一、前言
今天遇到了一个关于position: fixed 层级的css问题
设置了position属性为非static的时候,他的层级是怎样比较的呢?
二、代码
是根据z-index属性的大小来比较的。
那么看下面代码:
<div class="box1">
<div class="fixed1">
</div>
</div>
<div class="fixed2"/>
<style>
.box1 {
position: relative;
}
.box1 .fixed1 {
position: fixed;
z-index: 1000;
height: 10px;
width: 10px;
background-color: red;
left: 0;
top: 0;
}
.fixed2 {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
left: 0;
top: 0;
background-color: blue;
position: fixed;
z-index: 10;
}
</style>
我的理想效果是,红色放在蓝色的上面
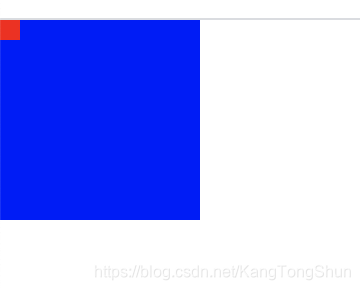
但是实际效果确是

方案1:我们需要设置红色块的父级元素的z-index值大于蓝色块的值
方案2:不要为红色块的父级元素设置position属性(或为static)
三、结论
引用JandyPam的总结
1、首先是遵循DOM的规则,同级的后面居上。
2、一般有定位属性的元素会高于无定位属性的同级元素。
3、都有定位属性的同级元素,z-index大者居上 。
4、如果是非同级的元素且(祖先元素设置了非static的position值)时,则会忽略元素本身z-index,取与对比元素同级的祖先元素的z-index属性,大者居上。










 本文探讨了CSS中使用z-index属性来控制元素层级的方法,并通过具体示例解释如何解决position:fixed元素的显示顺序问题。
本文探讨了CSS中使用z-index属性来控制元素层级的方法,并通过具体示例解释如何解决position:fixed元素的显示顺序问题。
















 2274
2274

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








