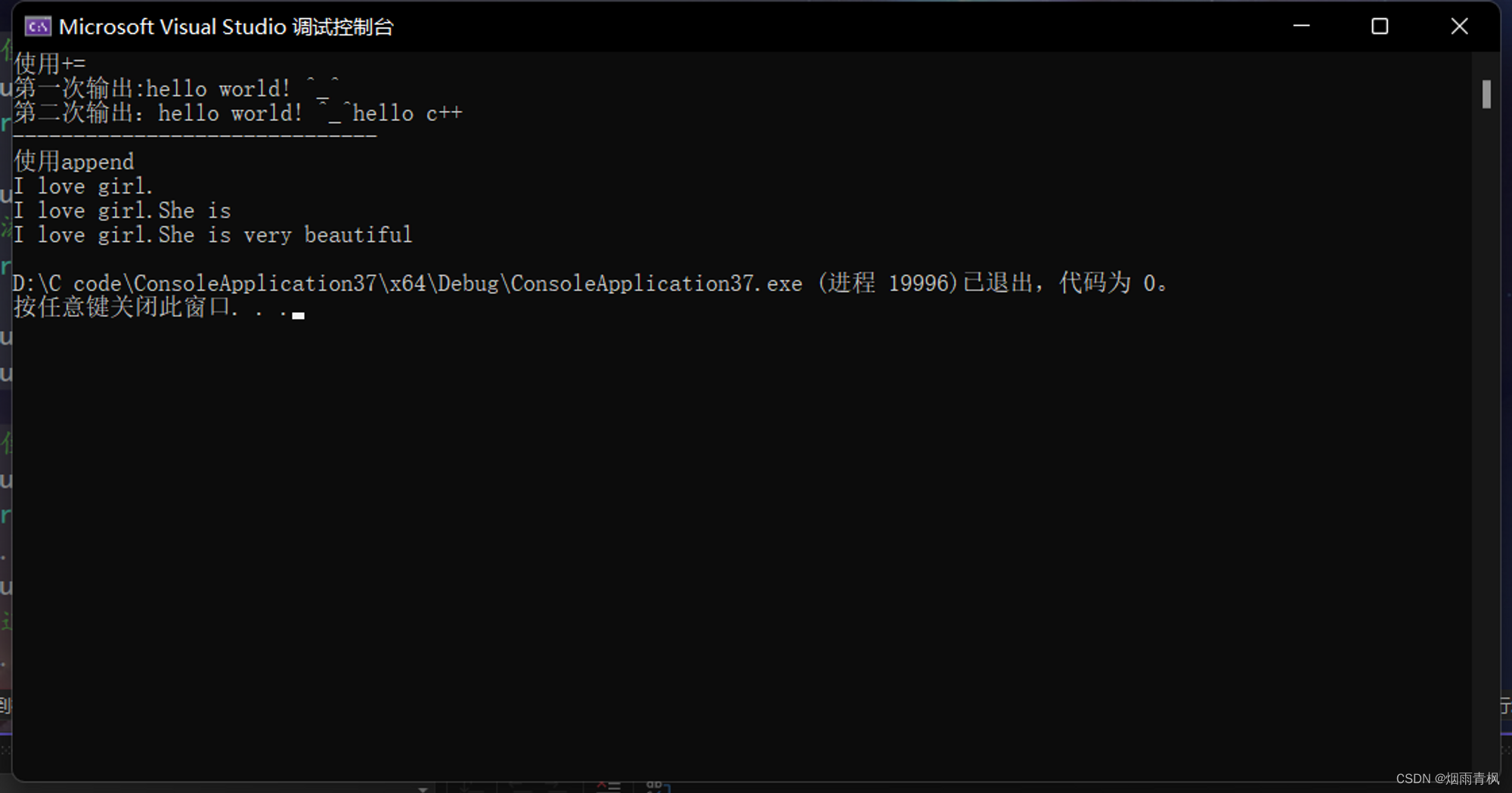
//使用+=
cout << "使用+=" << endl;
string s1 = "hello";
s1 += " world! ^_^";
cout <<"第一次输出:" << s1 << endl;
//添加一个字符串对象
string s2 = "hello c++";
s1 += s2;
cout << "第二次输出:" << s1 << endl;
cout << "------------------------------" << endl;
//使用append
cout << "使用append" << endl;
string s3 = "I ";
s3.append("love girl.");
cout << s3 << endl;;
//追加某个字符串的前n个字符
s3.append("She is very beautiful!", 6);
cout << s3 << endl;
//从某个字符串的某个位置起截取多少个
string s4 = "She is very beautiful!";
s3.append(s4, 6, 15);
cout << s3 << endl;
}
int main()
{
//test01();
test03();
}
```
![\[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-6kdvds9P-1673535764844)(https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/secure.notion-static.com/ce569155-a8e5-407a-bcd5-cdfd6a6d04b8/Untitled.png)\]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6aada0547f0a43cb903d1292bd0340c4.png)
### string 的查找和替换
- 查找 find rfind
- find 从左往右查找
- rfind从右往左找
- 替换 replace
```cpp
//字符串的查找和替换
void test04()
{
//查找
cout << "查找" << endl;
string str1 = "abcdefghijklmndefgdwd";
int pos = str1.find("d");
cout <<"字符d第一次出现的位置(find):" << pos << endl;
pos = str1.rfind("d");
cout << "字符串d最后一次出现的位置(rfind):" << pos << endl;
pos = str1.find('z'); //如果找不到返回-1
cout << "未找到字符的情况:" << pos << endl;
cout << "----------------------------" << endl << "替换 " << endl;
//替换操作
string str2 = "abcdefg";
str2.replace(2, 3, "hello"); //从2号位置起,3个字符替换为"hello"
cout << str2 << endl;
}
int main()
{
//test01();
//test03();
test04();
}
字符串比较
方法:compare
如果返回值 = 0,说明两个字符串相等
如果返回值 < 0,说明前者字符串小于后者字符串
如果返回值 > 0,说明前者字符串大于后者字符串
//字符串比较
void test05()
{
string str1 = "hello";
string str2 = "aello";
int pos = str1.compare(str2);
if (pos == 0)
{
cout << "str1 = str2" << endl;
}
if (pos < 0)
{
cout << "str1 < str2" << endl;
}
if (pos > 0)
{
cout << "str1 > str2" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
//test01();
//test03();
//test04();
test05();
}
字符存取
- 使用[]
- 使用at
//字符存取
void test06()
{
//读取
string str = "hello world";
cout << "使用[]读取:" << str[0] << endl;
cout << "使用at读取:" << str.at(1) << endl;
//修改
str[0] = 'x';
str.at(1) = 'Y';
cout << "使用[]修改:" << str[0] << endl;
cout << "使用at修改:" << str.at(1) << endl;
}
int main()
{
//test01();
//test03();
//test04();
//test05();
test06();
}
字符串的插入和删除
- insert插入
- erase删除
//字符串的插入和删除
void test07()
{
//insert
string str = "hello";
str.insert(1, "TTT"); //从下标为1处开始插入字符串"TTT"
cout << "insert: " << str << endl;
//erase
str.erase(1, 3);
cout << "erase: " << str << endl;
}
int main()
{
//test01();
//test03();
//test04();
//test05();
//test06();
test07();
}
子串获取
- substr()
void test08()
{
string str = "abcdefg";
cout << str.substr(2, 3);//从下标为1处开始获取长度为3的子串
}
int main()
{
//test01();
//test03();
//test04();
//test05();
//test06();
//test07();
test08();
}























 745
745











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










