Solitaire
Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 65536/32768K (Java/Other)
Total Submission(s) : 10 Accepted Submission(s) : 5
Font: Times New Roman | Verdana | Georgia
Font Size: ← →
Problem Description
Solitaire is a game played on a chessboard 8x8. The rows and columns of the chessboard are numbered from 1 to 8, from the top to the bottom and from left to right respectively.
There are four identical pieces on the board. In one move it is allowed to:
> move a piece to an empty neighboring field (up, down, left or right),
> jump over one neighboring piece to an empty field (up, down, left or right).
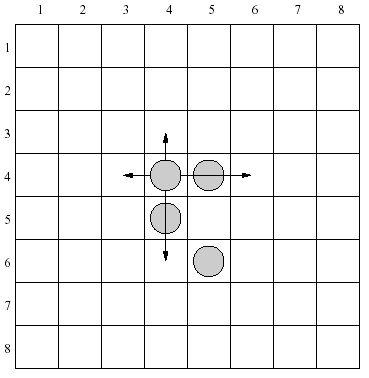
There are 4 moves allowed for each piece in the configuration shown above. As an example let's consider a piece placed in the row 4, column 4. It can be moved one row up, two rows down, one column left or two columns right.
Write a program that:
> reads two chessboard configurations from the standard input,
> verifies whether the second one is reachable from the first one in at most 8 moves,
> writes the result to the standard output.
There are four identical pieces on the board. In one move it is allowed to:
> move a piece to an empty neighboring field (up, down, left or right),
> jump over one neighboring piece to an empty field (up, down, left or right).

There are 4 moves allowed for each piece in the configuration shown above. As an example let's consider a piece placed in the row 4, column 4. It can be moved one row up, two rows down, one column left or two columns right.
Write a program that:
> reads two chessboard configurations from the standard input,
> verifies whether the second one is reachable from the first one in at most 8 moves,
> writes the result to the standard output.
Input
Each of two input lines contains 8 integers a1, a2, ..., a8 separated by single spaces and describes one configuration of pieces on the chessboard. Integers a2j-1 and a2j (1 <= j <= 4) describe the position of one piece - the row number and the column number respectively. Process to the end of file.
Output
The output should contain one word for each test case - YES if a configuration described in the second input line is reachable from the configuration described in the first input line in at most 8 moves, or one word NO otherwise.
Sample Input
4 4 4 5 5 4 6 5 2 4 3 3 3 6 4 6
Sample Output
YES
Source
Southwestern Europe 2002
——————————————————————————————————————————————
题意:
问在8步之内能否从前一个状态到后一个状态,棋子只能上下左右走或者如图中的方式走(跳过相邻的一个棋子)。
思路:开8维数组记录状态直接bfs
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
bool vir[8][8][8][8][8][8][8][8];
int ed[8][10];
int dir[4][2]= {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
struct node
{
int x[4],y[4],cnt;
};
bool check(node d)
{
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
if(d.x[i]<0||d.x[i]>=8||d.y[i]<0||d.y[i]>=8)
return 0;
}
if(vir[d.x[0]][d.y[0]][d.x[1]][d.y[1]][d.x[2]][d.y[2]][d.x[3]][d.y[3]])
{
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
int out(node d)
{
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
if(ed[d.x[i]][d.y[i]]==0)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
int pan(int x,int y,node b,int k)
{
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
if(i!=k&&x==b.x[i]&&y==b.y[i])
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void bfs(node a)
{
queue<node>q;
node f,d;
f=a;
vir[f.x[0]][f.y[0]][f.x[1]][f.y[1]][f.x[2]][f.y[2]][f.x[3]][f.y[3]]=1;
q.push(f);
while(!q.empty())
{
f=q.front();
q.pop();
if(f.cnt>=8)
{
printf("NO\n");
return;
}
if(out(f))
{
printf("YES\n");
return;
}
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<4; j++)
{
d=f;
d.x[i]=f.x[i]+dir[j][0];
d.y[i]=f.y[i]+dir[j][1];
if(!check(d))
continue;
if(!pan(d.x[i],d.y[i],f,i))
{
if(out(d))
{
printf("YES\n");
return;
}
vir[d.x[0]][d.y[0]][d.x[1]][d.y[1]][d.x[2]][d.y[2]][d.x[3]][d.y[3]]=1;
d.cnt=f.cnt+1;
q.push(d);
}
else
{
d.x[i]=d.x[i]+dir[j][0];
d.y[i]=d.y[i]+dir[j][1];
if(!check(d))
continue;
if(!pan(d.x[i],d.y[i],f,i))
{
if(out(d))
{
printf("YES\n");
return;
}
vir[d.x[0]][d.y[0]][d.x[1]][d.y[1]][d.x[2]][d.y[2]][d.x[3]][d.y[3]]=1;
d.cnt=f.cnt+1;
q.push(d);
}
}
}
}
}
printf("NO\n");
}
int main()
{
node a;
int o,di,dj;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&di,&dj))
{
a.x[0]=di-1;
a.y[0]=dj-1;
memset(ed,0,sizeof(ed));
for(int i=1; i<4; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&di,&dj);
a.x[i]=di-1;
a.y[i]=dj-1;
}
for(int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&di,&dj);
ed[di-1][dj-1]=1;
}
memset (vir,0,sizeof(vir));
a.cnt=0;
bfs(a);
}
return 0;
}
























 627
627

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








