1.什么是图结构
1.1 图是由点的集合和边的集合构成
1.2 虽然存在有向图和无向图的概念,但实际上都可以用有向图来表达
1.3 边上可能带有权值
如下就是一个图结构
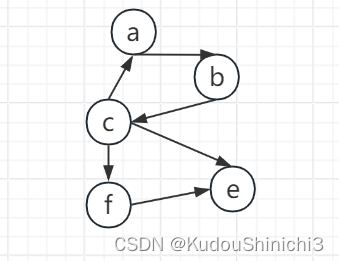
图 一
从图片上来看,该图的边是有方向的,所以该图是一个有向图,其实,所有的图都可以认为是一个有向图。例如下面一张图


左图的边没有方向,是一张无向图,其实,每一条边我们完全可以把它当成两条有向的边,如右图所示。所以我们说任何图都是有向图,或者说任何图都可以转为有向图。
2.图的表达
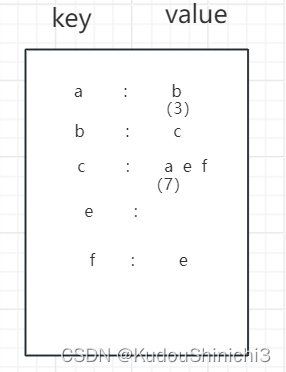
2.1 邻接表法
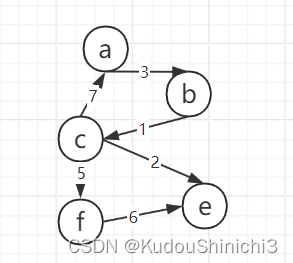
我们将上图加上权重,整张记录是一张表,key是他自己,value为它的邻居,上述图一可以用如下邻接表来表达:邻居下方括号内容表示权重,下图没有完全都写出来。
当然该表示方法也可以表示带权重的,例如如果a到b的权重是3,那么可以在表示的b下面加一个小的数据项3,来表示权重
2.2 邻接矩阵法
我们将所有的值放在一个矩阵中,自己到自己我们可以认为是0,自己不能直接到的我们认为是无穷,例如下图,a到a是0,a到b是3,a不能直接到c,所以下图a行c列为无穷,所以用下图我们可以表示一个图结构。

当然除了上述两种方式,还有很多种表达方式。
因为图的表达结构有很多种方式,所以我们要有一个我们最熟悉的一个方式,每个人最熟悉的方式可能不同,我们在做题的时候,就可以把各种各样的图结构转换为自己最熟悉的结构,然后去解题,下面介绍一种比较清晰的结构:
点的描述:
//点结构的表述
public class Node {
//点自己的值
public int value;
//该点的入度,指的是有几个指向该点
public int in;
//该点的出度,指的是该点有几个指向别的点
public int out;
//该点的邻居
public List<Node> nexts;
//指向该点邻居的边
public List<Edge> edges;
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
in = 0;
out = 0;
nexts = new ArrayList<>();
edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
边的描述:
//边的集合
public class Edge {
//该边的权重
public int weight;
//该边的起点
public Node from;
//该边指向的点
public Node to;
public Edge(int weight,Node from,Node to){
this.weight = weight;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
}图的描述:
//图的描述
public class Graph {
public HashMap<Integer,Node> nodes;
public HashSet<Edge> edges;
public Graph(){
nodes = new HashMap<>();
edges = new HashSet<>();
}
}将其他的图结构,转换为自己的图结构
public class GraphGenerator {
//matrix 所有的边
//N * 3 的矩阵
//[weight,from 节点上的值,to 节点上的值]
//
//[5,0,7]
//[3,0,1]
public static Graph createGraph(int[][] matrix){
Graph graph = new Graph();
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
int weight = matrix[i][0];
int from = matrix[i][1];
int to = matrix[i][2];
if (!graph.nodes.containsKey(from)){
graph.nodes.put(from,new Node(from));
}
if (!graph.nodes.containsKey(to)){
graph.nodes.put(to,new Node(to));
}
Node fromNode = graph.nodes.get(from);
Node toNode = graph.nodes.get(to);
Edge edge = new Edge(weight,fromNode,toNode);
toNode.in++;
fromNode.out++;
fromNode.nexts.add(toNode);
fromNode.edges.add(edge);
graph.edges.add(edge);
}
return graph;
}
}3.图的宽度优先遍历和宽度优先遍历
3.1宽度优先遍历
之前文章有写二叉树的宽度优先遍历,是通过一个队列来实现的。图里面的宽度优先遍历,也是通过对列来实现的,不过要加一个set结构,因为图里面是有回路的,如果我们不加一个set,那么某一个点就有可能多次进入这个队列,就导致可能永远也遍历不完。
public class GraphBFS {
//从node出发,进行宽度优先遍历
public static void graphBFS(Node node){
if (node == null){
return;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Set<Node> set = new HashSet<>();
queue.add(node);
set.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
Node poll = queue.poll();
System.out.println(poll.value);
List<Node> nexts = poll.nexts;
for (Node next : nexts) {
if (!set.contains(next)){
set.add(next);
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
}
}3.2 深度优先遍历
深度优先遍历,我们需要准备一个栈和一个set来实现,set用来保证不会重复入栈,我们把节点入栈和入set,然后打印,我们先弹出一个节点,接下来就开始遍历该节点邻居,如果不在set里面,就添加到set里面,并把刚刚弹出的节点再压入栈,并把新的节点压入栈中,结束本次循环。
代码如下:
public class GraphDFS {
//图的深度优先遍历
public void graphDFS(Node node){
if (node == null){
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Set<Node> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(node);
stack.add(node);
System.out.println(node.value);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
Node pop = stack.pop();
for (Node next : pop.nexts) {
if (!set.contains(next)){
stack.push(pop);
stack.push(next);
set.add(next);
System.out.println(next.value);
break;
}
}
}
}
}4.图的拓扑排序
1.在图中找到所有入度为0的点输出
2.把所有入度为0的点在图中删掉,继续找入度为0的点输出,周而复始
3.图中所有的点都被删除后,依次输出的顺序就是拓扑排序
要求:有向图且其中没有环
应用:时间安排,编译顺序
public class SortedTopology {
public List<Node> sortedTopology(Graph graph){
//存储图中每个节点和它的入度
HashMap<Node,Integer> inMap = new HashMap();
//入度为0的点的队列
Queue<Node> zeroInQueue = new LinkedList<>();
for (Node node : graph.nodes.values()) {
inMap.put(node,node.in);
if (node.in == 0){
zeroInQueue.add(node);
}
}
List<Node> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (!zeroInQueue.isEmpty()){
Node poll = zeroInQueue.poll();
result.add(poll);
for (Node next : poll.nexts) {
inMap.put(next,inMap.get(next) - 1);
if (inMap.get(next) == 0){
zeroInQueue.add(next);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}5.最小生成树算法
5.1 Kruskal
1.总是从权值最小的边开始考虑,依次考察权值依次变大的边
2.当前的边要么进入最小生成树的集合,要么丢弃
3.如果当前边进入最小生成树集合不会形成环,就要当前边
4.如果当前边进入最小生成树集合会形成环,就不要当前边
5.考察完所有边之后,最小生成树的集合也就得到了。
public class Kruskal {
public static class UnionFind{
public HashMap<Node,Node> parentMap;
public HashMap<Node,Integer> sizeMap;
public UnionFind(){
parentMap = new HashMap<>();
sizeMap = new HashMap<>();
}
public void makeSet(Collection<Node> nodes){
parentMap.clear();
sizeMap.clear();
for (Node node:nodes) {
parentMap.put(node,node);
sizeMap.put(node,1);
}
}
public Node findParent(Node node){
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (node != parentMap.get(node)){
stack.add(node);
node = parentMap.get(node);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
parentMap.put(stack.pop(),node);
}
return node;
}
public boolean isSameSet(Node a,Node b){
return findParent(a) == findParent(b);
}
public void union(Node a,Node b){
if (a == null || b == null){
return;
}
Node aParent = findParent(a);
Node bParent = findParent(b);
if (aParent != bParent){
int aSize = sizeMap.get(aParent);
int bSize = sizeMap.get(bParent);
if (aSize <= bSize){
parentMap.put(aParent,bParent);
sizeMap.put(bParent,aSize+bSize);
sizeMap.remove(aParent);
}else {
parentMap.put(bParent,aParent);
sizeMap.put(aParent,aSize + bSize);
sizeMap.remove(bParent);
}
}
}
}
public static Set<Edge> kruskalMST(Graph graph){
UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind();
unionFind.makeSet(graph.nodes.values());
PriorityQueue<Edge> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2)->o1.weight - o2.weight);
for (Edge edge : graph.edges) {
priorityQueue.add(edge);
}
Set<Edge> result = new HashSet<>();
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()){
Edge poll = priorityQueue.poll();
Node from = poll.from;
Node to = poll.to;
boolean sameSet = unionFind.isSameSet(from, to);
if (!sameSet){
result.add(poll);
unionFind.union(from,to);
}
}
return result;
}
}
5.2 prim算法
1.可以从任意节点出发来寻找最小生成树
2.某个点加入到被选取的点中后,解锁这个点出发的所有新的边
3.在所有解锁的边中选最小的边,然后看看这个边会不会形成环
4.如果会,不要当前边,继续考察剩下解锁的边中最小的边,重复3)
5.如果不会,要当前边,将该边的指向点加入到被选取的点中,重复2)
6.当所有点都被选取,最小生成树就得到了
public static Set<Edge> primMST(Graph graph){
PriorityQueue<Edge> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2)->o1.weight-o2.weight);
HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet<>();
HashSet<Edge> result = new HashSet<>();
for (Node value : graph.nodes.values()) {
if (!set.contains(value)){
set.add(value);
for (Edge edge : value.edges) {
priorityQueue.add(edge);
}
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()){
Edge poll = priorityQueue.poll();
Node node = poll.to;
if (!set.contains(node)){
result.add(poll);
set.add(node);
for (Edge edge : node.edges) {
priorityQueue.add(edge);
}
}
}
}
break;
}
return result;
}6.迪瑞克斯拉算法
6.1什么是迪瑞克斯拉算法
迪瑞特斯拉算法必须是有向无负权重的图,可以有环。其实,严格来说,上面的说法有些不太对,迪瑞克斯拉算法是没有一个环,环路的累加和是负数。迪瑞克斯拉算法是不处理负权值的边的,这是考虑到迪瑞克斯拉算法的显示意义。当然,它原本的要求是没有负的环就行。
1.Dijkstra算法必须指定一个源点
2.生成一个源点到各个点的最小距离表,一开始只有一条记录,即源点到自己的最小距离为0,源点到其他所有点的最小距离都为正无穷大
3.从距离表中拿出没拿过记录里的最小记录,通过这个点发出的边,更新源点到各个点的最小距离表,不断重复这一步
4.源点到所有的点记录如果都被拿过一遍,过程停止,最小距离表就得到了。
public class Dijkstra {
public HashMap<Node,Integer> dijkstra(Node from){
HashMap<Node,Integer> distanceMap = new HashMap<>();
distanceMap.put(from,0);
HashSet<Node> selectNodes = new HashSet<>();
Node minNode = getDistanceAndUnSelectNode(distanceMap,selectNodes);
while (minNode != null){
int distance = distanceMap.get(minNode);
for (Edge edge:minNode.edges){
Node toNode = edge.to;
if (!distanceMap.containsKey(toNode)){
distanceMap.put(toNode,distance + edge.weight);
}else {
distanceMap.put(toNode,Math.min(distanceMap.get(toNode),edge.weight+distance));
}
}
selectNodes.add(minNode);
minNode = getDistanceAndUnSelectNode(distanceMap,selectNodes);
}
return distanceMap;
}
private Node getDistanceAndUnSelectNode(HashMap<Node, Integer> distanceMap, HashSet<Node> selectNodes) {
Integer min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Node minNode = null;
for (Map.Entry<Node,Integer> entry:distanceMap.entrySet()){
Node key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
if (!selectNodes.contains(key) && value < min){
minNode = key;
min = value;
}
}
return minNode;
}
}在该实现中,每次获取最小的节点时都会遍历这个distanceMap,每次获取都会遍历,是很傻的实现,那有没有什么能优化获取最小节点这个过程呢,答案是肯定的,我们可以通过加强堆来实现。
public class DijkstraWithStrengthenHeap {
public class StrengthenHeap{
private Node[] nodes;
private HashMap<Node,Integer> distanceMap;
private HashMap<Node,Integer> heapIndexMap;
private int heapSize;
public StrengthenHeap(int size){
nodes = new Node[size];
distanceMap = new HashMap<>();
heapIndexMap = new HashMap<>();
this.heapSize = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return heapSize == 0;
}
public boolean isEntered(Node node){
return heapIndexMap.containsKey(node);
}
public boolean inHeap(Node node){
return isEntered(node) && heapIndexMap.get(node) != -1;
}
public void swap(int i,int j){
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[i],j);
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[j],i);
Node temp = nodes[i];
nodes[i] = nodes[j];
nodes[j] = temp;
}
public void addOrUpdateOrIgnore(Node node,Integer distance){
if (inHeap(node)){
distanceMap.put(node,Math.min(distanceMap.get(node),distance));
heapInsert(node,heapIndexMap.get(node));
}
if (!isEntered(node)){
nodes[heapSize] = node;
heapIndexMap.put(node,heapSize);
distanceMap.put(node,distance);
heapInsert(node,heapSize++);
}
}
public void heapInsert(Node node,Integer index){
Integer parentIndex = (index - 1)/2;
while (distanceMap.get(nodes[index]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[parentIndex])){
swap(index,parentIndex);
index = parentIndex;
}
}
public NodeRecord pop(){
NodeRecord record = new NodeRecord(nodes[0],distanceMap.get(nodes[0]));
swap(0,heapSize-1);
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[heapSize-1],-1);
distanceMap.remove(nodes[heapSize-1]);
nodes[heapSize - 1] = null;
heapfy(0,--heapSize);
return record;
}
public void heapfy(Integer index,int heapSize){
Integer leftChildIndex = (index * 2) + 1;
while (leftChildIndex < heapSize){
int smallIndex = leftChildIndex +1 < heapSize && distanceMap.get(nodes[leftChildIndex+1]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[leftChildIndex])
? leftChildIndex + 1 : leftChildIndex;
smallIndex = distanceMap.get(nodes[smallIndex]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[index]) ? smallIndex : index;
if (smallIndex == index){
break;
}
swap(smallIndex,index);
index = smallIndex;
leftChildIndex = leftChildIndex * 2 + 1;
}
}
}
public class NodeRecord{
private Node node;
private int distance;
public NodeRecord(Node node,Integer distance){
this.node = node;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
public HashMap<Node,Integer> dijkstra(Node head,int size){
StrengthenHeap heap = new StrengthenHeap(size);
heap.addOrUpdateOrIgnore(head,0);
HashMap<Node,Integer> result = new HashMap<>();
while (!heap.isEmpty()){
NodeRecord record = heap.pop();
Node cur = record.node;
Integer distance = record.distance;
for (Edge edge:cur.edges){
heap.addOrUpdateOrIgnore(edge.to,edge.weight+distance);
}
result.put(cur,distance);
}
return result;
}
}






 本文介绍了图的基本概念,包括有向图和无向图的区别,以及邻接表和邻接矩阵的表达方式。重点讲解了宽度优先遍历、深度优先遍历、拓扑排序和最小生成树算法(Kruskal、Prim和迪杰斯特拉),适用于时间安排和编译顺序等问题。
本文介绍了图的基本概念,包括有向图和无向图的区别,以及邻接表和邻接矩阵的表达方式。重点讲解了宽度优先遍历、深度优先遍历、拓扑排序和最小生成树算法(Kruskal、Prim和迪杰斯特拉),适用于时间安排和编译顺序等问题。















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








