文章目录
请求映射处理适配器:RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
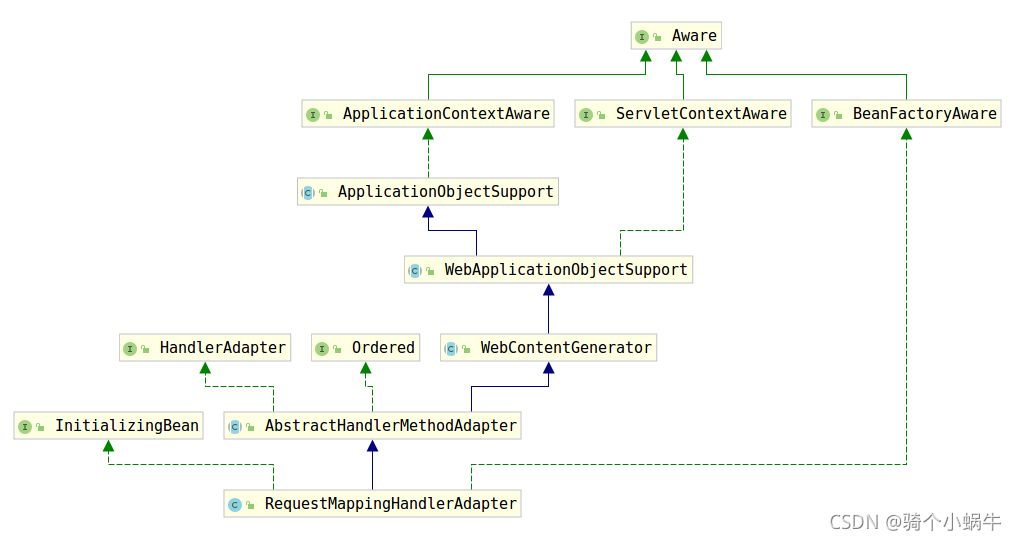
参数解析器:HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver和AbstractNamedValueMethodArgumentResolver是解析策略的上层定义和抽象。
关于这两个类可以参考https://securitit.blog.csdn.net/article/details/110110872的解析。
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver是个接口,只有俩个方法
public interface HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter var1);
@Nullable
Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter var1, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer var2, NativeWebRequest var3, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory var4) throws Exception;
}
- supportsParameter:用于判定是否需要处理该参数分解,返回true为需要,并会去调用下面的方法resolveArgument。
- resolveArgument:真正用于处理参数分解的方法,返回的Object就是controller方法上的形参对象。
获取默认参数解析器
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.getDefaultArgumentResolvers()
private List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> getDefaultArgumentResolvers() {
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = new ArrayList<>();
// 基于注解的参数解析
resolvers.add(new RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory(), false));
resolvers.add(new RequestParamMapMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new PathVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new MatrixVariableMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new MatrixVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor(false));
resolvers.add(new RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor(getMessageConverters(), this.requestResponseBodyAdvice));
resolvers.add(new RequestPartMethodArgumentResolver(getMessageConverters(), this.requestResponseBodyAdvice));
resolvers.add(new RequestHeaderMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory()));
resolvers.add(new RequestHeaderMapMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new ServletCookieValueMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory()));
resolvers.add(new ExpressionValueMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory()));
resolvers.add(new SessionAttributeMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new RequestAttributeMethodArgumentResolver());
// 基于类型的参数解析
resolvers.add(new ServletRequestMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new ServletResponseMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new HttpEntityMethodProcessor(getMessageConverters(), this.requestResponseBodyAdvice));
resolvers.add(new RedirectAttributesMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new ModelMethodProcessor());
resolvers.add(new MapMethodProcessor());
resolvers.add(new ErrorsMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new SessionStatusMethodArgumentResolver());
resolvers.add(new UriComponentsBuilderMethodArgumentResolver());
// 自定义参数解析
if (getCustomArgumentResolvers() != null) {
resolvers.addAll(getCustomArgumentResolvers());
}
// Catch-all
resolvers.add(new RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver(getBeanFactory(), true));
resolvers.add(new ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor(true));
return resolvers;
}
参数处理相关注解
参数绑定常用注解:
-
处理request uri 部分(这里指uri template中variable,不含queryString部分)的注解: @PathVariable;
-
处理request header部分的注解: @RequestHeader, @CookieValue;
-
处理request body部分的注解:@RequestParam, @RequestBody;
-
处理attribute类型的注解: @SessionAttributes, @ModelAttribute;
1.@PathVariable
当使用@RequestMapping URI template 样式映射时, 即 someUrl/{paramId}, 这时的paramId可通过 @Pathvariable注解绑定它传过来的值到方法的参数上。
@Controller
@RequestMapping(“/owners/{ownerId}”)
public class RelativePathUriTemplateController {
@RequestMapping(“/pets/{petId}”)
public void findPet(@PathVariable String ownerId, @PathVariable String petId, Model model) {
}
}
若方法参数名称和需要绑定的uri template中变量名称不一致,需要在@PathVariable(“name”)指定uri template中的名称。
使用的参数解析器:
-
PathVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver
在某些条件成立的情况下才会使用此类进行解析:- 方法参数由@PathVariable注解注释。
- 方法参数类型必须是Map类型。
- 注释方法参数的@PathVariable的value属性不能有值。
-
PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver
在某些条件成立的情况下才会使用此类进行解析:- 方法参数由@PathVariable注解注释。
- 当方法参数类型是Map时,要求其必须由@PathVariable注解注释,同时@PathVariable的value属性必须有值。
2.@RequestHeader
@RequestHeader 注解,可以把Request请求header部分的值绑定到方法的参数上。
Host localhost:8080
Accept text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9
Accept-Language fr,en-gb;q=0.7,en;q=0.3
Accept-Encoding gzip,deflate
Accept-Charset ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.7
Keep-Alive 300
@RequestMapping(“/displayHeaderInfo.do”)
public void displayHeaderInfo(@RequestHeader(“Accept-Encoding”) String encoding,
@RequestHeader(“Keep-Alive”) long keepAlive) {
}
request header部分的 Accept-Encoding的值,绑定到参数encoding上了, Keep-Alive header的值绑定到参数keepAlive上。
使用的参数解析器:
-
RequestHeaderMapMethodArgumentResolver
在某些条件成立的情况下才会使用此类进行解析:- 方法参数由@RequestHeader注解注释。
- 方法参数类型必须是Map类型。
-
RequestHeaderMethodArgumentResolver
在某些条件成立的情况下才会使用此类进行解析:- 方法参数由@RequestHeader注解注释。
- 方法参数类型不能为Map类型。
@RequestHeader是用来处理Web请求头中的信息,随着网站的多样和多元化,@RequestHeader使用频率会越来越广泛。
3.@CookieValue
@CookieValue 可以把Request header中关于cookie的值绑定到方法的参数上。
例如有如下Cookie值:
JSESSIONID=415A4AC178C59DACE0B2C9CA727CDD84
@RequestMapping(“/displayHeaderInfo.do”)
public void displayHeaderInfo(@CookieValue(“JSESSIONID”) String cookie) {
}
即把JSESSIONID的值绑定到参数cookie上。
使用的参数解析器:
- ServletCookieValueMethodArgumentResolver
ServletCookieValueMethodArgumentResolver实现了最主要的resolveName(…)方法,用于进行参数解析。- Cookie使用WebUtils.getCookie(…)从NativeWebRequest中解析。
- 若方法参数是Cookie类型,那么直接返回Cookie类型。
- 若方法参数非Cookie类型,那么urlPathHelper.decodeRequestString(…)解析得到String类型的值。
@CookieValue注解在实际应用中,作用还是很大的,传统Web开发中,Cookie是不可绕过的一环,掌握如何快速的通过Spring框架取值,可以帮助我们更快更好的完成任务。
4.@RequestParam
-
常用来处理简单类型的绑定,通过Request.getParameter() 获取的String可直接转换为简单类型的情况( String–> 简单类型的转换操作由ConversionService配置的转换器来完成);因为使用request.getParameter()方式获取参数,所以可以处理get 方式中queryString的值,也可以处理post方式中 body data的值;
-
用来处理Content-Type: 为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded编码的内容,提交方式GET、POST;
-
该注解有两个属性: value、required; value用来指定要传入值的id名称,required用来指示参数是否必须绑定;
使用的参数解析器:
-
RequestParamMapMethodArgumentResolver
-
RequestParamMethodArgumentResolve
1)RequestParamMapMethodArgumentResolver
实现了HandlerMethodArgumentResolver的supportsParameter(…)和resolveArgument(…)方法。
使用条件:
- 方法参数由@RequestParam注解注释
- 方法参数类型必须是Map类型
- 参数类型为MultiValueMap时,返回LinkedMultiValueMap实例,包含所有请求参数
- 参数类型为Map时,返回LinkedHashMap实例,包含所有请求参数
- @RequestParam注解的name不能有值
2)RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver
RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver继承自抽象AbstractNamedValueMethodArgumentResolver
除了能处理@RequestParam注解外,还可以处理@RequestPart注解。
处理@RequestParam注解的条件:
- 方法参数由@RequestParam注解注释。
- 方法参数若是Map类型时,@RequestParam的name属性不能为空。
- 方法参数若不是Map类型时,都可以处理。
处理@RequestPart注解的条件
- 方法参数不可由@RequestPart注解注释。
- 方法参数类型为org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile、org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile集合、org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile数组、javax.servlet.http.Part、javax.servlet.http.Part集合或javax.servlet.http.Part数组。
- 一个简单类型的方法参数,包括:boolean、byte、char、short、int、long、float、double、Enum.class、CharSequence.class、Number.class、Date.class、URI.class、URL.class、Locale.class或Class.class。
@RequestParam是用来处理Web请求头中的信息,随着网站的多样和多元化,@RequestParam使用频率会越来越广泛。
5.@RequestPart
@RequestPart用于将multipart/form-data类型数据映射到控制器处理方法的参数中。除了@RequestPart注解外,@RequestParam同样可以用于此类操作。
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class RequestPartController {
/**
* 跳转页面.
*/
@GetMapping("test1")
public ModelAndView requestPartHtml(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res, ModelMap modelMap)
throws Exception {
}
/**
* RequestPart-MultipartFile接收参数.
*/
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("test2")
public String requestPartMultipartFile(@RequestPart("file") MultipartFile multipartFile) throws Exception {
}
/**
* RequestPart-Part接收参数.
*/
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("test3")
public String requestPartPart(@RequestPart("file") Part part) throws Exception {
}
/**
* RequestParam-MultipartFile接收参数.
*/
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("test4")
public String requestParamMultipartFile(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile multipartFile) throws Exception {
}
/**
* RequestParam-Part接收参数.
*/
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("test5")
public String requestParamPart(@RequestParam("file") Part part) throws Exception {
}
/**
* Part接收参数.
*/
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("test6")
public String part(HttpServletRequest req) throws Exception {
Part part = req.getPart("file");
}
}
使用的参数解析器:
-
RequestPartMethodArgumentResolver
-
RequestHeaderMapMethodArgumentResolver
在某些条件成立的情况下才会使用此类进行解析:- 方法参数由@RequestPart注解注释。
- 方法参数不可由@RequestParam注解注释。
- 方法参数类型为org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile、org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile集合、org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile数组、javax.servlet.http.Part、javax.servlet.http.Part集合或javax.servlet.http.Part数组。
-
RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver
参考@RequestParam中的RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver用法
@RequestPart和@RequestParam都可以处理multipart/form-data类型数据,本质上并没有区别,使用任何一个都能达到期望的效果。文件上传在实际应用中也是必不可少的。
6.@RequestBody
-
该注解常用来处理Content-Type: 不是application/x-www-form-urlencoded编码的内容,例如application/json, application/xml等;
-
它是通过使用HandlerAdapter 配置的HttpMessageConverters来解析post data body,然后绑定到相应的bean上的。
-
因为配置有FormHttpMessageConverter,所以也可以用来处理 application/x-www-form-urlencoded的内容,处理完的结果放在一个MultiValueMap<String, String>里,这种情况在某些特殊需求下使用
Spring MVC中使用HandlerMethodArgumentResolver策略接口来定义处理器方法参数解析器,
使用的参数解析器:
-
RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor
RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor实现相对比较负责,其功能涉及范围较广,参数绑定仅是其功能之一。RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor实现了HandlerMethodArgumentResolver的supportsParameter(…)和resolveArgument(…)方法。
使用此类进行解析的条件:
- 方法参数由@RequestBody注解注释。
具体使用流程:
通过resolveArgument(…)方法中readWithMessageConverters(…)用来进行请求正文的读取,方法具体内容:- 获取请求的Content-Type,用于后续消息转换。
- 获取参数类型,用于参数实例化及初始化。
- 遍历消息转换器,通过参数类型匹配可用的消息转换。
- 调用参数转换器进行请求正文的转换。
- 处理请求增强器:RequestBodyAdvice方法beforeBodyRead(…)、afterBodyRead(…)和handleEmptyBody(…)。
7.@SessionAttributes
该注解用来绑定HttpSession中的attribute对象的值,便于在方法中的参数里使用。
该注解有value、types两个属性,可以通过名字和类型指定要使用的attribute 对象;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(“/editPet.do”)
@SessionAttributes(“pet”)
public class EditPetForm {
}
使用的参数解析器:
- SessionAttributeMethodArgumentResolver
8.@ModelAttribute
该注解有两个用法,一个是用于方法上,一个是用于参数上;
-
用于方法上时: 通常用来在处理@RequestMapping之前,为请求绑定需要从后台查询的model;
-
用于参数上时: 用来通过名称对应,把相应名称的值绑定到注解的参数bean上;要绑定的值来源于:
- @SessionAttributes 启用的attribute 对象上;
- @ModelAttribute 用于方法上时指定的model对象;
- 上述两种情况都没有时,new一个需要绑定的bean对象,然后把request中按名称对应的方式把值绑定到bean中。
用到方法上:
@ModelAttribute
public Account addAccount(@RequestParam String number) {
return accountManager.findAccount(number);
}
这种方式实际的效果就是在调用@RequestMapping的方法之前,为request对象的model里put(“account”, Account)。
用在参数上:
@RequestMapping(value=“/owners/{ownerId}/pets/{petId}/edit”, method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String processSubmit(@ModelAttribute Pet pet) {
}
首先查询 @SessionAttributes有无绑定的Pet对象,若没有则查询@ModelAttribute方法层面上是否绑定了Pet对象,若没有则将URI template中的值按对应的名称绑定到Pet对象的各属性上。






















 907
907











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








