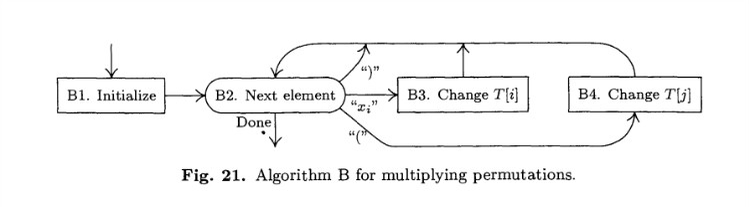
Algorithm B
Algorithm B (Multiply permutations in cycle form). This algorithm accom-
plishes essentially the same result as Algorithm A. Assume that the elements per-
muted are named X1,X2, … ,Xn. We use an auxiliary table T[1],T[2],…,T[n];
upon termination of this algorithm, Xi goes to Xj under the input permutation
if and only if T[i] = j.
B1. [Initialize.] Set T[k] <– k for 1 <= k <= n. Also, prepare to scan the input
from right to left.
B2. [Next element.] Examine the next element of the input (right to left). If
the input has been exhausted, the algorithm terminates. If the element is a
“)”, set Z <– 0 and repeat step B2; if it is a “(“, go to B4. Otherwise the
element is xi for some i; go on to B3.
B3. [Change T[i].] Exchange Z <–> T[i]. If this makes T[i] = 0, set j <– i. Return
to step B2.
B4. [Change T[j].] Set T[j] <– Z. (At this point, j is the row that shows a “)”
entry in the notation of Table 2, corresponding to the right parenthesis that
matches the left parenthesis just scanned.) Return to step B2. |
Flow diagram
Data table
Java program
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: 1O1O
* Date: 12/18/13
* Time: 6:52 PM
* :)~
* Multiply permutations in cycle form-2:ALGORITHMS
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String input;
System.out.println("Please input the permutations:");
input = br.readLine();
char max = input.charAt(1);
for(int i=2; i<input.length(); i++){
if(input.charAt(i) > max){
max = input.charAt(i);
}
}
/*We know the value of n here*/
int n=(int)max-96;
int[] T = new int[n+1];
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){ /*B1*/
T[i]=i;
}
int Z=0;
int j=0;
/*Kernel of the Algorithm*/
for(int i=input.length()-1; i>=0; i--){ /*B2*/
if(input.charAt(i) == ')'){
Z=0;
}else if(input.charAt(i) == '('){
T[j] = Z; /*B4*/
}else {
int temp = Z; /*B3*/
Z = T[(int)input.charAt(i)-96];
T[(int)input.charAt(i)-96] = temp;
if(T[(int)input.charAt(i)-96] == 0){
j=(int)input.charAt(i)-96;
}
}
}
/*Print values of T[i], 1<=i<=n*/
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Print values of T[i] (1<=i<=n):");
for(int k=1; k<=n; k++){
System.out.println("T["+k+"]="+T[k]);
}
/*Print the final results*/
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The final results is:");
int[] tag = new int[n+1];
for(int k=1; k<=n; k++){
if(tag[k] == 0){
System.out.print('(');
System.out.print((char)(k+96));
tag[k] = 1;
int index=k;
while (T[index] != k){
index = T[index];
System.out.print((char)(index+96));
tag[index] = 1;
}
System.out.print(')');
}
}
}
}Inputs & Outputs
Please input the permutations:
(acfg)(bcd)(aed)(fade)(bgfae)
Print values of T[i] (1<=i<=n):
T[1]=4
T[2]=3
T[3]=5
T[4]=7
T[5]=2
T[6]=6
T[7]=1
The final results is:
(adg)(bce)(f)
Reference
<< The Art of Computer Programming: Fundamental Algorithms >> VOLUME 1, DONALD E. KNUTH























 542
542

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








