【实验目的】
- 理解哈夫曼树的特征及其应用;
- 学会哈夫曼树的构造并利用构造的哈夫曼树进行编码和译码
- 练习字符的哈夫曼树编码及存储,字符的译码与串的匹配算法。
【实验原理】
-
哈夫曼树的构建过程是从一个集合中不断挑选权值两个最小的元素,生成新的结点,加入集合中再循环直到为空。
-
哈弗曼编码即沿着哈弗曼树的根节点往下走,左0右1。一个字符串转换成哈弗曼编码即在构建好的哈弗曼树中遍历字符对应的01编码。
-
C++语言中,用ifstream实现文件读操作,用ofstream实现写操作。getline实现按行读取。
【实验内容】
-
问题描述:利用哈夫曼编码进行通信可以大大提高信道利用率,缩短信息传输时间,降低传输成本。但是,这要求在发送端通过一个编码系统对待传数据预先编码,在接收端将传来的数据进行译码(解码)。对于双工信道(即可以双向传输信息的信道),每端都需要一个完整的编/译码系统。试为这样的信息收发站设计一个哈夫曼编译码系统。
-
基本要求 :
(1)初始化(Initialzation)。从数据文件DataFile.data中读入字符及每个字符的权值,建立哈夫曼树HuffTree;
(2)编码(EnCoding)。用已建好的哈夫曼树,对文件ToBeTran.data中的文本进行编码形成报文,将报文写在文件Code.txt中;
(3)译码(Decoding)。利用已建好的哈夫曼树,对文件CodeFile.data中的代码进行解码形成原文,结果存入文件Textfile.txt中;
(4)输出(Output)。输出DataFile.data中出现的字符以及各字符出现的频度(或概率);输出ToBeTran.data及其报文Code.txt;输出CodeFile.data及其原文Textfile.txt; -
重点、难点
重点:
(1)通过实验理解哈夫曼树的特征及其应用;
(2)哈夫曼树的构造算法设计;
(3)利用构造的哈夫曼树进行编码和译码。
难点:
(1)字符的哈夫曼树编码及存储;
(2)字符的译码与串的匹配算法。
【程序代码与运行结果】
Huffman.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define OK 1
#define ERR 0
#define MAXSIZE 200
int weight[MAXSIZE];
string list;
int len;//当前字符串的长度
int TreeNum = 0;//标记是否成功创建哈夫曼树
typedef struct
{
int weight;
int parent, lchild, rchild;
}HTNode, *HuffmanTree;
typedef char **HuffmanCode;
//选择两个双亲域为0且权值最小的结点
void Select(HuffmanTree HTree, int end, int &s1, int &s2)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= end; i++)
{
if (HTree[i].parent == 0)
{
s1 = i;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= end; i++)
{
if (HTree[i].weight < HTree[s1].weight && HTree[i].parent == 0)
s1 = i;//最小权值
}
for (int i = 1; i <= end; i++)
{
if (HTree[i].parent == 0 && i != s1)
{
s2 = i;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= end; i++)
{
if (HTree[i].weight < HTree[s2].weight && i != s1 && HTree[i].parent == 0)
s2 = i;//次小权值
}
}
//初始化哈夫曼树
void InitTree(HuffmanTree &HTree)
{
list.clear();
string filename = "测试文件//DataFile.data";
ifstream infile(filename.c_str());
getline(infile, list); //读取第一行的字符
len = list.length();
cout << "读入的字符串:";
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++)
{
list[i] == ' ' ? cout << "\' \' " : cout << list[i] << " ";
}
//初始化哈夫曼树
if (len <= 1) return;
HTree = new HTNode[2 * len];
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * len - 1; i++)
{
HTree[i].parent = 0;
HTree[i].lchild = 0;
HTree[i].rchild = 0;
}
//对一行由空格分开的数字字符串进行分割和转换
string weight;
getline(infile, weight);//读取文件中第二行的权重
vector<int> res;
while (!weight.empty())
{
if (weight.find(" ") == string::npos)
{
res.push_back(stoi(weight));
weight.clear();
break;//将最后一个整数字符转换为数字加入数组后结束循环
}
string s_temp = weight.substr(0, weight.find(" "));
res.push_back(stoi(s_temp));
weight.erase(0, weight.find(" ") + 1); //通过find函数删除空格
}
cout << "\n对应的权值:";
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++)
{
HTree[i].weight = res[i - 1];
cout << HTree[i].weight << " ";
}
cout << endl;
infile.close();//读取完毕后关闭文件
//构建哈夫曼树
for (int i = len + 1; i <= 2 * len - 1; i++)
{
int s1, s2;
Select(HTree, i - 1, s1, s2);
HTree[s1].parent = i;
HTree[s2].parent = i;
HTree[i].lchild = s1; HTree[i].rchild = s2;
HTree[i].weight = HTree[s1].weight + HTree[s2].weight;
}
//打印哈夫曼树
cout << "\n\n" << endl;
cout << " 哈夫曼树如下" << endl;
cout << "序号---" << "字符---" << "权值---" << "双亲---" << "左孩子---" << "右孩子---" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * len - 1; i++)
{
if (i <= len)
cout << i << " " << list[i - 1] << " " << HTree[i].weight << " " << HTree[i].parent << " " << HTree[i].lchild << " " << HTree[i].rchild << endl;
if (i > len)
cout << i << " " << HTree[i].weight << " " << HTree[i].parent << " " << HTree[i].lchild << " " << HTree[i].rchild << endl;
}
TreeNum = 1;
}
//哈夫曼编码
void EnCoding(HuffmanTree HTree, HuffmanCode& HCode)
{
//逐个求解l个字符的编码
char *cd;
int start, c, f;
HCode = new char*[len + 1];//0-n,0不用
cd = new char[len];
cd[len - 1] = '\0';
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++)
{
start = len - 1;
c = i; f = HTree[i].parent;
while (f != 0)
{
--start;
if (HTree[f].lchild == c) cd[start] = '0';
else cd[start] = '1';
c = f; f = HTree[f].parent;
}
HCode[i] = new char[len - start];
strcpy(HCode[i], &cd[start]);
}
delete cd;
cout << " 序号" << " 字符" << " 哈夫曼码" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++)
{
int j = 0;
cout << " " << i << " (" << list[i - 1] << ") ";
while (HCode[i][j] != '\0')
{
cout << HCode[i][j];
j++;
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//读取文件ToBeTran.data,将文本编码成报文
ifstream tobetran("测试文件//ToBeTran.data");
string Tobetran;
getline(tobetran, Tobetran);
cout << "读取ToBeTran.data:" << Tobetran << endl;
ofstream code("测试文件//Code.txt");
for (int i = 0; i < Tobetran.length(); i++)//每一个字符
{
int i_index;
if (list.find(Tobetran[i]) != EOF)
i_index = list.find(Tobetran[i]) + 1;//对于这个字符,在哈夫曼树中找到这个字符
else
{
cout << "在您构造的哈夫曼树中找不到字符 '" << Tobetran[i] << "' !" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "'" << Tobetran[i] << "' index:" << i_index << " " << "code:";
int j = 0;
while (HCode[i_index][j] != '\0')
{
code << HCode[i_index][j];//将得到的编码写入Code.txt中
cout << HCode[i_index][j];
j++;
}//每一个字符的哈夫曼编码
cout << endl;
}
cout << " 编码已成功写入Code.txt文件中!" << endl;
code.close();
}
//哈夫曼译码
void Decoding(HuffmanTree HTree)
{
string str;
ifstream codefile("测试文件//CodeFile.data");
getline(codefile, str);
cout << "读取CodeFile.data:" << str << endl;
ofstream textfile("测试文件//Textfile.txt");
cout << "译码结果为:";
int i = 0;
int q = 2 * len - 1;//根节点下标
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
if (str[i] == '0') {
q = HTree[q].lchild;
}
else if (str[i] == '1') {
q = HTree[q].rchild;
}
if (HTree[q].lchild == 0 && HTree[q].rchild == 0)
{//当该节点为叶子节点时
textfile << list[q - 1];
cout << list[q - 1];
q = 2 * len - 1;
}
}
cout << "\n译码结果已保存在Textfile.txt中!" << endl;
}
//显示输出所有文件
void ShowAll(HuffmanTree HTree, HuffmanCode& HCode)
{
cout << "\n" << endl;
cout << "// DataFile.data" << endl;
float sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++)
{
sum = sum + HTree[i].weight;
}
cout << "字符---权重----频度" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << list[i] << " " << HTree[i + 1].weight << " " << HTree[i + 1].weight / sum << endl;
}
string temp;
cout << "\n" << endl;
cout << "// ToBeTran.data" << endl;
ifstream buff1("测试文件//ToBeTran.data");
getline(buff1, temp);
cout << temp << endl;
buff1.close();
temp.clear();
cout << "// Code.txt" << endl;
ifstream buff2("测试文件//Code.txt");
getline(buff2, temp);
cout << temp << endl;
buff2.close();
temp.clear();
cout << "\n" << endl;
cout << "// CodeFile.data" << endl;
ifstream buff3("测试文件//CodeFile.data");
getline(buff3, temp);
cout << temp << endl;
buff3.close();
temp.clear();
cout << "// Textfile.txt" << endl;
ifstream buff4("测试文件//Textfile.txt");
getline(buff4, temp);
cout << temp << endl;
buff4.close();
temp.clear();
}
void main()
{
HuffmanTree hTree = NULL;
HuffmanCode hCode;
int num;
while (true)
{
cout << "\n" << endl;
cout << "■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■" << endl;
cout << "----------创建哈夫曼树请选1-------------" << endl;
cout << "------------进行编码请选2---------------" << endl;
cout << "------------进行译码请选3---------------" << endl;
cout << "------------输出结果请选4---------------" << endl;
cout << "------------结束程序请选5---------------" << endl;
cout << "■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■■" << endl;
cout << "选择:";
cin >> num;
switch (num)
{
case 1:
{
cout << "\n============================================================" << endl;
InitTree(hTree);
cout << "============================================================\n\n" << endl;
}break;
case 2:
{
if (TreeNum == 0)
{
cout << "哈夫曼树尚未创建!" << endl;
break;
}
cout << "\n============================================================" << endl;
cout << " Huffman Encode\n" << endl;
EnCoding(hTree, hCode);
cout << "============================================================\n\n" << endl;
}break;
case 3:
{
if (TreeNum == 0)
{
cout << "哈夫曼树尚未创建!" << endl;
break;
}
cout << "\n============================================================" << endl;
cout << " Huffman Decode\n" << endl;
Decoding(hTree);
cout << "============================================================\n\n" << endl;
}break;
case 4:
{
cout << "\n============================================================" << endl;
ShowAll(hTree, hCode);
cout << "============================================================\n" << endl;
}break;
case 5:
{
exit(0);
}break;
}
}
}
测试文件资源已上传至这里
哈夫曼树构建
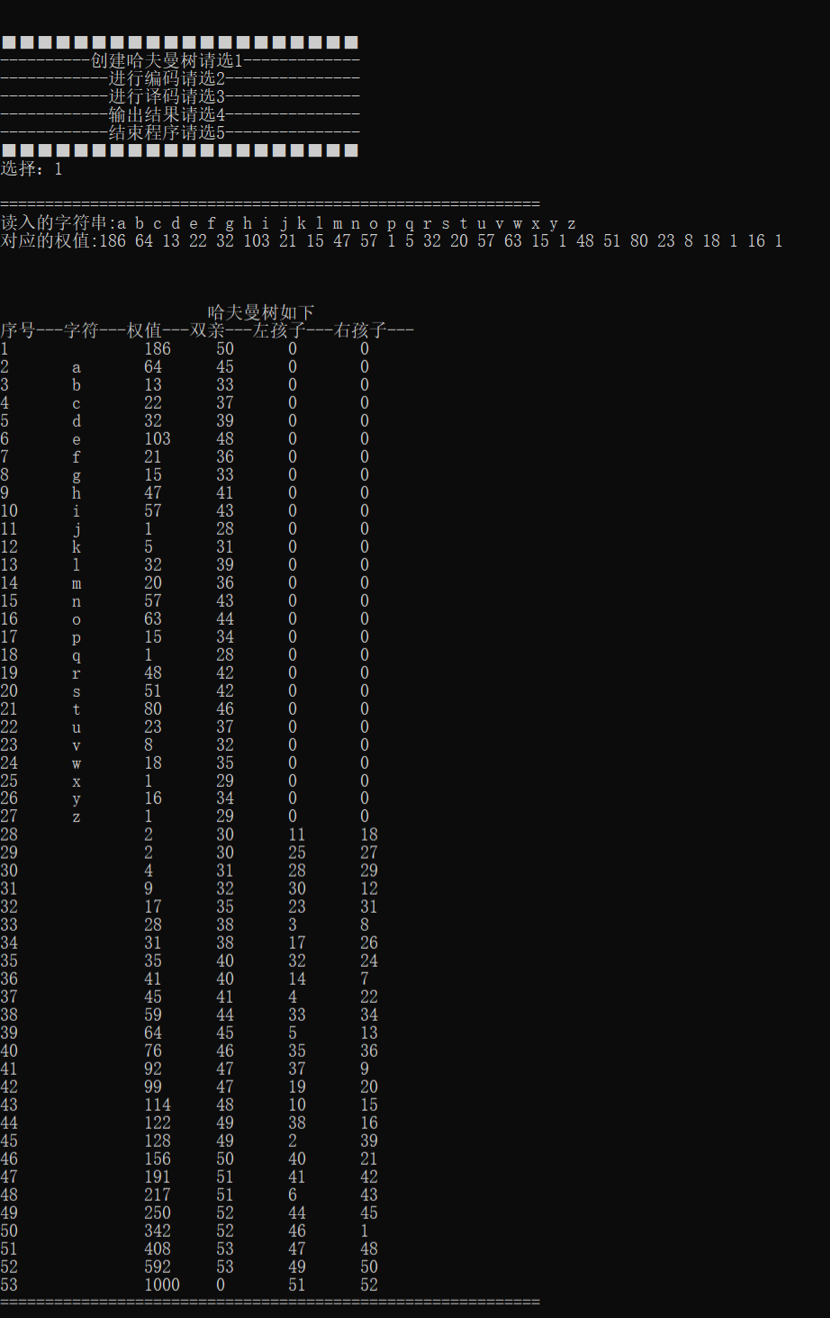
编码


译码

查看测试文件和生成文件

这次实验中最大的挑战主要在文件的读写上,第一次接触文件读写,不知道使用UTF格式,文件愣是读不出来。。。
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








