1.css的认识
-
1.行内样式:使用style属性,所有的标签都有style属性,不推荐使用
-
2.内部样式:使用style标签,style标签要在head标签中,练习时使用
-
3.使用外部样式:需要创建外部文件,通过link标签引入,开发时推荐使用
-
优先级:1行内>内部和外部(就近原则:)
2.css的选择器(类选择器)
-
每个标签都有class属性,class,属性的值叫做 类名
-
类名由:数字,字母,下划线,中划线组成,不能用数字开头
-
一个标签可以有多个类名,类名中间用空格隔开
-
.一个类名可以在多个标签中使用
-
类使用符号 . 来表示
-
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>类选择器</title> <style> .p1{ color: aqua; } .p2{ background-color: black; } </style> </head> <body> <p class="p1">1.每个标签都有class属性,class,属性的值叫做 类名</p> <p class="p1">2.类名由:数字,字母,下划线,中划线组成,不能用数字开头</p> <p class="p1 p2">3.一个标签可以有多个类名,类名中间用空格隔开</p> <p>4.一个类名可以在多个标签中使用</p> <p>5.类使用符号 . 来表示</p> </body> </html>id选择器
- 每个标签都有id属性
- 每个标签只能有一个id
- 一个id只能对应一个标签
- id选择器使用#代表
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>id选择器</title> <style> #p1{ color: aqua; } </style> </head> <body> <p id="p1"> 1.每个标签都有id属性 2.每个标签只能有一个id 3.一个id只能对应一个标签 4.id选择器使用#代表 </p> </body> </html>标签选择器
致自己本身的标签
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>标签选择器</title> <style> li{ color: #795; } </style> </head> <body> <ul> <li>标签</li> <li>标签</li> <li>标签</li> <li>标签</li> <li>标签</li> <li>标签</li> </ul> </body> </html>结构伪类选择器
first-of-type 第一个
last-of-type 最后一个
nth-child(odd) 奇数
nth-child(even) 偶数
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>结构伪类选择器</title> <style> .a>div:first-of-type{ color:red; } .a>div:last-of-type{ color:blue; } .a div:nth-child(2){ background-color: aquamarine; } /* 奇数 */ table tr:nth-child(odd){ background-color: aqua; } /* 偶数 */ table tr:nth-child(even){ background-color: rgb(50, 191, 90); } .a2 p:nth-child(-n+2){ font-size: 50px; } .a2 p:nth-child(n+2){ font-size: 50px; } .a2 p:nth-child(n){ color: red; } .a2 p:nth-last-child(-n+2){ color: bisque; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="a"> <p>ssssss</p> <div class="a1"> <p>sss</p> <p>aaaa</p> </div> <div class="a2"> <p>2222</p> <p>34532</p> <p>3454</p> <p>1234532</p> <p>234453</p> <p>3245</p> </div> </div> <table border="1" width="500px" height="800px"> <tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> <tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> <tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> <tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr><tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> <tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> <tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> <tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> <tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr><tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> <tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> <tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> <tr> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> <td></td> </tr> </table> </body> </html>优先级选择器
通配符<标签选择器<类选择器<id选择器>
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>选择器 的优先级</title> <style> *{ color: red; } h2{ color: aqua; } .h2{ color: blue; } #h{ color: chocolate; } </style> </head> <body> <h2 class="h" id="h">选择器的优先级</h2> <p> 通配符<标签选择器<类选择器<id选择器> </p> </body> </html>通配符
通配符:选择所有标签
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>通配符</title> <style> *{ color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>通配符:选择所有标签</h1> <p>极少使用</p> </body> </html>伪元素
::before用于在元素内容之前插入一些内容,::after用于在元素内容之后插入一些内容,其他方面的都相同。写法就是只要在想要添加的元素选择器后面加上::before或::after即可,有些人会发现,写一个冒号和两个冒号都可以有相应的效果,那是因为在css3中,w3c为了区分伪类和伪元素,用双冒号取代了伪元素的单冒号表示法,所以我们以后在写伪元素的时候尽量使用双冒号。不同于其他伪元素,
::before和::after在使用的时候必须提供content属性,可以为字符串和图片,也可以是空,但不能省略该属性,否则将不生效<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>伪元素</title> <style> h1::after{ content: "这是添加的文字" } h2::before{ content: url(img/icon.jpg); vertical-align: middle; } </style> </head> <body> <h1></h1> <h2>在前边加一个图片</h2> </body>
css字体样式
font-weight字体宽度
取值:normal正常
bold加粗
bolder 更粗
italic 倾斜
font-family 字体系列
font简写(复合属性,连写):倾斜 加粗 大小 系列
<html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>字体样式</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../day03/css/font.css"> </head> <body> <p>字体样式</p> <p class="p1">1.font-size</p> <p class="p2"> 2.font-weight字体宽度 取值:normal正常 bold加粗 bolder 更粗 100~900 </p> <p class="p3"> 3.font-style 字体样式(是否倾斜)<br> normal 正常 italic 倾斜 </p> <p class="p4"> 4.font-family 字体系列 </p> <p class="p5"> 5.font简写(复合属性,连写):倾斜 加粗 大小 系列 </p> </body> </html>css背景图片
背景平铺background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-color: aqua;
背景尺寸 background-size
背景定位 background-position
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>背景图片</title> <style> body{ height: 800px; width: 1000%; /* 背景图片 */ background-image: url(img/自己.jpg); /* 背景平铺 */ background-repeat: no-repeat; background-color: aqua; /* 背景尺寸*/ background-size :100px 800px; /* 背景定位 */ background-position: 300px 100px } </style> </head> <body> </body> </html>css交集选择器
交集选择器中的选择器之间是紧挨着的,没有东西分隔
交集选择器中如果有标签选择器,标签选择器必须写在最前面<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>交集选择器</title> <style> p.a{ color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <p class="a"> 交集选择器中的选择器之间是紧挨着的,没有东西分隔 交集选择器中如果有标签选择器,标签选择器必须写在最前面 </p> <p class="b"> asdfgg </p> <p> <a href="#" class="a">阿萨德</a> </p> </body> </html>css并集选择器
并集选择器中的每组选择器之间通过
并集选择器中的每组选择器可以是基础选择器或者复合选择器
并集选择器中的每组选择器通常一行写一个,提高代码的可读性
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>并集选择器</title> <style> /* li1 红 li2 li3 黄 */ .li1 { color: red; } .li2, .li3 { color: yellow; } .p1, .li2>p { font-size: 30px; } ul p, ul span { color: hotpink; } </style> </head> <body> <p class="f1">并集选择器 </p> <ul> <li class="li1"> 并集选择器中的每组选择器之间通过 </li> <li class="li2"> <p class="p2"> 并集选择器中的每组选择器可以是基础选择器或者复合选择器</p> <span>asdfgh</span> </li> <li class="li3"> 并集选择器中的每组选择器通常一行写一个,提高代码的可读性 <span>asdfgh</span> </li> </ul> <span>asdfgh</span> </body> </html>css后代选择器
后代选择器又称为包含选择器,可以选择父元素里面子元素。其写法就是外层标签写在前面,内标签写在后面,中间用空格分隔。当标签发生嵌套时,内层标签就成为外层标签的后代。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>后代选择器</title> <style> /* 要求,只修改ul中的p标签的文字大小*/ ul p { /* ul中的所有p标签 */ font-size: 40px; } /* ul中所有的li */ ul li { color: red; } ul .p2 { text-align: center; } /* 子元素:直接子元素 */ body>p { color: yellow; } ul>p { color: gold; } </style> </head> <body> <p>这是外边的p标签</p> <ul> <li> <p>这是ul的孙子</p> </li> <li> <p class="p2">这是li的儿子</p> </li> <li> <a href="#" id="a1">这是body的重孙子</a> </li> </ul> </body> </html>css背景颜色
- 颜色名
- 16进制
- rgb
- rgba
- hsl
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>背景颜色</title> <style> ul{ /* 颜色名 */ background-color: chocolate; /* 16进制 */ background-color: #55dcd1; /* rgb */ background-color: rgb(255,134,189); /* rgba */ background-color: rgba(255,145,178,8%); /* hsl */ background-color: hsl(360,77%,55%, 0.8) } li{ background-color: #31955f; } </style> </head> <body> <ul> <li>1111</li> <li>2222</li> <li>3333</li> </ul> </body> </html>css元素显示模式
变块display: block;
变行内 display: inline;
隐藏 display: none;
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>元素显示模式</title> <style> a{ /* 变块 */ display: block; height: 100px; width: 200px; background-color: aqua; } p{ /* 变行内 */ display: inline; background: blueviolet; } .img1{ /* 隐藏 */ display: none; } .d1{ height: 300px; background-color: brown; } .d1:hover .img3{ display: none; } </style> </head> <body> <a href="#">行内--块</a> <a href="#">行内--块</a> <p>块--行内</p> <img src="img/头像.jpg" class="img1"> <img src="img/头像.jpg" class="img2"> <div class="d1"> <img src="img/头像.jpg" alt="" class="img3"> </div> </body> </h
css的继承
CSS继承性就是CSS允许结构的外围样式不仅可以应用于某个特定的元素,还可以应用于它包含的、可匹配的标签
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>继承</title>
<style>
.a{
height: 300px;
background-color: yellowgreen;
color: red;
}
div{
width: 200px;
color:white;
color:blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
这个是父亲
<p>这是个儿子</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
css圆角边框
四个值: 左上 右上 右下 左下
圆,要求是正方形
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>圆角边框</title>
<style>
body {
background-color: aqua;
}
.img1 {
height: 300px;
border-radius: 150px;
/* 四个值: 左上 右上 右下 左下 */
border-radius: 10px 20px 30px 40px;
/* 一个角 */
border-top-left-radius: 50%;
}
.img2 {
height: 3000px;
width: 300px;
/* 圆,要求是正方形 */
border-radius: 50%;
}
.img3{
/* 右半圆 */
height: 300px;
width: 150px;
border-radius:0 150px 150px 0;
}
.img4{
/* 左半圆 */
height: 300px;
width: 150px;
border-radius: 150px 0 0 150px ;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img src="../day05/img/头像.jpg" alt="" class="img1">
<img src="../day05/img/头像.jpg" alt="" class="img2">
<img src="../day05/img/头像.jpg" alt="" class="img3">
<img src="../day05/img/自己.jpg" alt="" class="img4">
</body>
</html>
边框
- 边框的粗细 border-width
- 边框颜色 border-color
- 边框样式 border-style
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>边框</title>
<style>
div {
height: 300px;
width: 500px;
}
.a1 {
/* 边框的粗细 */
border-width: 2px;
/* 边框颜色 */
border-color: blue;
/* 边框样式 */
border-style: solid;
}
.a2 {
/* 边框的粗细 */
border-width: 2px;
/* 边框颜色 */
border-color: rgb(77, 245, 231);
/* 边框样式 */
border-style: solid;
/* 上边框 */
/* border-top-width: 10px; */
/* 上 top 下 bottom 左 left 右 right */
/* 上右下左 */
border-color: rgb(44, 129, 203) blue gold fuchsia;
/* 三个时 上 , 左右, 下 */
border-color: blue gold fuchsia;
/* 俩个时 上下 左右 */
border-color: gold fuchsia;
/* 一个 上下左右 */
border-color: fuchsia;
border-width: 5px 10px 15px 20px;
border-style: dashed dotted double solid;
}
.a3{
/* 简写:宽度 样式 颜色 */
border: 1px solid red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a1"></div>
<div class="a2"></div>
<div class="a3"></div>
</body>
</html>
css绝对定位
相对于非静态定位的父元素进行移动
1.不保留原来的位置
2.脱离了标准文档流
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style>
.a{
height: 500px;
width: 800px;
background-color: aquamarine;
position: relative;
}
.b{
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: blue;
position: absolute;
top:300px;
right:0px;
}
.c{
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: rgb(255, 0, 0);
top:300px;
left:0px;
position: relative;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<div class="b">
绝对定位:
<!-- 相对于非静态定位的父元素进行移动 -->
1.不保留原来的位置
2.脱离了标准文档流
</div>
<div class="c"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
css相对定位
相对定位:相对 于自身进行移动
1.没有脱标
2.会保留原来的位置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>相对定位</title>
<style>
div{
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
background-color:aqua;
}
.b{
background-color: rgb(229, 15, 15);
position: relative;
left:150px;
top:-150px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a"></div>
<div class="b">
相对定位:相对 于自身进行移动
1.没有脱标
2.会保留原来的位置
</div>
<div class="c"></div>
</body>
</html>
清除浮动
子元素的浮动不会对父元素外的标签产生影响
需要设置父元素的高度,否则会造成 父元素的边框塌陷
额外标签法:
在父元素的最后田间一个块元素
设置样式clear:both
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>清除浮动</title>
<style>
.a {
border: 1px solid red;
height: 400px;
}
.b {
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
margin: 5px;
background-color: yellowgreen;
float: left;
}
.c{
background-color: aqua;
height: 300px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<div class="b">
子元素的浮动不会对父元素外的标签产生影响
</div>
<div class="b">
需要设置父元素的高度,否则会造成:<br>
父元素的边框塌陷
</div>
<div class="b"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
</div>
<div class="c">
c
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>清除浮动:额外标签法</title>
<style>
.a {
border: 1px solid red;
height: 400px;
}
.b {
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
margin: 5px;
background-color: yellowgreen;
float: left;
}
.c {
background-color: aqua;
height: 300px;
}
.d{
clear:both;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<div class="b">
额外标签法:
在父元素的最后田间一个块元素
设置样式clear:both
</div>
<div class="b">
不建议使用:增加了页面复杂度
</div>
<div class="b"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
<div class="d"></div>
</div>
<div class="c">
c
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>清除浮动:伪元素清楚法</title>
<style>
.a {
border: 1px solid red;
height: 400px;
}
.b {
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
margin: 5px;
background-color: yellowgreen;
float: left;
}
.c {
background-color: aqua;
height: 300px;
}
.cl::after{
/* 文字,图片 */
content:"";
display: block;
clear: both;
/* 补充写法 */
height: 0px;
/* 隐藏元素 */
visibility: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a cl">
<div class="b"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
</div>
<div class="c">
c
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>清除浮动:双伪元素清楚法</title>
<style>
.a {
border: 1px solid red;
height: 400px;
}
.b {
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
margin: 5px;
background-color: yellowgreen;
float: left;
}
.c {
background-color: aqua;
height: 300px;
}
.cl::before,
.cl::after{
/* 文字,图片 */
content:"";
display: table;
}
.cl::after{
clear: both;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a cl">
<div class="b"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
</div>
<div class="c">
c
</div>
</body>
</html>
浮动
:浮动元素会脱离文档流并向左/向右浮动,直到碰到父元素或者另一个浮动元素。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>nth-of-type</title>
<style>
/* nth-child: 先查数量,后看类型 */
div p:nth-child(5){
color: aqua;
}
/* 先找类型,在查数量 */
div p:nth-of-type(5){
background-color:blueviolet
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>1</p>
<p>2</p>
<p>3</p>
<h3>4</h3>
<p>5</p>
<p>6</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>浮动</title>
<style>
div{
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
}
.a{
background-color: aqua;
}
.b{
background-color: blue;
}
.c{
background-color: aquamarine;
}
.d{
background-color: chartreuse;
}
/* 浮动 */
.a{
float: left;
}
.b{
float: left;
}
.c{
float: left;
}
.d{
float: left;
}
.e{
height: 300px;
width: 100%;
background-color: yellowgreen;
/* both两边 left 左 right 右
none: 不清楚 */
clear: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">a</div>
<div class="b">b</div>
<div class="c">c</div>
<div class="d">d</div>
<div class="e">e</div>
</body>
</html>
固定定位
固定定位
相对于浏览器进行移动
脱离标准文档流
原来的位置不再保留
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>固定定位</title>
<style>
body{
height: 5000px;
background-image: url(../day06/img/女神.jpg);
}
.a{
background-color: aqua;
height: 400px;
width: 100px;
/* 固定定位 */
position: fixed;
right: 0px;
top: 200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<p>
固定定位
相对于浏览器进行移动<br>
脱离标准文档流<br>
原来的位置不再保留<br>
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
+++
+++
css移动端
移动端布局
1.流式布局
2.flex布局
3.rem适配布局
流式布局就是百分比布局,也被称为非固定像素布局。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>h5布局标签</title>
<style>
header {
height: 100px;
background-color: aqua;
}
nav {
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(0, 249, 166);
}
section {
height: 900px;
width: 1240px;
background-color: bisque;
margin: 0 auto;
}
aside {
height: 500px;
width: 50px;
position: fixed;
top: 200px;
left: 0px;
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
footer{
height: 300px;
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<header>
相当于class="header"的div
</header>
<nav>
导航
</nav>
<section>
内容
</section>
<aside>
侧边栏,广告栏
</aside>
<footer>
底部
</footer>
</body>
</html>
过渡
过渡属性要写在没有改变之前的样式中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>transition过渡</title>
<style>
.a {
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid red;
position: relative;
}
.a1 {
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
/* 过渡属性要写在没有改变之前的样式中 */
transition: all 10s;
}
.a:hover .a1 {
left: 1200px;
background-color: #7a7a7a;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<div class="a1"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
旋转
| none | 定义不进行转换。 |
|---|---|
| matrix(n,n,n,n,n,n) | 定义 2D 转换,使用六个值的矩阵。 |
| matrix3d(n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n) | 定义 3D 转换,使用 16 个值的 4x4 矩阵。 |
| translate(x,y) | 定义 2D 转换。 |
| translate3d(x,y,z) | 定义 3D 转换。 |
| translateX(x) | 定义转换,只是用 X 轴的值。 |
| translateY(y) | 定义转换,只是用 Y 轴的值。 |
| translateZ(z) | 定义 3D 转换,只是用 Z 轴的值 |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>旋转</title>
<style>
.a {
height: 400px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
.a1 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color: aqua;
transition: all 3s;
}
.a:hover .a1 {
transform: rotate(3600deg);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<div class="a1">
wery
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
缩放
语法:
transform:scale(x,y)
说明:
x表示元素沿着水平方向(X轴)缩放的倍数,y表示元素沿着垂直方向(Y轴)缩放的倍数。
注意,Y是一个可选参数,如果没有设置Y值,则表示X、Y两个方向的缩放倍数是一样的(同时放大相同倍数)。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>缩放</title>
<style>
.a {
height: 800px;
width: 1200px;
border: 1px solid black;
margin: 0 auto;
overflow: hidden;
}
.a img {
height: 800px;
width: 1200px;
transition: all 1s;
}
.a:hover img {
transform: scale(0.8);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<img src="../test/img/女神.jpg" alt="">
</div>
</body>
</html>
2D转换
rotate() 方法
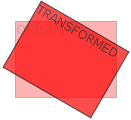
rotate()方法,在一个给定度数顺时针旋转的元素。负值是允许的,这样是元素逆时针旋转
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| matrix(n,n,n,n,n,n) | 定义 2D 转换,使用六个值的矩阵。 |
| translate(x,y) | 定义 2D 转换,沿着 X 和 Y 轴移动元素。 |
| translateX(n) | 定义 2D 转换,沿着 X 轴移动元素。 |
| translateY(n) | 定义 2D 转换,沿着 Y 轴移动元素 |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>2D转换</title>
<style>
.a {
height: 800px;
border: 1px solid red;
position: relative;
}
.a1 {
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
background-color: aqua;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
/* -50%元素自身的50% */
/* transform: translate(100px, 200px); */
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<div class="a1"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
3D转换
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| matrix3d(n,n,n,n,n,n, n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n) | 定义 3D 转换,使用 16 个值的 4x4 矩阵。 |
| translate3d(x,y,z) | 定义 3D 转化。 |
| translateX(x) | 定义 3D 转化,仅使用用于 X 轴的值。 |
| translateY(y) | 定义 3D 转化,仅使用用于 Y 轴的值。 |
| translateZ(z) | 定义 3D 转化,仅使用用于 Z 轴的值。 |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>3d转换</title>
<style>
.a{
height: 800px;
border: 1px solid red;
perspective: 1200px;
}
.a1{
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: yellow;
margin-bottom: 20px;
transition: all 2s;
}
.a2{
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: rgb(15, 238, 246);
transform: translateX(100px) translateY(100px) translateZ(-300px) ;
}
.a:hover .a1{
transform: rotateX(3600deg) rotateY(3600deg) rotateZ(3600deg);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<div class="a1">
啊是电饭锅 <br>
asdfghj <br>
adsffhgj <br>
awsedfghkhjgfdss <br>
qwertuhjhfdsa <br>
</div>
<div class="a2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>3d2.0</title>
<style>
.a {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
border: 1px solid red;
background-color: aqua;
/* 让子元素处于3d空间 */
transform-style: preserve-3d;
transform: rotateX(-30deg) rotateY(45deg);
margin: 100px auto;
position: relative;
/* transition: all 2s linear; */
animation: a 15s linear infinite;
}
.a div {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
}
.a1 {
background-color: blue;
/* 左 */
transform: rotateX(90deg) translateZ(100px);
}
.a2 {
background-color: bisque;
/* 右 */
transform: rotateX(-90deg) translateZ(100px);
}
.a3 {
background-color: rgb(0, 242, 255);
transform: rotatey(90deg) translateZ(100px);
}
.a4 {
background-color: rgb(244, 142, 17);
transform: rotatey(-90deg) translateZ(100px);
}
.a5 {
background-color: rgb(0, 242, 255);
transform: rotatey(360deg) translateZ(100px);
}
.a6 {
background-color: rgb(242, 2, 255);
transform: rotatey(180deg) translateZ(100px);
}
/* .a:hover {
transform: rotateY(-3600deg) rotateX(4500deg);
} */
@keyframes a {
100% {
transform: rotateY(3600deg) rotateX(4500deg);
}
}
.a:hover .a1 {
transform: rotateX(90deg) translateZ(200px);
}
.a:hover .a2 {
transform: rotateX(-90deg) translateZ(200px);
}
.a:hover .a3 {
transform: rotatey(90deg) translateZ(200px);
}
.a:hover .a4 {
transform: rotatey(-90deg) translateZ(200px);
}
.a:hover .a5 {
transform: rotatey(360deg) translateZ(200px);
}
.a:hover .a6 {
transform: rotatey(180deg) translateZ(200px);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<div class="a1"></div>
<div class="a2"></div>
<div class="a3"></div>
<div class="a4"></div>
<div class="a5"></div>
<div class="a6"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
动画
动画是使元素从一种样式逐渐变化为另一种样式的效果。
您可以改变任意多的样式任意多的次数。
请用百分比来规定变化发生的时间,或用关键词 “from” 和 “to”,等同于 0% 和 100%。
0% 是动画的开始,100% 是动画的完成。
为了得到最佳的浏览器支持,您应该始终定义 0% 和 100% 选择器。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>动画</title>
<style>
.a {
height: 600px;
border: 1px solid red;
position: relative;
}
.a1 {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: aqua;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
/* 动画名称 执行时间 延迟时间 执行曲线 */
animation: a1 10s 1s linear infinite alternate;
}
.a2 {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: rgb(179, 225, 225);
position: absolute;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
animation: a2 10s 1s linear infinite alternate;
}
@keyframes a1 {
0% {
left: 0;
top: 0;
background-color: aqua;
}
25% {
left: 482px;
top: 500px;
background-color: rgb(86, 237, 237);
}
50% {
left: 680px;
top: 0px;
background-color: rgb(48, 3, 3);
}
75% {
left: 1246px;
top: 500px;
background-color: rgb(226, 43, 128);
}
100% {
left: 1535px;
top: 0px;
background-color: rgb(53, 40, 23);
}
}
@keyframes a2 {
0% {
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
background-color: aqua;
}
25% {
left: 380px;
bottom: 500px;
background-color: rgb(12, 96, 96);
}
50% {
left: 760px;
bottom: 0px;
background-color: brown;
}
75% {
left: 1146px;
bottom: 500px;
background-color: blueviolet;
}
100% {
left: 1530px;
bottom: 0px;
background-color: burlywood;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<div class="a1"></div>
<div class="a2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
翻转
CSS 的 rotate() 函数定义了一种将元素围绕一个定点(由transform-origin属性指定)旋转而不变形的转换。指定的角度定义了旋转的量度。若角度为正,则顺时针方向旋转,否则逆时针方向旋转。旋转 180° 也被称为点反射。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>翻转</title>
<style>
.a{
background-color: aqua;
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
transition: all 1s;
}
.a:hover{
transform: skew( 30deg, 45deg);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
asdfhd阿萨德高富帅 <br>
阿森松岛方法示范区 <br>
</div>
</body>
</html>
布局
百分比,流失布局
- 流式布局,就是百分比布局,也称非固定像素布局
- 通过将盒子的宽度设置成百分比,从而根据屏幕的宽度来进行伸缩,不受固定像素的限制,内容向两侧填充
- 流式布局的方式是移动web开发使用比较常见的布局方式
注意事项
- 制作过程中,需要定义页面的最大和最小支持宽度
- Max-width 最大宽度(max-height最大高度)
- Min-width 最小宽度 (min-height最小高度)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>百分比,流式布局</title>
<style>
ul {
list-style: none;
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
width: 100%;
}
ul li {
float: left;
height: 60px;
width: 20%;
text-align: center;
}
ul li img {
height: 60px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li><img src="img/car.png" alt=""></li>
<li><img src="img/classify.png" alt=""></li>
<li><img src="img/index.png" alt=""></li>
<li><img src="img/jd.png" alt=""></li>
<li><img src="img/login.png" alt=""></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
flex布局
- 1、在不同方向排列元素
- 2、重新排列元素的显示顺序
- 3、更改元素的对齐方式
- 4、动态地将元素装入容器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>flex布局</title>
<style>
ul{
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
list-style: none;
/* 给父元素加上弹性布局 :
把父元素变成了弹性容器
父元素的直接子元素会变成弹性盒子
弹性盒子默认延主轴方向排列相当于添加了一个浮动*/
display: flex;
/* 从终点开始排列 */
justify-content: flex-end;
/* 主轴居中 */
justify-content: center;
/* 空白间距均匀分在弹性盒子两测 */
justify-content: space-around;
/* 空白间距均分在相邻盒子之间 */
justify-content: space-between;
/* 弹性盒子与容器之间间距相等 */
justify-content: space-evenly;
}
img{
height: 40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li><img src="img/classify.png" alt=""></li>
<li><img src="img/classify.png" alt=""></li>
<li><img src="img/classify.png" alt=""></li>
<li><img src="img/classify.png" alt=""></li>
<li><img src="img/classify.png" alt=""></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
垂直布局
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>垂直布局</title>
<style>
.a{
display: flex;
border-bottom: 2px solid black;
/* 改变主轴方向:垂直 */
flex-direction: column;
/* 侧轴居中 */
align-items: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
<img src="img/media.png" alt="">
<p>媒体</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
waper
当网页缩小到页面不足以容纳元素的排列,使盒子中的元素压缩,失去原来的形状,希望能换行展示,则使用
flex-wrap:wrap;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>waper</title>
<style>
body{
margin: 0;
}
ul {
list-style: none;
width: 100%;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
display: flex;
text-align: center;
/* 允许弹性盒子换行 */
flex-wrap: wrap;
/* 主轴对齐 */
justify-content: space-evenly;
/* 行的对齐 */
align-content: space-evenly;
height: 500px;
}
li {
padding: 5px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>
<img src="img/media.png" alt="">
<p>asdf</p>
</li>
<li>
<img src="img/media.png" alt="">
<p>asdf</p>
</li>
<li>
<img src="img/media.png" alt="">
<p>asdf</p>
</li>
<li>
<img src="img/media.png" alt="">
<p>asdf</p>
</li>
<li>
<img src="img/media.png" alt="">
<p>asdf</p>
</li>
<li>
<img src="img/media.png" alt="">
<p>asdf</p>
</li>
<li>
<img src="img/media.png" alt="">
<p>asdf</p>
</li>
<li>
<img src="img/media.png" alt="">
<p>asdf</p>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
rem用法
单位
rem是根元素字体的单位,比如 html{font-size:16px;} ,1rem相当于16px
放弃px单位,使用rem作为单位,这样在不同尺寸的设备上,通过修改根节点的font-size大小,实现等比例缩放
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>rem单位</title>
<style>
/* 1rem= 1html-fontsize */
html{
font-size: 16px;
}
.a{
height: 10rem;
width: 20rem;
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a"></div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>rem用法</title>
<style>
/* rem的宽度是视口宽度的1/9 */
@media (width:375px) {
html {
font-size: 37.5px;
}
}
@media (width:1024px) {
html {
font-size: 102.4px;
}
}
@media (width:414px) {
html {
font-size: 41.4px;
}
}
.a {
height: 5rem;
width: 5rem;
background-color: yellowgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">
阿萨德
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
@media(width:375px){
html{
font-size: 37.5px;
}
html{
font-size: 14px;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a"></div>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
@media(width:375px){
html{
font-size: 37.5px;
}
html{
font-size: 14px;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a"></div>
</body>
</html>
vw/vh
- vw:1vw 等于视口宽度的1%
- Vh:1vh 等于视口高度的1%
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>vm/vh</title>
<style>
.a{
background-color: aqua;
/* 1vw=1/100 的视口宽度 */
/* width: 10vw;
height: 10vh; */
width: 18.6667vw;
height: 4.4977vh;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a"></div>
<img src="img/0d44bda8f549ad652e58387442a0b4b3_5207495995630505697.webp" alt="">
</body>
</html>
补充\
big 大字号
small 小字号
kbd 键入
samp 定义计算机代码样本
q 短的引用
blockquote 定义长的引用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>补充</title>
</head>
<body>
<big>大字号</big>
<small>小字号</small><br>
<code>
var a=33;
var b-66;
let a:string='你好';
</code>
<kbd>键入</kbd>
<samp>定义计算机代码样本</samp>
<samp>ae</samp>
<tt>打印机代码</tt>
<var>定义变量</var>
<pre>
定义预格式文本
格式和书写样式一样
会随着内容 样式改变而改变
</pre>
<abbr title="asdfgdsefsdtrwf">asdfh</abbr>
<acronym title="qwertesd">wefhg</acronym>
<address>地址:阿斯蒂芬规划局可</address>
<bdo dir="rtl">定义文字方向 ltr默认 rtl 从右到左</bdo>
<blockquote>
定义长的引用
</blockquote>
<q>短的引用</q>
<cite>阿斯蒂芬规划局可------保尔 </cite>
<dfn>dnf</dfn>
<img src="img/0d44bda8f549ad652e58387442a0b4b3_5207495995630505697.webp" alt="">
<map name="plnetmap" id="plnetmap">
<area shape="circle" coords="100,100,300" href="#" alt="venus">
<area shape="circle" coords="100,100,300" href="#" alt="venus">
<area shape="rect" coords="100,100,300" href="#" alt="venus">
</map>
<!-- 表格 -->
<table border="1" width="700px" height="300px">
<col align="left" />
<col align="content" />
<col align="right" />
<col align="left" />
<col align="left" />
<tr>
<td>1</td>
<td>1</td>
<td>1</td>
<td>1</td>
<td>1</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
</table>
<table width="100%" border="1">
<colgroup span="2" align="left"></colgroup>
<colgroup align="right" style="color: antiquewhite;"></colgroup>
<tr>
<th>1</th>
<th>1</th>
<th>1</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>1</th>
<th>1</th>
<th>1</th>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
samp 定义计算机代码样本
q 短的引用
blockquote 定义长的引用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>补充</title>
</head>
<body>
<big>大字号</big>
<small>小字号</small><br>
<code>
var a=33;
var b-66;
let a:string='你好';
</code>
<kbd>键入</kbd>
<samp>定义计算机代码样本</samp>
<samp>ae</samp>
<tt>打印机代码</tt>
<var>定义变量</var>
<pre>
定义预格式文本
格式和书写样式一样
会随着内容 样式改变而改变
</pre>
<abbr title="asdfgdsefsdtrwf">asdfh</abbr>
<acronym title="qwertesd">wefhg</acronym>
<address>地址:阿斯蒂芬规划局可</address>
<bdo dir="rtl">定义文字方向 ltr默认 rtl 从右到左</bdo>
<blockquote>
定义长的引用
</blockquote>
<q>短的引用</q>
<cite>阿斯蒂芬规划局可------保尔 </cite>
<dfn>dnf</dfn>
<img src="img/0d44bda8f549ad652e58387442a0b4b3_5207495995630505697.webp" alt="">
<map name="plnetmap" id="plnetmap">
<area shape="circle" coords="100,100,300" href="#" alt="venus">
<area shape="circle" coords="100,100,300" href="#" alt="venus">
<area shape="rect" coords="100,100,300" href="#" alt="venus">
</map>
<!-- 表格 -->
<table border="1" width="700px" height="300px">
<col align="left" />
<col align="content" />
<col align="right" />
<col align="left" />
<col align="left" />
<tr>
<td>1</td>
<td>1</td>
<td>1</td>
<td>1</td>
<td>1</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
</table>
<table width="100%" border="1">
<colgroup span="2" align="left"></colgroup>
<colgroup align="right" style="color: antiquewhite;"></colgroup>
<tr>
<th>1</th>
<th>1</th>
<th>1</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>1</th>
<th>1</th>
<th>1</th>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








