关于scrollWidth() clientWidth() offsetWidth() style.width() screen.height()
谷歌和火狐默认滚动条的宽度是 17px(Firefox Chrome IE 表现一致)
一、计算宽高
方法有:
①offsetWidth、offsetHeight
②clientWidth、clientHeight
③style.width、style.height
④scrollWidth、scrollHeight
⑤screen.height、 screen.width 、window.screen.availHeight、window.screen.availWidth
以计算宽度的方法来举例说明,计算高度的方法和计算宽度的方法同理:
offsetWidth,offsetHeight
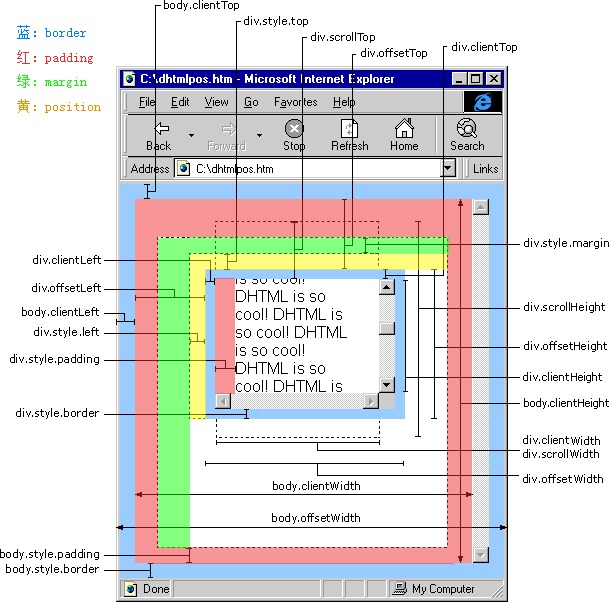
不受滚动条(宽度/高度)影响,但包含滚动条(宽度/高度)在内。没有margin外边距,但包含border边框,书面上叫做内容的实际宽度(各个浏览器表现一致)
offsetWidth=width + leftPadding + rightPadding + leftBorder + rightBorder
offsetHeight同理
clientWidth,clientHeight
宽高都受滚动条影响,没有margin外边距和border 书面上叫做内容可视区的宽度
1、有滚动条时
clientWidth=width +leftPadding + rightPadding - 滚动条宽度
2、没有滚动条时
clientWidth=width +padding
clientHeight同理
scrollWidth
scrollWidth 的值不受竖向滚动条影响 (Firefox Chrome IE 表现一致)
1、scrollWidth的值包含竖向滚动条(如果存在)的宽度(在父盒子和子盒子两个盒子嵌套,且子盒子内容宽度大于父盒子,导致父盒子出现横向滚动条的情况下,子盒子的margRight的值是无效值)
scrollWidth=子盒子width+子盒子padding +子盒子border+子盒子marginLeft+父盒子paddingLeft
2、scrollHeight 的值不受竖向滚动条影响(Firefox Chrome IE 表现不一致)
scrollHeight的值包含横向滚动条(如果存在)的高度,在有竖向滚动条条,也有横向滚动条的情况下,在求scrollHeight的值时,竖向滚动条对其求值没有影响,不管竖向滚动条存不存在,其值都不会因它而变化
scrollHeight=子盒子height+子盒子paddingTop+子盒子paddingBottom +子盒子borderTop+子盒子borderBottom+子盒子marginTop+子盒子marginBottom+父盒子paddingTop+父盒子paddingBottom
当没有滚动条的时候scrollWidth==clientWidth;
**需要提一下:**CSS中的margin属性,与clientWidth,clientHeight,offsetWidth,offsetHeight,scrollWidth,scrollHeight,style.width,style.Height均无关
style.width
style.width=width +padding+border
screen.width
显示器的宽度也可以理解为显示器的分辨率
window.screen.availWidth
屏幕可用工作区宽度
注意:offsetWidth(offsetHeight)与style.width(style.height)的区别
1. style.height 返回的是字符串,如28px,offsetWidth返回的是数值28,如果需要对取得的值进
行计算,用offsetWidth比较方便;如果拿到offsetWidth设置style.left的值,需加’px’。
2. style.width/style.height与scrollWidth/scrollHeight是可读写的属性,clientWidth/clientHeight与offsetWidth/offsetHeight是只读属性
3. style.height的值需要事先定义,否则取到的值为空。而且必须要定义在html里,如果定义在css里,style.height的值仍然为空,但元素偏移有效;而offsetWidth则仍能取到。
4.与style.width属性的区别在于:如对象的宽度设定值为百分比宽度,则无论页面变大还是变小,style.width都返回此百分比,而offsetWidth则返回在不同页面中对象的宽度值而不是百分比值
例:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>所有列表索引</title>
<script src="http://libs.baidu.com/jquery/1.9.0/jquery.js"></script>
</head>
<style>
body{background: #13e0de;margin:150px 0 0 150px;}
#divs{background: yellow;width:500px;height:415px;position:relative;border:10px solid #ccc;margin:20px 200px;padding:17px 26px;overflow-x:scroll;}
#spans{display:inline-block;width:600px;padding:30px;margin:50px;border:5px solid #f00;background: #deac00;}
</style>
<body>
<input type="button" value="点我设置obj2的scrollLeft值" onclick="move()">
<div id="divs"><span id="spans">offsetWidth、clientWidth、width、scrollWidth区别offsetWidth、clientWidth、width、scrollWidth区别offsetWidth、clientWidth、width、scrollWidth区别offsetWidth、clientWidth、width、scrollWidth区别offsetWidth、clientWidth、width、scrollWidth区别</span></div>
</body>
<script>
var obj1 = document.getElementById("divs");
var obj2=document.getElementById("spans");
console.log('这里输出obj1')
console.log('offsetWidth:'+obj1.offsetWidth);
console.log('clientWidth:'+obj1.clientWidth);
console.log('scrollWidth:'+obj1.scrollWidth);
console.log('screen.width:'+screen.width);
console.log('这里输出obj2')
console.log('offsetTop:'+obj2.offsetTop);
console.log('clientTop:'+obj2.clientTop);
console.log('scrolTop:'+obj2.scrolTop);
console.log('screenLeft:'+screenLeft)
function move(){
a=eval(20);
obj1.scrollLeft+=a;
console.log('输出scrollLeft:'+obj1.scrollLeft);
}
</script>
</html>二、计算边距
方法有;
①offsetTop offsetLeft
②clientTop clientLeft
③scrollTop scrollLeft
④style.top style.left
⑤screenTop screenLeft
以计算左边距的方法来举例说明,计算上边距的方法和计算左边距的方法同理:
offsetTop
Firefox Chrome IE 表现均不一致
当前元素(不包含border和padding在内)到浏览器有效区域(可以显示网页内容的区域)的顶部的距离、
offsetLeft
Firefox Chrome IE 表现均不一致
当前元素(不包含border和padding在内)到浏览器有效区域(可以显示网页内容的区域)左边的距离
clientTop clientLeft
当前元素的borderTop的高度 borderLeft的宽度,也就是border边框的宽度或高度
scrollTop
由于scrollTop在各个浏览器的表现均不一致,所以scrollTop的值在各个浏览器的表现也不一致
scrollLeft
网页被卷去的长度
style.top style.left
定位元素与包含它的矩形左边界(或上边界)的偏移量
screenTop screenLeft
浏览器外边缘距显示屏可视区域的长度
三、计算坐标
方法有:
①offsetX
②clientX
③pageX
④screen.X
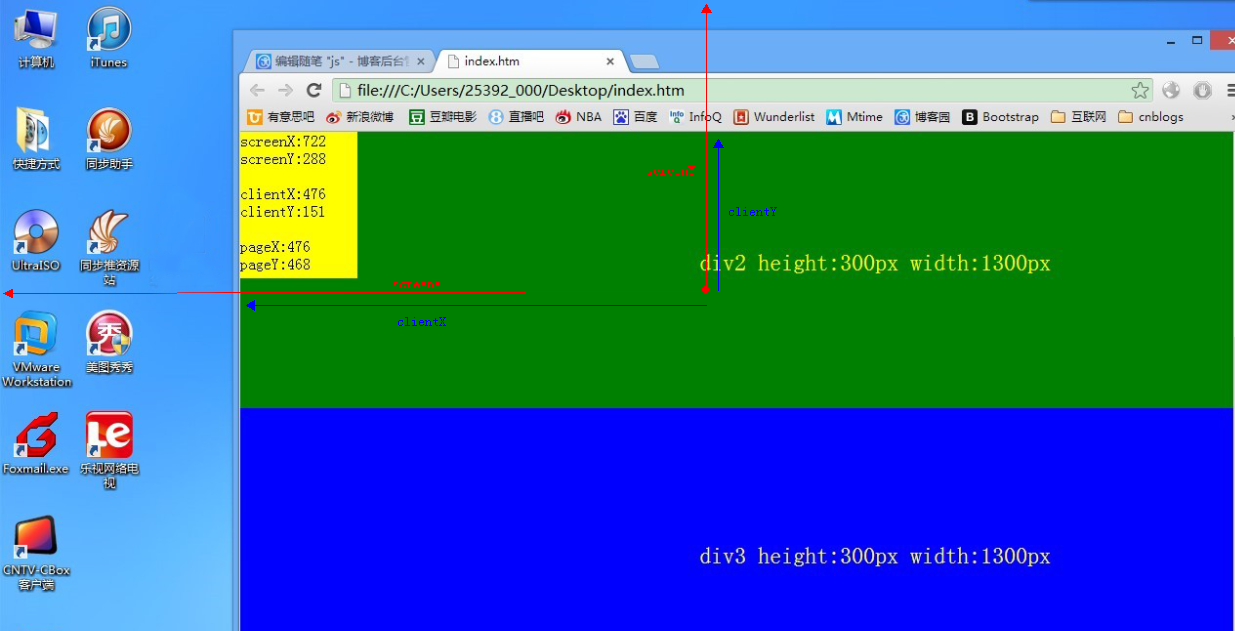
offsetX
只有IE事件有这2个属性,标准事件没有对应的属性。获取鼠标指针位置相对于触发事件的对象的 x 坐标,也就是说事件在哪个对象上被触发就以那个对象的左上角为原点获取坐标
clientX
不随页面滚动改变,始终是以当前可视区域左上角为原点
pageX
随着页面滚动改变 以文档的左上角为原点
screen.X
鼠标位置相对于用户屏幕水平偏移量,而screenY也就是垂直方向的,此时的参照点也就是原点 是屏幕的左上角creenX,screenY的最大值不会超过你的屏幕分辨率
例:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>无标题文档</title>
<style>
body{margin:0;padding:0;}
.div{width:1300px;height:300px;color:#ff0;text-align:center;font-size:24px;line-height:300px;}
#d1{background-color:red;}
#d2{background-color:green;}
#d3{background-color:#00f;}
#d4{position:absolute;top:0;width:120px;height:150px;background-color:#ff0;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="d1" class="div">div1 height:300px width:1300px</div>
<div id="d2" class="div">div2 height:300px width:1300px</div>
<div id="d3" class="div">div3 height:300px width:1300px</div>
<div id="d4"></div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function() {
window.onscroll = function() {
$("#d4").css("top", getScrollTop());
};
document.onmousemove = function(e) {
if (e == null) {
e = window.event;
}
var html = "screenX:" + e.screenX + "<br/>";
html += "screenY:" + e.screenY + "<br/><br/>";
html += "clientX:" + e.clientX + "<br/>";
html += "clientY:" + e.clientY + "<br/><br/>";
if (e.pageX == null) {
html += "pageX:" + e.x + "<br/>";
html += "pageY:" + e.y + "<br/>";
} else {
html += "pageX:" + e.pageX + "<br/>";
html += "pageY:" + e.pageY + "<br/>";
}
$("#d4").html(html);
};
});
function getScrollTop() {
var top = (document.documentElement && document.documentElement.scrollTop) || document.body.scrollTop;
return top;
}
</script>
</html>最后附上两张张详细的讲解图,如果以上所述实在不懂,配着图看。应该就不难理解了






















 394
394

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








