Algorithm L
Algorithm L (List insertion). Records
R1,...,RN
are assumed to contain keys
K1,...,KN
, together with link fields
L1,...,LN
capable of holding the numbers
0
through
R0
at the beginning of the file. This algorithm sets the link fields so that the
records are linked together in ascending order. Thus, if
p(1)...p(N)
is the stable
permutation that makes
Kp(1)<=...<=Kp(N)
, this algorithm will yield
L0=p(1);Lp(i)=p(i+1)
, for
1<=i<N;Lp(N)=0
.
L1. [Loop on j.] Set
L0←N,LN←0
. (Link
L0
acts as the “head” of the list,
and
0
acts as a null link; hence the list is essentially circular.) Perform steps
L2 through L5 for
L2. [Set up
p,q,K
] Set
p←L0,q←0,K←Kj
. (In the following steps we
will insert
Rj
into its proper place in the linked list, by comparing
K
with
the previous keys in ascending order. The variables
to the current place in the list, with
L3. [Compare
K:Kp
] If
K<=Kp
, go to step L5. (We have found the desired
position for record
R
, between
L4. [Bump
p,q
] Set
q←p,p←Lq
. If
p>0
, go back to step
L3
. (If
p=0
,
K
is the largest key found so far; hence record
list, between
Rq
and
R0
.)
L5. [Insert into list.] Set
Lq←j,Lj←p
. |
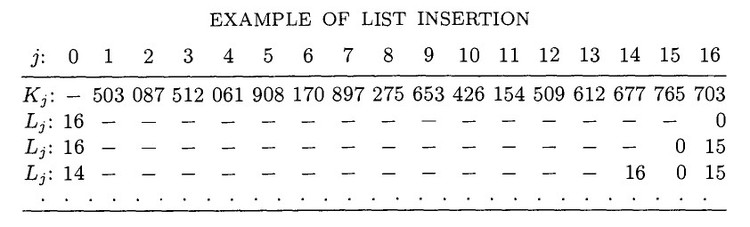
Data table
Java program
In this program, R1,…,RN were simplified to K1,…,KN.
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: 1O1O
* Date: 11/24/13
* Time: 10:01 PM
* :)~
* List insertion:Sorting by Insertion:Internal Sorting
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 16;
int[] K = new int[17];
int[] L = new int[17];
L[0] = N;
L[N] = 0;
/*Prepare the data*/
K[1] = 503;
K[2] = 87;
K[3] = 512;
K[4] = 61;
K[5] = 908;
K[6] = 170;
K[7] = 897;
K[8] = 275;
K[9] = 653;
K[10] = 426;
K[11] = 154;
K[12] = 509;
K[13] = 612;
K[14] = 677;
K[15] = 765;
K[16] = 703;
/*Output unsorted Ks*/
System.out.println("Unsorted Ks:");
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){
System.out.println(i+":"+K[i]);
}
System.out.println();
/*Kernel of the Algorithm!*/
for(int j=N-1; j>=1; j--){
int p = L[0];
int q = 0;
int Key = K[j];
while (p > 0){
if(Key <= K[p]){
break;
}else {
q = p;
p = L[q];
}
}
L[q] = j;
L[j] = p;
}
/*Output sorted Ks*/
System.out.println("Sorted Ks:");
int index = 0;
int pos = 0;
while (L[index] != 0){
pos++;
System.out.println(pos+":"+K[L[index]]);
index = L[index];
}
}
}Outputs
Unsorted Ks:
1:503
2:87
3:512
4:61
5:908
6:170
7:897
8:275
9:653
10:426
11:154
12:509
13:612
14:677
15:765
16:703
Sorted Ks:
1:61
2:87
3:154
4:170
5:275
6:426
7:503
8:509
9:512
10:612
11:653
12:677
13:703
14:765
15:897
16:908Reference
<< The art of computer programming: Sorting and Searching >> VOLUME 3, DONALD E. KNUTH























 5232
5232











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








