一:背景
平衡二叉树(又称AVL树)是二叉查找树的一个进化体,由于二叉查找树不是严格的O(logN),所以引入一个具有平衡概念的二叉树,它的查找速度是O(logN)。所以在学习平衡二叉树之前,读者必须需要了解下二叉查找树,具体链接:二叉查找树
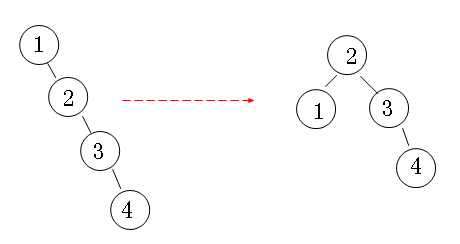
那么平衡是什么意思?我们要求对于一棵二叉查找树 ,它的每一个节点的左右子树高度之差不超过1。(对于树的高度的约定:空节点高度是0;叶子节点高度是1。)例如下图:
在进行下面的分析之前,我们先对AVL树作个概述,让读者先了解其运作机制,而后读者接下来的阅读才会容易许多。
我们为何说普通的二叉查找树不是严格的O(logN)复杂度呢?可以试想,如果我们插入的是一组有序上升或下降的数据,必然造成二叉查找树退化成一个单链表,其深度就是链表长度,查找效率为O(n),与我们想要的O(logN)比起相形见绌,因此我们想到“平衡”这个概念,继而引入二叉查找树,这就是我们接下来要讲的“平衡二叉树”,上图已经完美诠释了“平衡”的概念,读者可以再看一遍。
讲到平衡,那又如何去平衡呢?如何判断失衡呢?判断失衡很简单,我们只需在节点里加个变量,不妨设为m_height,其意义是该节点下的树的高度,在插入数据或者删除数据时我们要判断这个节点的左右儿子节点的高度之差是否大于1即可。
当我们发现该节点不平衡,我们自然需要对其做些处理,使其满足平衡。经过分析,在插入数据或者删除数据时只会有四种失衡的情况,所以我们需要对这四种情况分别写出应对的代码。这也就是我们第二部分即将要讲的四种应对之策----旋转。旋转学完,接下来的内容就不是很难了,无非就是插入,删除,查找,打印了,和二叉查找树差不多,唯一的区别就是判断失衡和失衡后的旋转,代码都有注释,一看就懂。
好,接下来先看下我们给AVL树定义的节点结构,代码如下:
typedef struct Node
{
int m_key;
int m_height;
Node* m_lChild;
Node* m_rChild;
Node(int key)
{
m_key = key;
m_height = 1;
m_rChild = m_lChild = nullptr;
}
}* PNode;
二:旋转算法
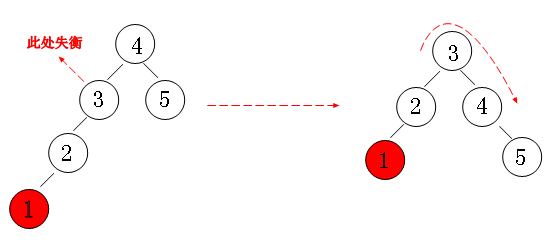
1.左左情况
节点3的左子树比右子树高2,左节点2的左子树比右子树高,这称为左左情况。
/* 左左情况,p指向失衡点,即图例中3 */
PNode LL_Rotate(PNode & p)
{
cout << "LL\n";
PNode top = p->m_lChild;
p->m_lChild = top->m_rChild;
top->m_rChild = p;
p->m_height = max(Height(p->m_lChild), Height(p->m_rChild)) + 1;
top->m_height = max(Height(top->m_lChild), Height(top->m_rChild)) + 1;
return top;
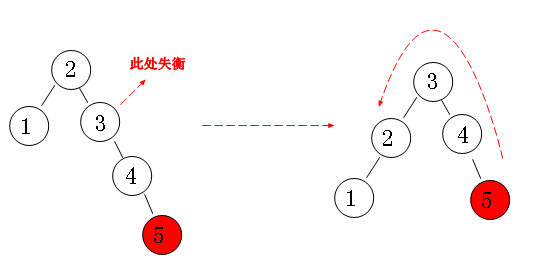
}2.右右情况
节点3的右子树比左子树高2,右节点4的右子树比左子树高,这称为右右情况。
/* 右右情况,p指向失衡点,即图例中3 */
PNode RR_Rotate(PNode & p)
{
cout << "RR\n";
PNode top = p->m_rChild;
p->m_rChild = top->m_lChild;
top->m_lChild = p;
p->m_height = max(Height(p->m_lChild), Height(p->m_rChild)) + 1;
top->m_height = max(Height(top->m_lChild), Height(top->m_rChild)) + 1;
return top;
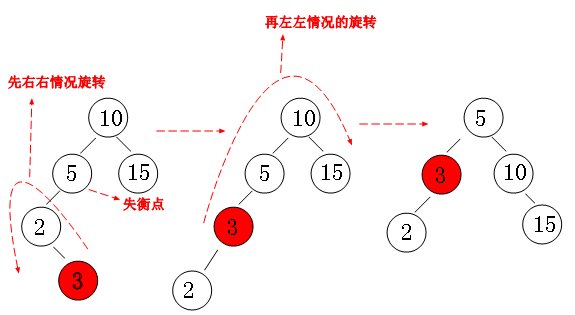
}3.左右情况
节点5的左子树比右子树高2,左节点2的右子树比左子树高,这称为左右情况。
/* 左右情况,p指向失衡点,即图例中5 */
PNode LR_Rotate(PNode & p)
{
cout << "LR\n";
p->m_lChild = RR_Rotate(p->m_lChild);
return LL_Rotate(p);
}4.右左情况
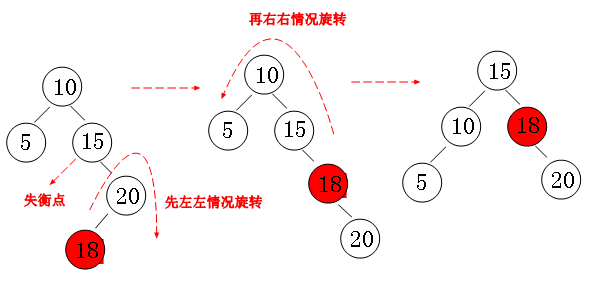
节点15的右子树比左子树高2,右节点20的左子树比右子树高,这称为右左情况。
/* 右左情况,p指向失衡点,即图例中15 */
PNode RL_Rotate(PNode & p)
{
cout << "RL\n";
p->m_rChild = LL_Rotate(p->m_rChild);
return RR_Rotate(p);
}三:其它算法实现
在写之前,先看两个辅助函数:
/* 计算当前节点的高度 */
int Height(PNode & p)
{
return (p == nullptr) ? 0 : p->m_height;
}
/* 找到该节点下的最小值节点,返回该最小值,注意参数不是引用传递 */
int FindMin(PNode p)
{
while (p->m_lChild)
p = p->m_lChild;
return p->m_key;
}1.插入
利用递归,我们先将节点插入,插入成功即递归结束,在一层一层的结束时,然后判断经过的每个节点的左右子树高度差,进行调整。
/* 添加操作 */
bool Add(int key, PNode & p)
{
if (p == nullptr)
{
p = new Node(key);
return true;
}
else
{
if (key == p->m_key)//已存在,直接退出
return false;
if (key < p->m_key)//左子树
{
if (Add(key, p->m_lChild))//是否成功插入
{
if (Height(p->m_lChild) - Height(p->m_rChild) == 2)//高度差等于2,得旋转调整
{
if (key < p->m_lChild->m_key)
p = LL_Rotate(p);//左左情况
else
p = LR_Rotate(p);//左右情况
}
p->m_height = max(Height(p->m_lChild), Height(p->m_rChild)) + 1;//更新高度
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
else //右子树
{
if (Add(key, p->m_rChild))
{
if (Height(p->m_lChild) - Height(p->m_rChild) == -2)
{
if (key > p->m_rChild->m_key)
p = RR_Rotate(p);
else
p = RL_Rotate(p);
}
p->m_height = max(Height(p->m_lChild), Height(p->m_rChild)) + 1;//更新高度
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
}
}2.删除
删除的节点一共三种类型:有左右孩子;没有左右孩子;只有一个孩子(左或者右)。
其中对于第一种情况,也就是该节点是有左右孩子的,这里用了一个巧妙的方法,利用转化的思想,具体看代码,把这种情况转化为第二种或第三种。
/* 删除操作 */
bool Delete(int key, PNode & p)
{
if (p == nullptr)
return false;
else
{
if (key == p->m_key)//找到该点
{
if (p->m_lChild && p->m_rChild)//左右孩子都存在
{
p->m_key = FindMin(p->m_rChild);//找到该节点下的最小节点
Delete(p->m_key, p->m_rChild);//转化为: 删除找到的这个最小节点
}
else if (!p->m_lChild && !p->m_rChild)//左右孩子都不存在
{
PNode t = p;//注意p是引用类型
p = nullptr;
delete t;
return true;
}
else//左右孩子只存在一个
{
PNode t = p;
p = (p->m_lChild == nullptr) ? p->m_rChild : p->m_lChild;
delete t;
return true;
}
}
else if (key < p->m_key)//在左子树删除
{
if (Delete(key, p->m_lChild))
{
if (Height(p->m_lChild) - Height(p->m_rChild) == 2)
{
if (key < p->m_lChild->m_key)
p = LL_Rotate(p);
else
p = LR_Rotate(p);
}
p->m_height = max(Height(p->m_lChild), Height(p->m_rChild)) + 1;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
else//在右子树删除
{
if (Delete(key, p->m_rChild))
{
if (Height(p->m_lChild) - Height(p->m_rChild) == -2)
{
if (key > p->m_rChild->m_key)
p = RR_Rotate(p);
else
p = RL_Rotate(p);
}
p->m_height = max(Height(p->m_lChild), Height(p->m_rChild)) + 1;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
}
}3.查找
/* 查找操作 */
bool Find(int key, PNode & p)
{
if (p == nullptr)
return false;
else
{
if (key == p->m_key)
return true;
else if (key < p->m_key)
return Find(key, p->m_lChild);
else
return Find(key, p->m_rChild);
}
}4.层次遍历
/* 层次遍历,和普通的层次遍历不一样,打印的结果模拟了树的形状 */
void PrintTheLevel(PNode & p, int level)
{
if (p == nullptr || level <= 0)
return;
if (level == 1)
{
cout << p->m_key << "," << p->m_height << " ";//输出节点及对应的高度
return;
}
PrintTheLevel(p->m_lChild, level - 1);
PrintTheLevel(p->m_rChild, level - 1);
}
void LevelOrder(PNode & p)
{
int depth = Height(p);
for (int i = 1; i <= depth; i++)
{
PrintTheLevel(p, i);//打印树的第i行
cout << endl;
}
}
四:完整代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE
#define _CRT_SECURE_CPP_OVERLOAD_STANDARD_NAMES 1
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node
{
int m_key;
int m_height;
Node* m_lChild;
Node* m_rChild;
Node(int key)
{
m_key = key;
m_height = 1;
m_rChild = m_lChild = nullptr;
}
}* PNode;
PNode pRoot = nullptr;//根节点
/* 计算当前节点的高度 */
int Height(PNode & p)
{
return (p == nullptr) ? 0 : p->m_height;
}
/* 找到该节点下的最小值节点,返回该最小值,注意参数不是引用传递 */
int FindMin(PNode p)
{
while (p->m_lChild)
p = p->m_lChild;
return p->m_key;
}
/* 左左情况 */
PNode LL_Rotate(PNode & p)
{
cout << "LL\n";
PNode top = p->m_lChild;
p->m_lChild = top->m_rChild;
top->m_rChild = p;
p->m_height = max(Height(p->m_lChild), Height(p->m_rChild)) + 1;
top->m_height = max(Height(top->m_lChild), Height(top->m_rChild)) + 1;
return top;
}
/* 右右情况 */
PNode RR_Rotate(PNode & p)
{
cout << "RR\n";
PNode top = p->m_rChild;
p->m_rChild = top->m_lChild;
top->m_lChild = p;
p->m_height = max(Height(p->m_lChild), Height(p->m_rChild)) + 1;
top->m_height = max(Height(top->m_lChild), Height(top->m_rChild)) + 1;
return top;
}
/* 左右情况 */
PNode LR_Rotate(PNode & p)
{
cout << "LR\n";
p->m_lChild = RR_Rotate(p->m_lChild);
return LL_Rotate(p);
}
/* 右左情况 */
PNode RL_Rotate(PNode & p)
{
cout << "RL\n";
p->m_rChild = LL_Rotate(p->m_rChild);
return RR_Rotate(p);
}
/* 添加操作 */
bool Add(int key, PNode & p)
{
if (p == nullptr)
{
p = new Node(key);
return true;
}
else
{
if (key == p->m_key)//已存在,直接退出
return false;
if (key < p->m_key)//左子树
{
if (Add(key, p->m_lChild))//是否成功插入
{
if (Height(p->m_lChild) - Height(p->m_rChild) == 2)//高度差等于2,得旋转调整
{
if (key < p->m_lChild->m_key)
p = LL_Rotate(p);//左左情况
else
p = LR_Rotate(p);//左右情况
}
p->m_height = max(Height(p->m_lChild), Height(p->m_rChild)) + 1;//更新高度
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
else //右子树
{
if (Add(key, p->m_rChild))
{
if (Height(p->m_lChild) - Height(p->m_rChild) == -2)
{
if (key > p->m_rChild->m_key)
p = RR_Rotate(p);
else
p = RL_Rotate(p);
}
p->m_height = max(Height(p->m_lChild), Height(p->m_rChild)) + 1;//更新高度
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
}
}
/* 删除操作 */
bool Delete(int key, PNode & p)
{
if (p == nullptr)
return false;
else
{
if (key == p->m_key)//找到该点
{
if (p->m_lChild && p->m_rChild)//左右孩子都存在
{
p->m_key = FindMin(p->m_rChild);//找到该节点下的最小节点
Delete(p->m_key, p->m_rChild);//转化为: 删除找到的这个最小节点
}
else if (!p->m_lChild && !p->m_rChild)//左右孩子都不存在
{
PNode t = p;//注意p是引用类型
p = nullptr;
delete t;
return true;
}
else//左右孩子只存在一个
{
PNode t = p;
p = (p->m_lChild == nullptr) ? p->m_rChild : p->m_lChild;
delete t;
return true;
}
}
else if (key < p->m_key)//在左子树删除
{
if (Delete(key, p->m_lChild))
{
if (Height(p->m_lChild) - Height(p->m_rChild) == 2)
{
if (key < p->m_lChild->m_key)
p = LL_Rotate(p);
else
p = LR_Rotate(p);
}
p->m_height = max(Height(p->m_lChild), Height(p->m_rChild)) + 1;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
else//在右子树删除
{
if (Delete(key, p->m_rChild))
{
if (Height(p->m_lChild) - Height(p->m_rChild) == -2)
{
if (key > p->m_rChild->m_key)
p = RR_Rotate(p);
else
p = RL_Rotate(p);
}
p->m_height = max(Height(p->m_lChild), Height(p->m_rChild)) + 1;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
}
}
/* 查找操作 */
bool Find(int key, PNode & p)
{
if (p == nullptr)
return false;
else
{
if (key == p->m_key)
return true;
else if (key < p->m_key)
return Find(key, p->m_lChild);
else
return Find(key, p->m_rChild);
}
}
/* 层次遍历,和普通的层次遍历不一样,打印的结果模拟了树的形状 */
void PrintTheLevel(PNode & p, int level)
{
if (p == nullptr || level <= 0)
return;
if (level == 1)
{
cout << p->m_key << "," << p->m_height << " ";//输出节点及对应的高度
return;
}
PrintTheLevel(p->m_lChild, level - 1);
PrintTheLevel(p->m_rChild, level - 1);
}
void LevelOrder(PNode & p)
{
int depth = Height(p);
for (int i = 1; i <= depth; i++)
{
PrintTheLevel(p, i);
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
return 0;
}
数据测试方面,请读者自行设计数据,针对各算法进行测试,博主设计的多组数据运行均正确。
若程序有错,请一定底下留言,博主会及时回复,谢谢。
返回目录---->数据结构与算法目录
图片资源来自及参考自:
http://www.cppblog.com/cxiaojia/archive/2012/08/20/187776.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/huangxincheng/archive/2012/07/22/2603956.html
























 1121
1121

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








