文章目录
二叉树的层次遍历
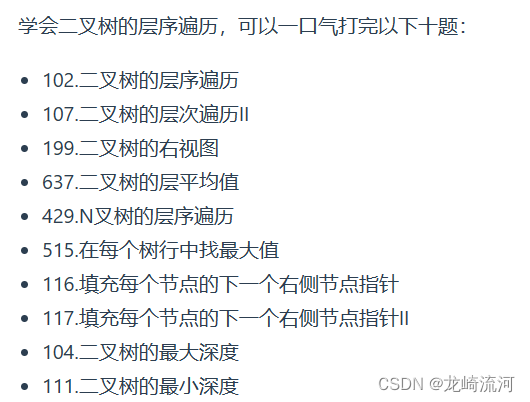
二叉树的层次遍历
bfs法:
关键点在于queue.size()
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
//关键
int len = queue.size();
while(len > 0){
TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
list1.add(temp.val);
if(temp.left != null) queue.add(temp.left);
if(temp.right != null) queue.add(temp.right);
len--;
}
list.add(list1);
}
return list;
}
}
dfs:
递归方式
此方法不太熟悉
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root,0);
return resList;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root,int k){
if(root == null) return;
//每层k的数字都是固定的
k++;
if(resList.size() < k){
List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<>();
resList.add(item);
}
resList.get(k - 1).add(root.val);
dfs(root.left,k);
dfs(root.right,k);
}
}
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
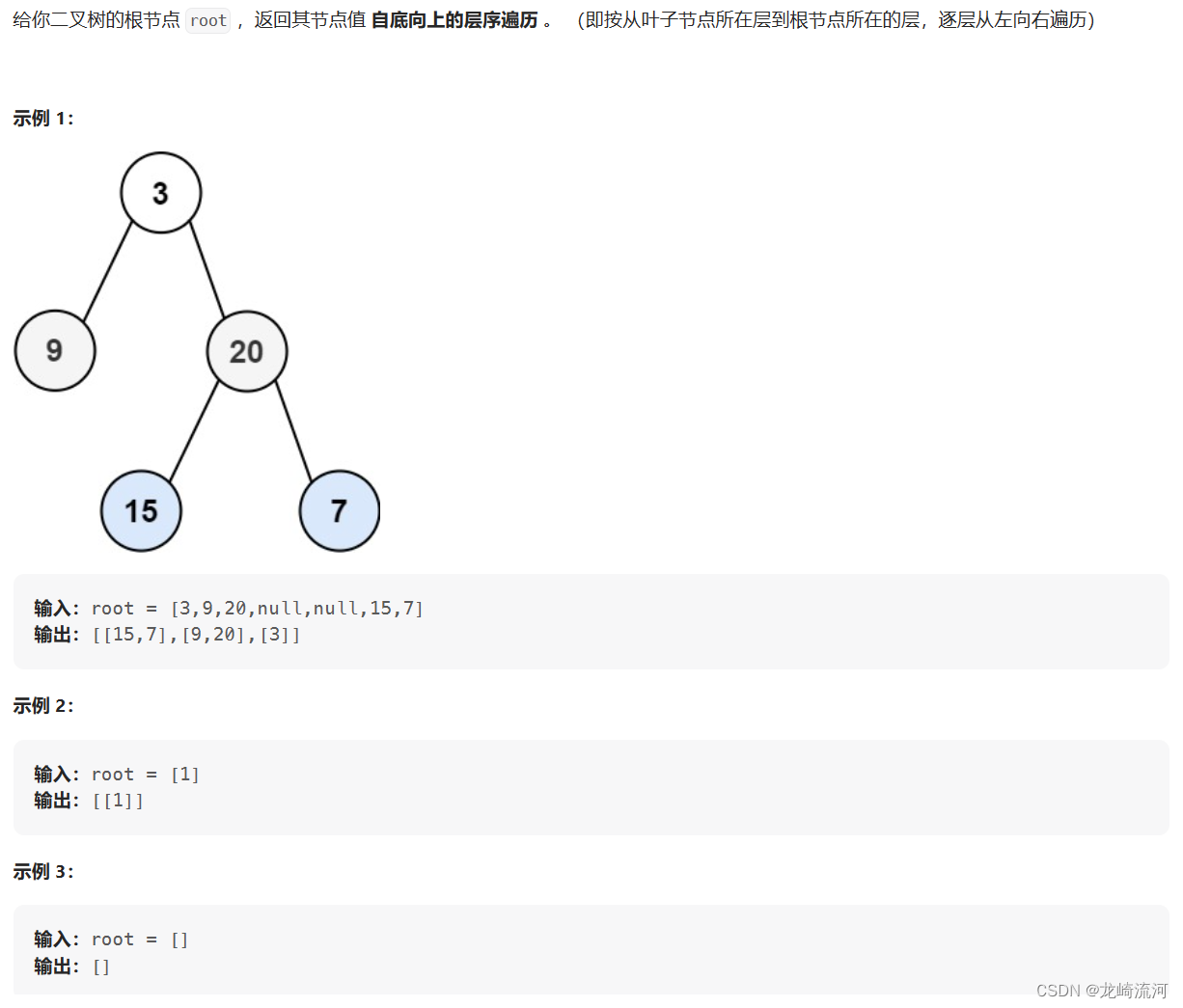
在上一题基础上反转结果即可Collections.reverse(),请记住这个方法。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
//关键
int len = queue.size();
while(len > 0){
TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
list1.add(temp.val);
if(temp.left != null) queue.add(temp.left);
if(temp.right != null) queue.add(temp.right);
len--;
}
list.add(list1);
}
Collections.reverse(list);
return list;
}
}
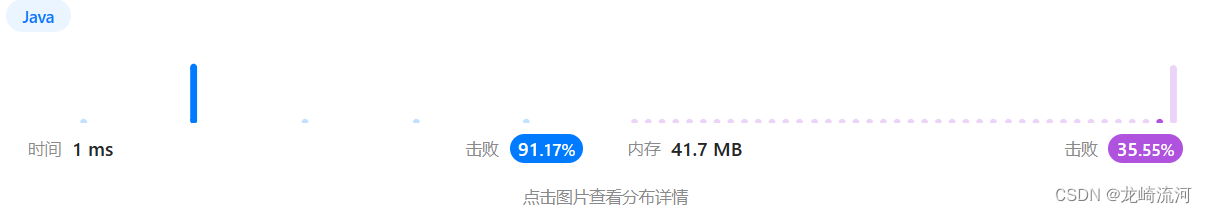
199. 二叉树的右视图
采用dfs思路
class Solution {
List<Integer> list;
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
f(root,0);
return list;
}
void f(TreeNode root,int depth){
if(root == null) return;
depth++;
if(list.size() < depth){
list.add(root.val);
}
f(root.right,depth);
f(root.left,depth);
}
}
bfs法:
// 199.二叉树的右视图
public class N0199 {
/**
* 解法:队列,迭代。
* 每次返回每层的最后一个字段即可。
*
* 小优化:每层右孩子先入队。代码略。
*/
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
if (root == null) {
return list;
}
que.offerLast(root);
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int levelSize = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
TreeNode poll = que.pollFirst();
if (poll.left != null) {
que.addLast(poll.left);
}
if (poll.right != null) {
que.addLast(poll.right);
}
if (i == levelSize - 1) {
list.add(poll.val);
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
637.二叉树的层平均值

class Solution {
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<Double> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
//关键
int len = queue.size();
int length = len;
double res = 0.0;
while(len > 0){
TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
res += temp.val;
if(temp.left != null) queue.add(temp.left);
if(temp.right != null) queue.add(temp.right);
len--;
}
res /= length;
list.add(res);
}
return list;
}
}
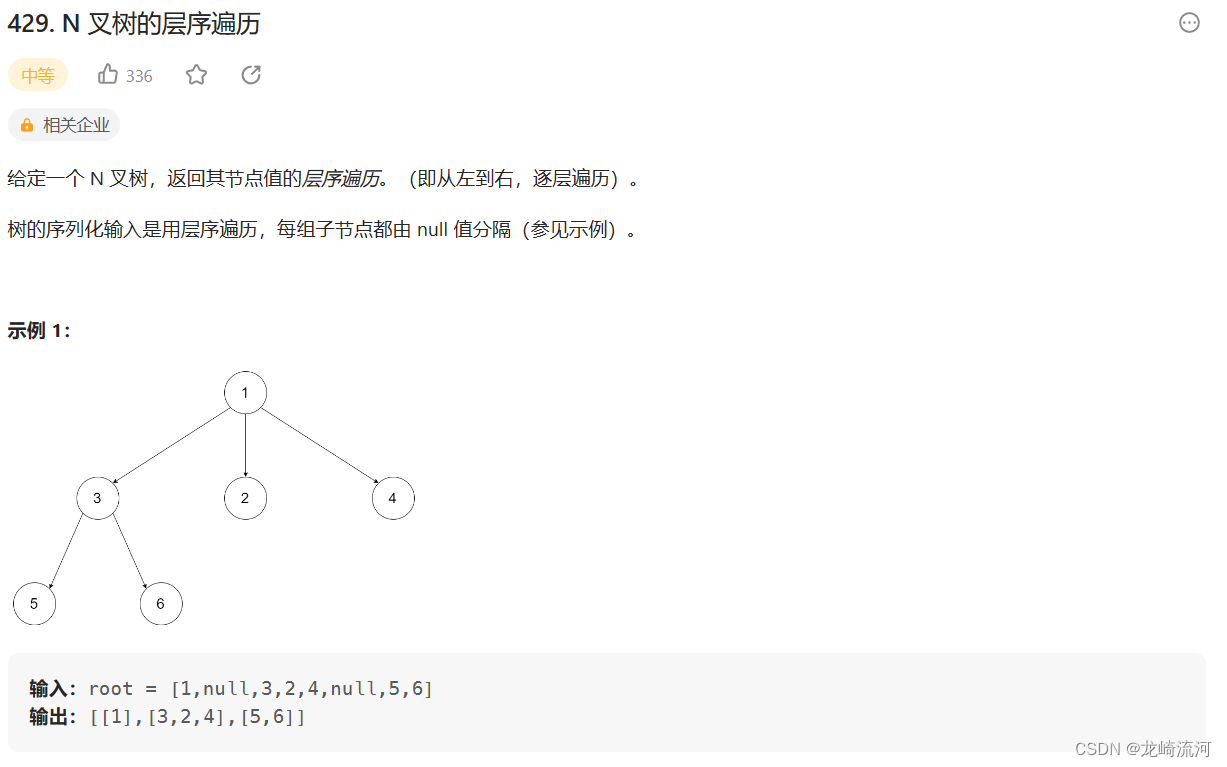
429. N 叉树的层序遍历
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
//关键
int len = queue.size();
while(len > 0){
Node temp = queue.poll();
list1.add(temp.val);
//关键点
List<Node> children = temp.children;
for (Node child : children) {
if (child != null) {
queue.offer(child);
}
}
len--;
}
list.add(list1);
}
return list;
}
}
515.在每个树行中找最大值

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> largestValues(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
//关键
int len = queue.size();
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
while(len > 0){
TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
res = Math.max(res,temp.val);
//关键点
if(temp.left != null) queue.offer(temp.left);
if(temp.right != null) queue.offer(temp.right);
len--;
}
list.add(res);
}
return list;
}
}
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
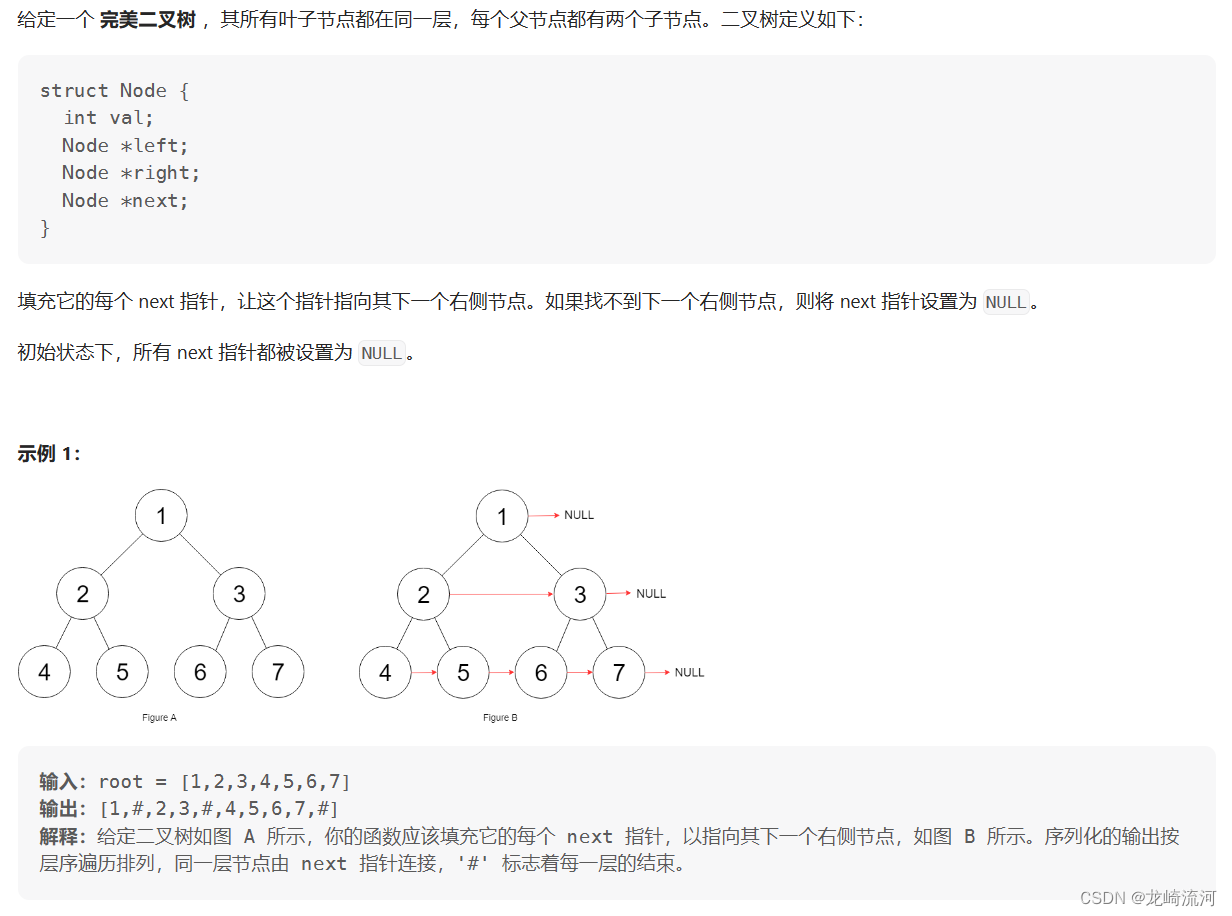
本题依然是层序遍历,只不过在单层遍历的时候记录一下本层的头部节点,然后在遍历的时候让前一个节点指向本节点就可以了
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) return null;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
//关键,遍历时提前拎出来头节点
int len = queue.size();
Node temp = queue.poll();
//关键点,先找到每行头节点
if(temp.left != null) queue.offer(temp.left);
if(temp.right != null) queue.offer(temp.right);
for(int index = 1;index < len;index++){
Node next = queue.poll();
if(next.left != null) queue.offer(next.left);
if(next.right != null) queue.offer(next.right);
temp.next = next;
temp = next;
}
}
return root;
}
填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II
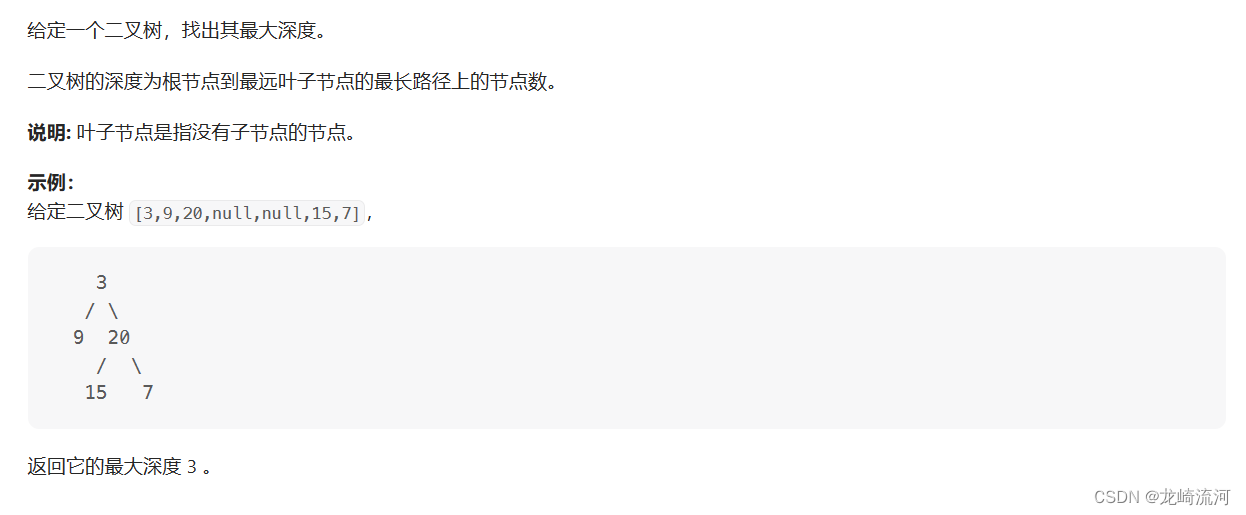
104.二叉树的最大深度
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int res = 0;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root,0);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root,int k){
if(root == null) return;
k++;
res = Math.max(k,res);
dfs(root.left,k);
dfs(root.right,k);
}
}
二叉树的最小深度
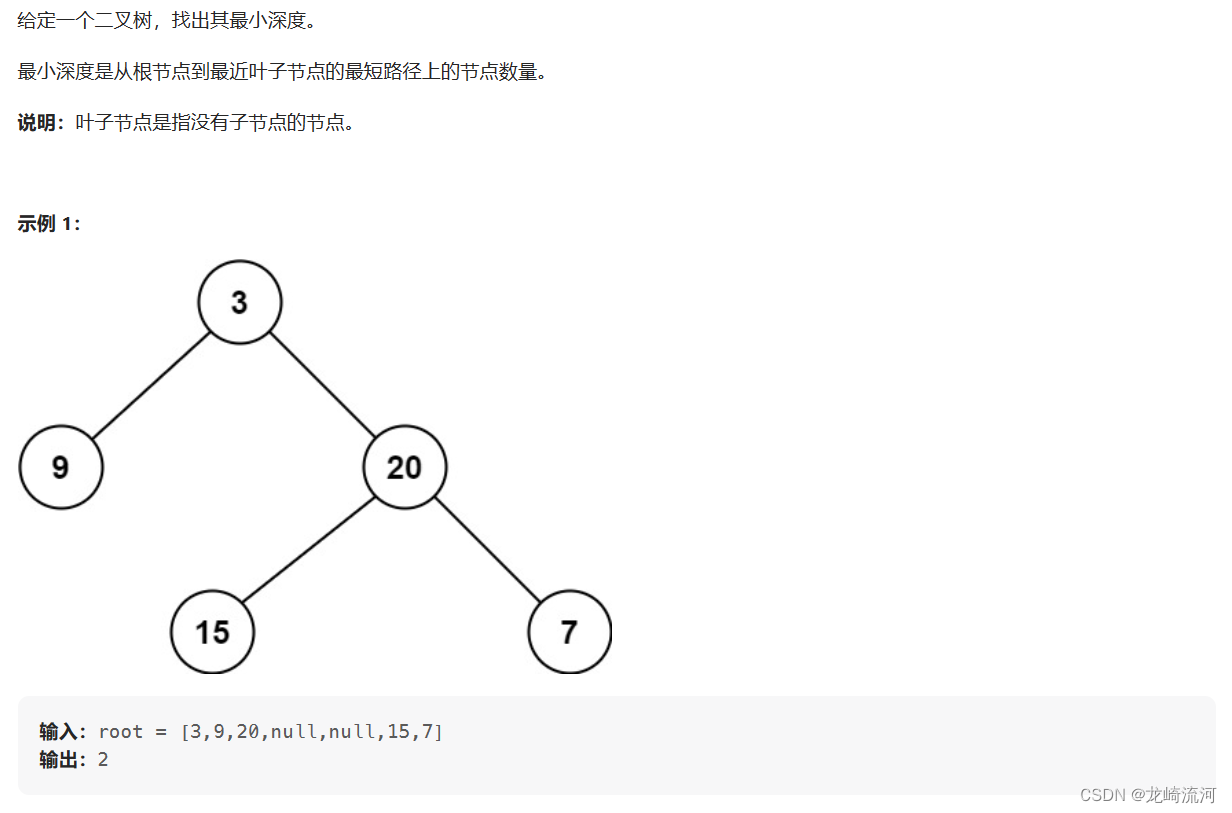
需要注意的是,只有当左右孩子都为空的时候,才说明遍历的最低点了。如果其中一个孩子为空则不是最低点.
dfs:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root,0);
return res == Integer.MAX_VALUE?0:res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root,int k){
if(root == null) return;
k++;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) res = Math.min(res,k);
dfs(root.left,k);
dfs(root.right,k);
}
}
bfs:
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root){
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
depth++;
TreeNode cur = null;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cur = queue.poll();
//如果当前节点的左右孩子都为空,直接返回最小深度
if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null){
return depth;
}
if (cur.left != null) queue.offer(cur.left);
if (cur.right != null) queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
return depth;
}
























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










