关于组合数取模和逆元的知识的参考
http://blog.csdn.net/acdreamers/article/details/8037918
http://blog.csdn.net/acdreamers/article/details/8220787#comments
题目:
有一个无限大的矩形,初始时你在左上角(即第一行第一列),每次你都可以选择一个右下方格子,并瞬移过去(如从下图中的红色格子能直接瞬移到蓝色格子),求到第n行第m列的格子有几种方案,答案对1000000007取模。

Input
单组测试数据。
两个整数n,m(2<=n,m<=100000)
Output
一个整数表示答案。
Input示例
4 5
Output示例
10
可通过打表或者其他理解得出
答案为C(m+n-4,m-2)或C(m+n-4,n-2)//可优化的地方
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <sstream>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef set<int> Set;
typedef vector<int> Vec;
typedef set<int>::iterator It;
typedef long long ll;
#define mem(s,n) memset(s,n,sizeof(s))
int p = 1000000007;
ll quick_mod(ll a,ll b)//a^b%p 快速幂
{
ll ans = 1;
a %= p;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
ans = ans * a % p;
b--;
}
b >>= 1;
a = a * a % p;
}
return ans;
}
ll C(ll n,ll m)//nCm %p
{
if(n < m) return 0;
ll ans = 1;
for(ll i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
ll a = (n - m + i) % p;
ll b = i % p;
ans = ans *(a * quick_mod(b,p-2) % p) % p;//逆元的知识
}
return ans;
}
ll Lucas(ll n,ll m)//Lucas定理
{
if(m == 0) return 1;
return C(n % p,m % p) * Lucas(n / p,m / p) % p;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
ll m,n,a,b;
scanf("%lld%lld",&m,&n);
b=m+n-4;
a=min(m-2,n-2);
printf("%lld\n",Lucas(b,a));
return 0;
}对于正整数 a 和 p,若 ax≡1 mod p, 则称a关于模f的乘法逆元为x。
也可表示为ax≡1(mod p)。逆元一般用扩展欧几里得算法来求得,如果为素数,那么还可以根据费马小定理得到逆元为
ap−2≡1a
(mod p)
实际应用主要用于处理除法取模 如组合数
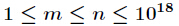
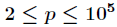
Lucas定理:
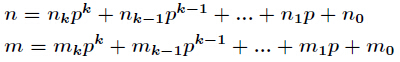
则有
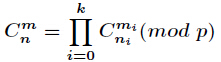
利用逆元计算即可
对于逆元和Lucas定理的理解还很浅显 需要更深入去了解
























 2868
2868

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








