Who's in the Middle
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 14785 Accepted Submission(s): 6644
Given an odd number of cows N (1 <= N < 10,000) and their milk output (1..1,000,000), find the median amount of milk given such that at least half the cows give the same amount of milk or more and at least half give the same or less.
* Lines 2..N+1: Each line contains a single integer that is the milk output of one cow.
5 2 4 1 3 5
3HintINPUT DETAILS: Five cows with milk outputs of 1..5 OUTPUT DETAILS: 1 and 2 are below 3; 4 and 5 are above 3.
点击打开题目链接
题意:输出n(n为奇数)个数中的中位数
大三即将结束,就要去面试找工作,将排序算法总结下。
参考《C++数据结构与算法》(第4版)[美] Adam Drozdek 著 徐丹 吴伟敏 译
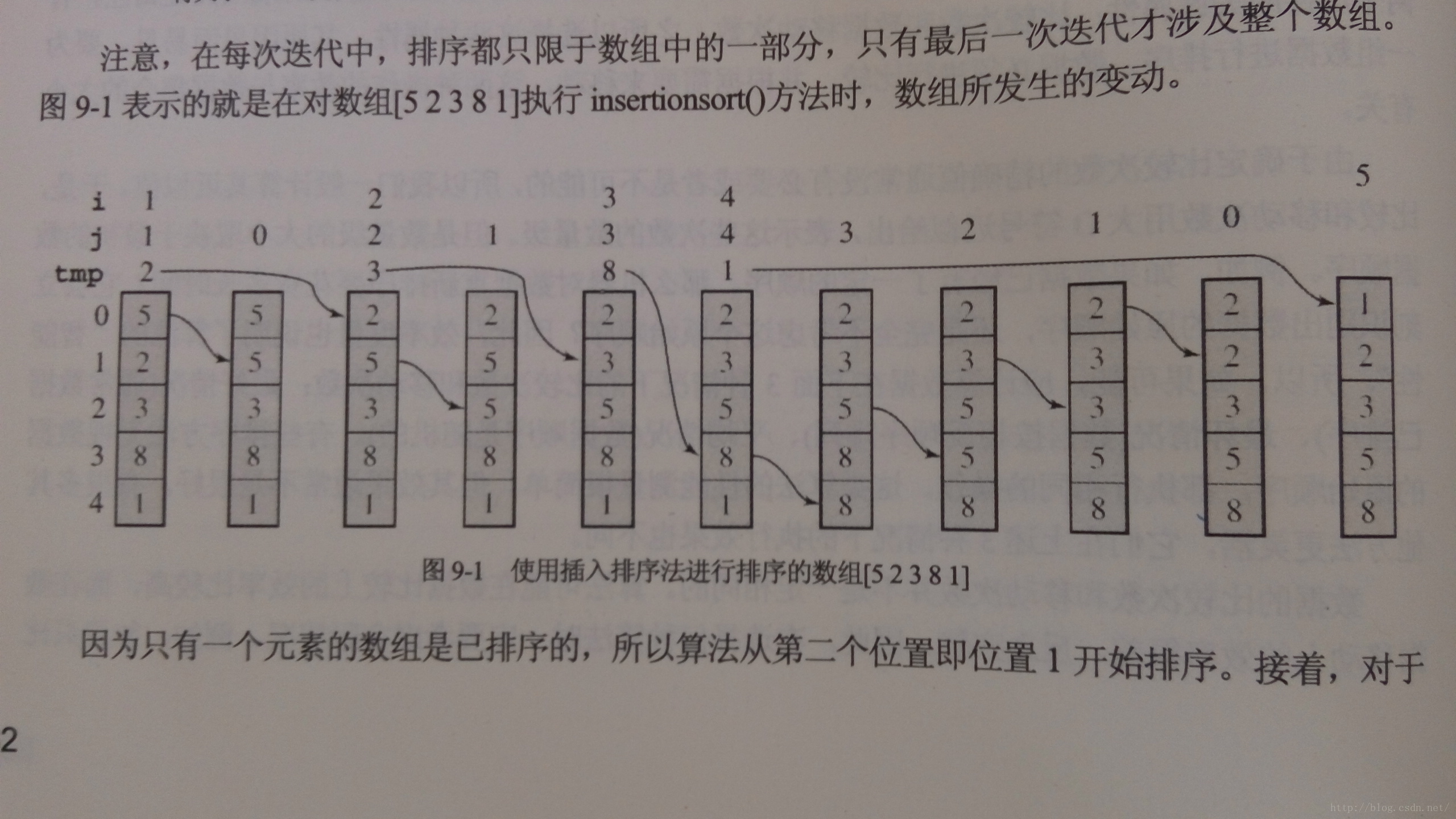
一:插入排序
首先考虑数组data中的前两个元素,即data[0]和data[1]。如果它们的次序颠倒了,就交换它们。
然后考虑第三个元素data[2],将其插入到合适的位置上。如果data[2]同时小于data[0]和data[1],那么data[0]和data[1]
都要移动一个位置;data[0]放在位置1上,data[1]放在位置2上,而data[2]放在位置0上。每个元素data[i]都要
插入到合适的位置j上,使0<=j<=i,所有比data[i]大的元素都要移动一个位置。
概要如下:
insertionsort(data[], int n)
for i = 1到 n - 1
将大于data[i]的所有元素data[j]都移动一个位置,将data[i]放到合适的位置上
实现代码:
template<class T>
void insertionsort(T data[], int n)
{
for (int i = 1, j; i < n; i++)
{
T tmp = data[i];
for (j = i; j > 0 && tmp < data[j - 1]; j--)
data[j] = data[j - 1];
data[j] = tmp;
}
}代码:
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e4 + 10;
//函数模板
template<class T>
void insertionsort(T data[], int n)
{
for (int i = 1, j; i < n; i++)//将data[i]插入到data[0]...data[i-1]这组数中的合适位置(此时data[i]...data[i-1]已经有序)
{
T tmp = data[i];
for (j = i; j > 0 && tmp < data[j - 1]; j--)//找到data[i]插入的位置,将比data[i]大的数后移
data[j] = data[j - 1];
data[j] = tmp;//将data[i]插入到j位置上
}
}
int main()
{
int n ;
int data[maxn];
while(cin >> n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> data[i];
insertionsort(data, n);
cout << data[n / 2] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
二:选择排序
选择排序就是先找到位置不合适的元素,再把它放在其最终的合适的位置上,很明确地直接交换数组元素。
基本思路:先找出数组中最小的元素,将其与第一个位置上的元素进行交换。然后在剩余元素data[1]...data[n-1]中找到
最小的元素,把它放到第二个位置上,,,直到最终数组有序。
selectionsort(data[], n)
for i = 0 到 n - 2
找出元素data[i]...data[n-1]中的最小的元素;
将其与data[i]交换
代码:
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e4 + 10;
//函数模板
template<class T>
void selectionsort(T data[], int n)
{
int j, least;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for (j = i + 1, least = i; j < n; j++) //从data[i]...data[n-1]中找到最小的数
if (data[j] < data[least])
least = j;
if (i != least) //避免冗余交换
swap(data[i], data[least]); //将找到的最小的数与data[i]交换
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
int data[maxn];
while(cin >> n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> data[i];
selectionsort(data, n);
cout << data[n / 2] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
三:冒泡排序
这个应该是最基本的排序了,每次比较两个相邻的数,如果逆序,则互换。
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e4 + 10;
//函数模板
template<class T>
void bubblesort(T data[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = n - 1; j > i; j--)
if (data[j] > data[j - 1])
swap(data[j], data[j - 1]);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
int data[maxn];
while(cin >> n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> data[i];
bubblesort(data, n);
cout << data[n / 2] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
梳、希尔、堆、快速、归并、基数、计数排序学习中。。。






















 236
236

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








