Overview
本文代码整理自Morvan Zhou(莫烦Python [1])的机器学习相关教程 - 强化学习 - DQN部分 [2]
Deep Q Network简称DQN,结合了Q learning和Neural networks的优势。如果我们使用tabular Q learning,对于每一个state,action我们都需要存放在一张q_table的表中。而在现实生活中,情况可就比迷宫的状况复杂多了,我们有千千万万个state,如果将这千万个state的值都放在表中,受限于我们计算机硬件,这样从表中获取数据,更新数据是没有效率的,这就是 DQN 产生的原因了。我们可以使用神经网络来估算这个state的值,这样就不需要一张表了。
算法流程:
网络结构:
为了使用Tensorflow来实现DQN,比较推荐的方式是搭建两个神经网络:target_net用于预测q_target值,不会及时更新参数;eval_net用于预测q_eval,这个神经网络拥有最新的神经网络参数。不过这两个神经网络结构是完全一样的,只是里面的参数不一样。

代码中还提供了一种修改版DQN:
将q_target的计算也加在了Tensorflow的graph里面。不过实测的时候效率会比之前的方法慢10%左右,原因我想应该是使用了one hot,而且貌似丢失了一点精度,因为在q_target转换的时候,之前是用numpy在做,而且是以float64的进度计算的,但是如果将q_target的计算全部挪进tf中,精度都是float32。不过这种结构还是有好处的,作为学习样本的话,计算结构全部在tensorboard上,代码结构也更好理解。

详细代码另可参考:GitHub [3]
Code
本教程代码主要基于一个简单的迷宫环境,重点在实现 DQN 算法
迷宫如下图所示,红色表示explorer,黄色表示paradise,黑色表示hell,白色表示ground(可自定义)
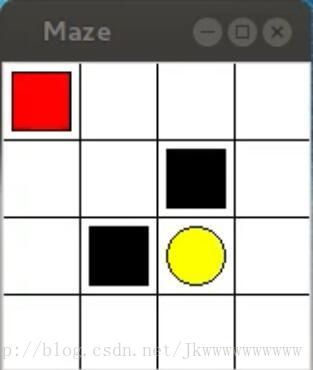
本算法主要模拟的是learn to move explorer to paradise的过程
之后我们可以再拿着做好的DQN算法去尝试其他更有意思的环境
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
###########################################################
# Title : Deep Q Network (DQN)
# Author : Alex Pan
# Info : Forked from Morvan Zhou (using tensorflow r1.2 gym 0.7.3)
#
# Tensorboard picture about this DQN structure:
# https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/machine-learning/reinforcement-learning/4-3-DQN3/#modification
###########################################################
from __future__ import print_function, division
import sys
import time
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
if sys.version_info.major == 2:
import Tkinter as tk
else:
import tkinter as tk
import ipdb
#################################### Initialization #####################################
# Set Random Seed
np.random.seed(1)
tf.set_random_seed(1)
#################################### Initialization #####################################
################################### Global Parameters ###################################
# Data Type
uintType = np.uint8 # cv2.imshow() ONLY support uint8[0, 255] & double[0, 1]
floatType = np.float32
################################### Global Parameters ###################################
######################################## Classes ########################################
# Deep Q Network off-policy
class DeepQNetwork(object):
def __init__(self, n_actions, n_features,
learning_rate = 0.01,
reward_decay = 0.9,
e_greedy = 0.9,
e_greedy_increment = None,
replace_target_iter = 300,
memory_size = 500,
batch_size = 32,
output_graph = False,
):
self.n_actions = n_actions
self.n_features = n_features
self.lr = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay
self.replace_target_iter = replace_target_iter
self.memory_size = memory_size
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.epsilon_max = e_greedy
self.epsilon_increment = e_greedy_increment
self.epsilon = 0 if e_greedy_increment is not None else self.epsilon_max
# consist of [target_net, evaluate_net]
self.__build_net()
# Get Parameters to be Updated
t_params = tf.get_collection('target_net_params')
e_params = tf.get_collection('eval_net_params')
self.replace_target_op = [tf.assign(t, e) for t, e in zip(t_params, e_params)]
# initialize zero memory [s, a, r, s_]
self.memory = np.zeros((self.memory_size, n_features * 2 + 2))
# total learning step & Cost Histogram
self.learn_step_counter = 0
self.cost_his = []
# Start Session
self.sess = tf.Session()
if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1: # tensorflow version < 0.12
self.sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
if output_graph:
# $ tensorboard --logdir=logs
writer = tf.train.SummaryWriter('logs/', self.sess.graph)
else: # tensorflow version >= 0.12
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
if output_graph:
# $ tensorboard --logdir=logs
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/', self.sess.graph)
def __build_net(self):
n_h1 = 10 # Hidden Layer
w_initializer, b_initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.3), tf.constant_initializer(0.1) # config of layers
# ------------------ build evaluate_net ------------------
self.s = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name = 's') # input
self.q_target = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_actions], name = 'Q_target') # for calculating loss
with tf.variable_scope('eval_net'):
# c_names(collections_names) are the collections to store variables
c_names = ['eval_net_params', tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES]
# first layer. collections is used later when assign to target net
with tf.variable_scope('l1'):
w1 = tf.get_variable('w1', [self.n_features, n_h1], initializer = w_initializer, collections = c_names)
b1 = tf.get_variable('b1', [1, n_h1], initializer = b_initializer, collections = c_names)
l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.s, w1) + b1)
# second layer. collections is used later when assign to target net
with tf.variable_scope('l2'):
w2 = tf.get_variable('w2', [n_h1, self.n_actions], initializer = w_initializer, collections = c_names)
b2 = tf.get_variable('b2', [1, self.n_actions], initializer = b_initializer, collections = c_names)
self.q_eval = tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2
# ------------------ loss & optimizer ------------------
with tf.variable_scope('loss'):
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(self.q_target, self.q_eval))
with tf.variable_scope('train'):
self.train_op = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(self.lr).minimize(self.loss)
# ------------------ build target_net ------------------
self.s_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name = 's_') # input
with tf.variable_scope('target_net'):
# c_names(collections_names) are the collections to store variables
c_names = ['target_net_params', tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES]
# first layer. collections is used later when assign to target net
with tf.variable_scope('l1'):
w1 = tf.get_variable('w1', [self.n_features, n_h1], initializer = w_initializer, collections = c_names)
b1 = tf.get_variable('b1', [1, n_h1], initializer = b_initializer, collections = c_names)
l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.s_, w1) + b1)
# second layer. collections is used later when assign to target net
with tf.variable_scope('l2'):
w2 = tf.get_variable('w2', [n_h1, self.n_actions], initializer = w_initializer, collections = c_names)
b2 = tf.get_variable('b2', [1, self.n_actions], initializer = b_initializer, collections = c_names)
self.q_next = tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2
def choose_action(self, observation):
# to have batch dimension when feed into tf placeholder
observation = observation[np.newaxis, :]
if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon:
# forward feed the observation and get q value for every actions
actions_value = self.sess.run(self.q_eval, feed_dict = {self.s: observation})
action = np.argmax(actions_value) # Returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis
else:
action = np.random.randint(0, self.n_actions)
return action
def store_transition(self, s, a, r, s_):
if not hasattr(self, 'memory_counter'):
self.memory_counter = 0
# replace the old memory with new memory
transition = np.hstack((s, [a, r], s_))
index = self.memory_counter % self.memory_size
self.memory[index, :] = transition
self.memory_counter += 1
def learn(self):
# check to replace target parameters
if self.learn_step_counter % self.replace_target_iter == 0:
self.sess.run(self.replace_target_op)
print('\n' + 'target_params_replaced' + '\n')
self.learn_step_counter += 1
# sample batch memory from all memory
if self.memory_counter > self.memory_size:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_size, size = self.batch_size) # Generates a random sample from a given 1-D array
else:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_counter, size = self.batch_size)
batch_memory = self.memory[sample_index, :]
q_next, q_eval = self.sess.run([self.q_next, self.q_eval],
feed_dict = {
self.s_: batch_memory[:, -self.n_features:], # fixed params
self.s: batch_memory[:, :self.n_features], # newest params
}
)
# change q_target w.r.t q_eval's action
q_target = q_eval.copy()
batch_index = np.arange(self.batch_size, dtype = np.int32)
action_index = batch_memory[:, self.n_features].astype(int) # Action Index of all batch memory, length equal to batch_index
reward = batch_memory[:, self.n_features + 1]
# Update Q Matrix
q_target[batch_index, action_index] = reward + self.gamma * np.max(q_next, axis = 1)
'''
For example in this batch we have 2 samples and 3 actions:
q_eval =
[[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]]
q_target = q_eval =
[[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]]
Then change q_target with the real q_target value w.r.t the q_eval's action.
For example in:
sample 0, I took action 0, and the max q_target value is -1;
sample 1, I took action 2, and the max q_target value is -2:
q_target =
[[-1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, -2]]
So the (q_target - q_eval) becomes:
[[(-1)-(1), 0, 0],
[0, 0, (-2)-(6)]]
We then backpropagate this error w.r.t the corresponding action to network,
leave other action as error=0 cause we didn't choose it.
'''
# train eval network
_, self.cost = self.sess.run([self.train_op, self.loss],
feed_dict = {self.s: batch_memory[:, :self.n_features],
self.q_target: q_target})
self.cost_his.append(self.cost)
# increasing epsilon
self.epsilon = self.epsilon + self.epsilon_increment if self.epsilon < self.epsilon_max else self.epsilon_max
def plot_cost(self):
plt.plot(np.arange(len(self.cost_his)), self.cost_his)
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.xlabel('training steps')
plt.show()
# Deep Q Network off-policy
class DeepQNetwork_modified(object):
def __init__(self, n_actions, n_features,
learning_rate = 0.01,
reward_decay = 0.9,
e_greedy = 0.9,
e_greedy_increment = None,
replace_target_iter = 300,
batch_size = 32,
memory_size = 500,
output_graph = False,
):
self.n_actions = n_actions
self.n_features = n_features
self.lr = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay
self.replace_target_iter = replace_target_iter
self.memory_size = memory_size
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.epsilon_max = e_greedy
self.epsilon_increment = e_greedy_increment
self.epsilon = 0 if e_greedy_increment is not None else self.epsilon_max
# consist of [target_net, evaluate_net]
self.__build_net()
# Get Parameters to be Updated
t_params = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES, scope = 'target_net')
e_params = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES, scope = 'eval_net')
self.target_replace_op = [tf.assign(t, e) for t, e in zip(t_params, e_params)]
# initialize zero memory [s, a, r, s_]
self.memory = np.zeros((self.memory_size, n_features * 2 + 2))
# total learning step & Cost Histogram
self.learn_step_counter = 0
self.cost_his = []
# Start Session
self.sess = tf.Session()
if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1: # tensorflow version < 0.12
self.sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
if output_graph:
# $ tensorboard --logdir=logs
writer = tf.train.SummaryWriter('logs/', self.sess.graph)
else: # tensorflow version >= 0.12
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
if output_graph:
# $ tensorboard --logdir=logs
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/', self.sess.graph)
def __build_net(self):
n_h1 = 20 # Hidden Layer
w_initializer, b_initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.3), tf.constant_initializer(0.1) # config of layers
# ------------------ all inputs ------------------------
self.s = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name = 's') # input State
self.s_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name = 's_') # input Next State
self.a = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None,], name = 'a') # input Action
self.r = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None,], name = 'r') # input Reward
# ------------------ build evaluate_net ------------------
with tf.variable_scope('eval_net'):
l1 = tf.layers.dense(self.s, n_h1, tf.nn.relu, kernel_initializer = w_initializer, bias_initializer = b_initializer)
self.q_eval = tf.layers.dense(l1, self.n_actions, kernel_initializer = w_initializer, bias_initializer = b_initializer)
with tf.variable_scope('q_eval'):
a_indices = tf.stack([tf.range(tf.shape(self.a)[0], dtype = tf.int32), self.a], axis = 1)
self.q_eval_wrt_a = tf.gather_nd(params = self.q_eval, indices = a_indices) # shape=(None,)
# ------------------ build target_net ------------------
with tf.variable_scope('target_net'):
l1 = tf.layers.dense(self.s_, n_h1, tf.nn.relu, kernel_initializer = w_initializer, bias_initializer = b_initializer)
self.q_next = tf.layers.dense(l1, self.n_actions, kernel_initializer = w_initializer, bias_initializer = b_initializer)
with tf.variable_scope('q_target'):
q_target = self.r + self.gamma * tf.reduce_max(self.q_next, axis = 1, name = 'Qmax_s_') # shape=(None,)
self.q_target = tf.stop_gradient(q_target)
# ------------------ loss & optimizer ------------------
with tf.variable_scope('loss'):
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(self.q_target, self.q_eval_wrt_a, name = 'TD_error'))
with tf.variable_scope('train'):
self.train_op = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(self.lr).minimize(self.loss)
def choose_action(self, observation):
# to have batch dimension when feed into tf placeholder
observation = observation[np.newaxis, :]
if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon:
# forward feed the observation and get q value for every actions
actions_value = self.sess.run(self.q_eval, feed_dict = {self.s: observation})
action = np.argmax(actions_value) # Returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis
else:
action = np.random.randint(0, self.n_actions)
return action
def store_transition(self, s, a, r, s_):
if not hasattr(self, 'memory_counter'):
self.memory_counter = 0
# replace the old memory with new memory
transition = np.hstack((s, [a, r], s_))
index = self.memory_counter % self.memory_size
self.memory[index, :] = transition
self.memory_counter += 1
def learn(self):
# check to replace target parameters
if self.learn_step_counter % self.replace_target_iter == 0:
self.sess.run(self.target_replace_op)
print('\n' + 'target_params_replaced' + '\n')
self.learn_step_counter += 1
# sample batch memory from all memory
if self.memory_counter > self.memory_size:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_size, size = self.batch_size) # Generates a random sample from a given 1-D array
else:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_counter, size = self.batch_size)
batch_memory = self.memory[sample_index, :]
_, cost = self.sess.run([self.train_op, self.loss],
feed_dict = {
self.s: batch_memory[:, :self.n_features],
self.a: batch_memory[:, self.n_features],
self.r: batch_memory[:, self.n_features + 1],
self.s_: batch_memory[:, -self.n_features:],
}
)
self.cost_his.append(cost)
# increasing epsilon
self.epsilon = self.epsilon + self.epsilon_increment if self.epsilon < self.epsilon_max else self.epsilon_max
def plot_cost(self):
plt.plot(np.arange(len(self.cost_his)), self.cost_his)
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.xlabel('training steps')
plt.show()
''' Reinforcement learning maze example
Red rectangle: explorer
Black rectangles: hells [reward = -1]
Yellow bin circle: paradise [reward = +1]
All other states: ground [reward = 0]
'''
class Maze(tk.Tk, object): # Forked from Tkinter
def __init__(self, unit_pixels = 40, grid_height = 4, grid_width = 4):
super(Maze, self).__init__() # Initialize Upper Object
self.UNIT = unit_pixels
self.MAZE_H = grid_height
self.MAZE_W = grid_width
self.action_space = ['u', 'd', 'l', 'r'] # up, down, left, right
self.n_actions = len(self.action_space) # 4
self.n_features = 2 # 2D map
self.title('Maze')
self.geometry('{0}x{1}'.format(self.MAZE_W * self.UNIT, self.MAZE_H * self.UNIT))
self.__build_maze()
def __build_maze(self):
# Create Canvas Widget to Display
self.canvas = tk.Canvas(self, bg = 'white', height = self.MAZE_H * self.UNIT, width = self.MAZE_W * self.UNIT)
# Create line with coordinates x1,y1,...,xn,yn (Grids)
for col in xrange(0, self.MAZE_W):
x0, y0 = col * self.UNIT, 0
x1, y1 = col * self.UNIT, self.MAZE_H * self.UNIT
self.canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x1, y1)
for row in xrange(0, self.MAZE_H):
x0, y0 = 0, row * self.UNIT
x1, y1 = self.MAZE_H * self.UNIT, row * self.UNIT
self.canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x1, y1)
# create origin, center of (0, 0)
origin = np.array([self.UNIT / 2, self.UNIT / 2])
# Hell 1 (black rect)
hell1_center = origin + np.array([self.UNIT * 2, self.UNIT]) # center of (2, 1)
x0, y0 = hell1_center[0] - 15, hell1_center[1] - 15
x1, y1 = hell1_center[0] + 15, hell1_center[1] + 15
self.hell1 = self.canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = 'black') # Create rectangle with coordinates x1,y1,x2,y2
# Hell 2 (black rect)
hell2_center = origin + np.array([self.UNIT, self.UNIT * 2]) # center of (1, 2)
x0, y0 = hell2_center[0] - 15, hell2_center[1] - 15
x1, y1 = hell2_center[0] + 15, hell2_center[1] + 15
self.hell2 = self.canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = 'black')
# Paradise (yellow oval)
oval_center = origin + self.UNIT * 2 # center of (2, 2)
x0, y0 = oval_center[0] - 15, oval_center[1] - 15
x1, y1 = oval_center[0] + 15, oval_center[1] + 15
self.paradise = self.canvas.create_oval(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = 'yellow') # Create oval with coordinates x1,y1,x2,y2
# Explorer (red rect)
x0, y0 = origin[0] - 15, origin[1] - 15
x1, y1 = origin[0] + 15, origin[1] + 15
self.explorer = self.canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = 'red')
# Pack All
self.canvas.pack()
def move(self, action):
coords = self.canvas.coords(self.explorer)
# Update Action with Boarder Constrains
base_action = np.array([0, 0])
if action == 0: # up
if coords[1] > self.UNIT:
base_action[1] -= self.UNIT
elif action == 1: # down
if coords[1] < (self.MAZE_H - 1) * self.UNIT:
base_action[1] += self.UNIT
elif action == 2: # right
if coords[0] < (self.MAZE_W - 1) * self.UNIT:
base_action[0] += self.UNIT
elif action == 3: # left
if coords[0] > self.UNIT:
base_action[0] -= self.UNIT
# Move Explorer
self.canvas.move(self.explorer, base_action[0], base_action[1]) # Move an item TAGorID given in ARGs
next_coords = self.canvas.coords(self.explorer) # next position
# reward function
if next_coords in [self.canvas.coords(self.paradise)]:
reward = 1
done = True
elif next_coords in [self.canvas.coords(self.hell1), self.canvas.coords(self.hell2)]:
reward = -1
done = True
else:
reward = 0
done = False
# return observation
observation_ = (np.array(next_coords[:2]) - np.array(self.canvas.coords(self.paradise)[:2])) / (self.MAZE_H * self.UNIT)
return observation_, reward, done
def reset(self):
# Enter event loop until all pending events have been processed by Tcl
self.update()
time.sleep(0.1)
# Reset Explorer
self.canvas.delete(self.explorer) # Delete items identified by all tag or ids contained in ARGS
origin = np.array([self.UNIT / 2, self.UNIT / 2])
x0, y0 = origin[0] - 15, origin[1] - 15
x1, y1 = origin[0] + 15, origin[1] + 15
self.explorer = self.canvas.create_rectangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill = 'red')
# return observation
return (np.asarray(self.canvas.coords(self.explorer)[:2]) - np.asarray(self.canvas.coords(self.paradise)[:2])) / (self.MAZE_H * self.UNIT)
def render(self):
time.sleep(0.01)
self.update()
######################################## Classes ########################################
####################################### Functions #######################################
def run_maze(M, DQN):
step = 0
for episode in xrange(300):
# initial observation
observation = M.reset()
while True:
step += 1
# fresh M
M.render()
# DQN choose action based on observation
action = DQN.choose_action(observation)
# DQN take action and get next observation and reward
observation_, reward, done = M.move(action)
DQN.store_transition(observation, action, reward, observation_)
if step > 200 and step % 5 == 0:
DQN.learn()
# update observation
observation = observation_
# break while loop when end of this episode
if done:
break
# end of game
print('Game Over.')
M.destroy()
####################################### Functions #######################################
######################################### Mains #########################################
# MAIN Function of DQN-Maze
def main():
# Initialize All
M = Maze()
DQN = DeepQNetwork(M.n_actions, M.n_features,
learning_rate = 0.01,
reward_decay = 0.9,
e_greedy = 0.9,
replace_target_iter = 200,
memory_size = 2000,
output_graph = False,)
# Run Maze
arg = (M, DQN)
M.after(100, run_maze, *arg) # Call function once after given time
M.mainloop() # Call the mainloop of Tk
# Plot
DQN.plot_cost()
######################################### Mains #########################################
##########################
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()References
[1] 教程一览 - 莫烦Python
[2] DQN算法更新 (Tensorflow) - 莫烦Python
[3] GitHub - MorvanZhou/tutorials
希望能够对大家有所帮助~
























 1173
1173

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








