Linux102系列会详细讲解Linux0.11版本中的102个文件,本文讲解linux0.11的第11个文件
kernel/vsprintf.c的文件源码。
1.vsprintf的主要作用
一句话:格式化字符串输出函数,主要作用是将可变参数列表按照指定格式转换为字符串并存储到指定的缓冲区中。
2.vsprintf用到的其他头文件解释
| stdarg.h | 移步:【Linux102】12-include/stdarg.h 可变参数机制实现 |
| string.h | 知识屏蔽,暂时不讲,知道其作用为字符串操作就好。 |
3.源码注释版本
/*
* linux/kernel/vsprintf.c
*
* (C) 1991 Linus Torvalds
*/
/* vsprintf.c -- Lars Wirzenius & Linus Torvalds. */
/*
* Wirzenius wrote this portably, Torvalds fucked it up :-)
*/
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
/* we use this so that we can do without the ctype library */
// 用于判断字符是否为数字。
#define is_digit(c) ((c) >= '0' && (c) <= '9')
// 跳过字符串中的数字字符,返回数字的整数值。
// 例如100xx,返回100
static int skip_atoi(const char **s)
{
int i = 0;
while (is_digit(**s))
i = i * 10 + *((*s)++) - '0';
return i;
}
// 这就是我们常说的,输出的格式控制。
// 格式化标志位(控制输出格式的开关)。
// 这些宏是位标志(每个宏对应一个二进制位),通过位运算(| 组合、& 判断)可以同时控制多种格式化规则。
// 例如 flags = ZEROPAD | PLUS 表示 “零填充且显示正号”。
// 这里对应了8位二进制数,每个位代表一种格式化规则。
// 利用位来代替规则的开关,通过位运算可以同时控制多种格式化规则。很妙的。
#define ZEROPAD 1 /* pad with zero,零填充 */
#define SIGN 2 /* unsigned/signed long ,有符号/无符号长整数 */
#define PLUS 4 /* show plus,展示加号 */
#define SPACE 8 /* space if plus,展示空格 */
#define LEFT 16 /* left justified,左对齐 */
#define SPECIAL 32 /* 0x or 0X for hex numbers */
#define SMALL 64 /* use 'abcdef' instead of 'ABCDEF' */
// 快速除法的宏
#define do_div(n, base) ({ \
int __res; \
__asm__("divl %4":"=a" (n),"=d" (__res):"0" (n),"1" (0),"r" (base)); \
__res; })
// 核心函数 number(数字转字符串的实现)
// 将整数 num 按 base 进制转换为字符串,根据 size(宽度)、precision(精度)和 type(格式标志)控制输出格式,
// 最终写入 str 指向的缓冲区,并返回更新后的指针。
static char *number(char *str, int num, int base /*转换的进制*/, int size, int precision /*精度控制*/, int type /*格式化标志,组合的格式化标志位*/)
{
char c, sign, tmp[36];
const char *digits = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
int i;
if (type & SMALL)
digits = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
if (type & LEFT)
type &= ~ZEROPAD;
if (base < 2 || base > 36) /*进制不满足控制范围*/
return 0;
c = (type & ZEROPAD) ? '0' : ' ';
if (type & SIGN && num < 0)
{
sign = '-';
num = -num;
}
else
sign = (type & PLUS) ? '+' : ((type & SPACE) ? ' ' : 0);
if (sign)
size--;
if (type & SPECIAL)
{
if (base == 16)
size -= 2;
else if (base == 8)
size--;
}
i = 0;
if (num == 0)
tmp[i++] = '0';
else
while (num != 0)
tmp[i++] = digits[do_div(num, base)];
if (i > precision)
precision = i;
size -= precision;
if (!(type & (ZEROPAD + LEFT)))
while (size-- > 0)
*str++ = ' ';
if (sign)
*str++ = sign;
if (type & SPECIAL)
{
if (base == 8)
*str++ = '0';
else if (base == 16)
{
*str++ = '0';
*str++ = digits[33];
}
}
if (!(type & LEFT))
while (size-- > 0)
*str++ = c;
while (i < precision--)
*str++ = '0';
while (i-- > 0)
*str++ = tmp[i];
while (size-- > 0)
*str++ = ' ';
return str;
}
/**
* func descp: 格式化输出函数,将可变参数列表按照格式化字符串的规则转换为字符串并存储到指定缓冲区。
* @param buf 输出缓冲区
* @param fmt 格式化字符串
* @param args 可变参数列表
* @return 输出字符串的长度
*/
int vsprintf(char *buf, const char *fmt, va_list args)
{
int len;
int i;
char *str;
char *s;
int *ip;
int flags; /* flags to number() */
int field_width; /* width of output field */
int precision; /* min. # of digits for integers; max
number of chars for from string */
int qualifier; /* 'h', 'l', or 'L' for integer fields */
for (str = buf; *fmt; ++fmt)
{
// 非格式化字符串,直接复制。要一直等到格式化字符(%开头的),才开始工作。
if (*fmt != '%')
{
*str++ = *fmt;
continue;
}
/* process flags */
flags = 0; // 格式化标志位
repeat:
++fmt; /* this also skips first '%' */
// 处理格式化标志位
switch (*fmt)
{
case '-':
flags |= LEFT;
goto repeat;
case '+':
flags |= PLUS;
goto repeat;
case ' ':
flags |= SPACE;
goto repeat;
case '#':
flags |= SPECIAL;
goto repeat;
case '0':
flags |= ZEROPAD;
goto repeat;
}
/* get field width */
field_width = -1;
if (is_digit(*fmt))
field_width = skip_atoi(&fmt);
else if (*fmt == '*')
{
/* it's the next argument */
field_width = va_arg(args, int);
if (field_width < 0)
{
field_width = -field_width;
flags |= LEFT;
}
}
/* get the precision */
precision = -1;
if (*fmt == '.')
{
++fmt;
if (is_digit(*fmt))
precision = skip_atoi(&fmt);
else if (*fmt == '*')
{
/* it's the next argument */
precision = va_arg(args, int);
}
if (precision < 0)
precision = 0;
}
/* get the conversion qualifier */
qualifier = -1;
if (*fmt == 'h' || *fmt == 'l' || *fmt == 'L')
{
qualifier = *fmt;
++fmt;
}
switch (*fmt)
{
// 对应的格式化字符是char类型
case 'c':
if (!(flags & LEFT))
while (--field_width > 0)
*str++ = ' ';
*str++ = (unsigned char)va_arg(args, int);
while (--field_width > 0)
*str++ = ' ';
break;
// 对应的格式化字符是char*类型
case 's':
s = va_arg(args, char *);
len = strlen(s);
if (precision < 0)
precision = len;
else if (len > precision)
len = precision;
if (!(flags & LEFT))
while (len < field_width--)
*str++ = ' ';
for (i = 0; i < len; ++i)
*str++ = *s++;
while (len < field_width--)
*str++ = ' ';
break;
// 对应的格式化字符是octal(8进制)类型
case 'o':
str = number(str, va_arg(args, unsigned long), 8,
field_width, precision, flags);
break;
// 对应的格式化字符是pointer类型
case 'p':
if (field_width == -1)
{
field_width = 8;
flags |= ZEROPAD;
}
str = number(str,
(unsigned long)va_arg(args, void *), 16,
field_width, precision, flags);
break;
// 对应的格式化字符是hex(16进制)类型
case 'x':
flags |= SMALL;
case 'X':
str = number(str, va_arg(args, unsigned long), 16,
field_width, precision, flags);
break;
// 对应的格式化字符是decimal(10进制)类型
case 'd':
// 对应的格式化字符是有符号数的decimal(10进制)类型,需要处理正负号
case 'i':
flags |= SIGN;
// 对应的格式化字符是unsigned decimal(10进制)类型
case 'u':
str = number(str, va_arg(args, unsigned long), 10,
field_width, precision, flags);
break;
// 对应的格式化字符是 n(记录输出长度)类型
// 功能:将当前已输出的字符数写入指针指向的整数变量
case 'n':
ip = va_arg(args, int *);
*ip = (str - buf);
break;
// 处理未知格式符或 % 本身
// 功能:若为 % 则直接输出,否则输出 % + 未知字符
default:
// 情况1:如果当前字符不是 %(即 % 后面跟了未知字符,如 %k 中的 'k')
if (*fmt != '%')
*str++ = '%'; // 先输出前面的 %
// 情况2:如果当前字符是 %(即 %% 中的第二个 %)
// 则不执行上面的 if,直接输出当前的 %
if (*fmt)
*str++ = *fmt; // 输出当前字符(未知字符或第二个 %)
else
--fmt; // 避免越界
break;
}
*str = '\0';/*标记内存中字符串结束*/
return str - buf; // 返回输出字符串的长度
}
3.亮点剖析
1.使用一个整数的各个位来表示标志位
#define ZEROPAD 1 /* pad with zero,零填充 */
#define SIGN 2 /* unsigned/signed long ,有符号/无符号长整数 */
#define PLUS 4 /* show plus,展示加号 */
#define SPACE 8 /* space if plus,展示空格 */
#define LEFT 16 /* left justified,左对齐 */
#define SPECIAL 32 /* 0x or 0X for hex numbers */
#define SMALL 64 /* use 'abcdef' instead of 'ABCDEF' */
这里是8为二进制数,用来分别控制字符串的格式化输出。这种用最小的单元(位),来完成某些状态的开关,是及其合适的!记住哦。!
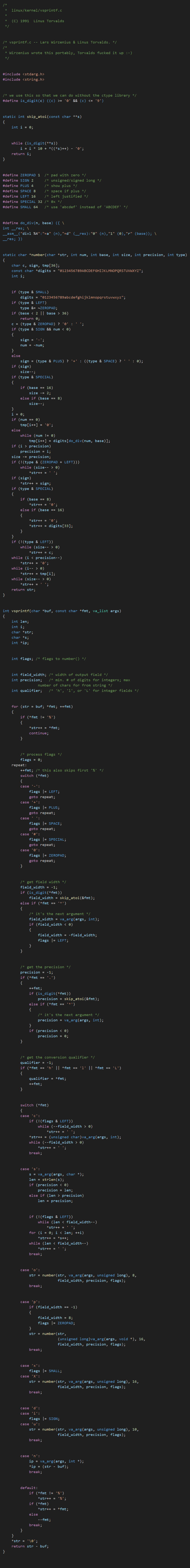
2.goto的巧妙运用
谁说goto就是最差的使用?在Linux内核中,goto的运用派上了大用场!
repeat:
++fmt; /* this also skips first '%' */
// 处理格式化标志位
switch (*fmt)
{
case '-':
flags |= LEFT;
goto repeat;
case '+':
flags |= PLUS;
goto repeat;
case ' ':
flags |= SPACE;
goto repeat;
case '#':
flags |= SPECIAL;
goto repeat;
case '0':
flags |= ZEROPAD;
goto repeat;
}
源码再剖析:

请问这段输出语句最终输出是?
结果:

这里唯一的思量就是这么多的-+,怎么解析呢?
其实看了这里的goto代码就明白了,这里-+只是置位的评判,不管多少个±,这里含义为±位都置位了,即左对齐了、显示+号了。那么显然就是输出对应格式的数据。
所以只有了解内核,才能彻底明白C。
4.源码源版本
/*
* linux/kernel/vsprintf.c
*
* (C) 1991 Linus Torvalds
*/
/* vsprintf.c -- Lars Wirzenius & Linus Torvalds. */
/*
* Wirzenius wrote this portably, Torvalds fucked it up :-)
*/
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
/* we use this so that we can do without the ctype library */
#define is_digit(c) ((c) >= '0' && (c) <= '9')
static int skip_atoi(const char **s)
{
int i = 0;
while (is_digit(**s))
i = i * 10 + *((*s)++) - '0';
return i;
}
#define ZEROPAD 1 /* pad with zero */
#define SIGN 2 /* unsigned/signed long */
#define PLUS 4 /* show plus */
#define SPACE 8 /* space if plus */
#define LEFT 16 /* left justified */
#define SPECIAL 32 /* 0x */
#define SMALL 64 /* use 'abcdef' instead of 'ABCDEF' */
#define do_div(n, base) ({ \
int __res; \
__asm__("divl %4":"=a" (n),"=d" (__res):"0" (n),"1" (0),"r" (base)); \
__res; })
static char *number(char *str, int num, int base, int size, int precision, int type)
{
char c, sign, tmp[36];
const char *digits = "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
int i;
if (type & SMALL)
digits = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
if (type & LEFT)
type &= ~ZEROPAD;
if (base < 2 || base > 36)
return 0;
c = (type & ZEROPAD) ? '0' : ' ';
if (type & SIGN && num < 0)
{
sign = '-';
num = -num;
}
else
sign = (type & PLUS) ? '+' : ((type & SPACE) ? ' ' : 0);
if (sign)
size--;
if (type & SPECIAL)
{
if (base == 16)
size -= 2;
else if (base == 8)
size--;
}
i = 0;
if (num == 0)
tmp[i++] = '0';
else
while (num != 0)
tmp[i++] = digits[do_div(num, base)];
if (i > precision)
precision = i;
size -= precision;
if (!(type & (ZEROPAD + LEFT)))
while (size-- > 0)
*str++ = ' ';
if (sign)
*str++ = sign;
if (type & SPECIAL)
{
if (base == 8)
*str++ = '0';
else if (base == 16)
{
*str++ = '0';
*str++ = digits[33];
}
}
if (!(type & LEFT))
while (size-- > 0)
*str++ = c;
while (i < precision--)
*str++ = '0';
while (i-- > 0)
*str++ = tmp[i];
while (size-- > 0)
*str++ = ' ';
return str;
}
int vsprintf(char *buf, const char *fmt, va_list args)
{
int len;
int i;
char *str;
char *s;
int *ip;
int flags; /* flags to number() */
int field_width; /* width of output field */
int precision; /* min. # of digits for integers; max
number of chars for from string */
int qualifier; /* 'h', 'l', or 'L' for integer fields */
for (str = buf; *fmt; ++fmt)
{
if (*fmt != '%')
{
*str++ = *fmt;
continue;
}
/* process flags */
flags = 0;
repeat:
++fmt; /* this also skips first '%' */
switch (*fmt)
{
case '-':
flags |= LEFT;
goto repeat;
case '+':
flags |= PLUS;
goto repeat;
case ' ':
flags |= SPACE;
goto repeat;
case '#':
flags |= SPECIAL;
goto repeat;
case '0':
flags |= ZEROPAD;
goto repeat;
}
/* get field width */
field_width = -1;
if (is_digit(*fmt))
field_width = skip_atoi(&fmt);
else if (*fmt == '*')
{
/* it's the next argument */
field_width = va_arg(args, int);
if (field_width < 0)
{
field_width = -field_width;
flags |= LEFT;
}
}
/* get the precision */
precision = -1;
if (*fmt == '.')
{
++fmt;
if (is_digit(*fmt))
precision = skip_atoi(&fmt);
else if (*fmt == '*')
{
/* it's the next argument */
precision = va_arg(args, int);
}
if (precision < 0)
precision = 0;
}
/* get the conversion qualifier */
qualifier = -1;
if (*fmt == 'h' || *fmt == 'l' || *fmt == 'L')
{
qualifier = *fmt;
++fmt;
}
switch (*fmt)
{
case 'c':
if (!(flags & LEFT))
while (--field_width > 0)
*str++ = ' ';
*str++ = (unsigned char)va_arg(args, int);
while (--field_width > 0)
*str++ = ' ';
break;
case 's':
s = va_arg(args, char *);
len = strlen(s);
if (precision < 0)
precision = len;
else if (len > precision)
len = precision;
if (!(flags & LEFT))
while (len < field_width--)
*str++ = ' ';
for (i = 0; i < len; ++i)
*str++ = *s++;
while (len < field_width--)
*str++ = ' ';
break;
case 'o':
str = number(str, va_arg(args, unsigned long), 8,
field_width, precision, flags);
break;
case 'p':
if (field_width == -1)
{
field_width = 8;
flags |= ZEROPAD;
}
str = number(str,
(unsigned long)va_arg(args, void *), 16,
field_width, precision, flags);
break;
case 'x':
flags |= SMALL;
case 'X':
str = number(str, va_arg(args, unsigned long), 16,
field_width, precision, flags);
break;
case 'd':
case 'i':
flags |= SIGN;
case 'u':
str = number(str, va_arg(args, unsigned long), 10,
field_width, precision, flags);
break;
case 'n':
ip = va_arg(args, int *);
*ip = (str - buf);
break;
default:
if (*fmt != '%')
*str++ = '%';
if (*fmt)
*str++ = *fmt;
else
--fmt;
break;
}
}
*str = '\0';
return str - buf;
}
5.源码图像版本

😉【C语言】C Token(C89 C99 C11)
😉【C语言】指针基础
😉【C语言】数组基础
😉【C语言】结构体对齐
😉【C语言】华为C语言进阶测试
😉【C语言】触发刷新到磁盘的方式总结
😉【C语言】C语言文件操作的mode详解
😉【C语言】C语言文件知识全讲解
😉【C语言】从extern到头文件包含的最优实践
😉【C语言】C语言的关键字与重载机制
😉【C语言】长字符串的2种处理方式
😉【C语言】C语言嵌入汇编程序
😉【C陷阱与缺陷】-1-词法陷阱
😉【C陷阱与缺陷】-2-语法陷阱
😉【C陷阱与缺陷】-3-语义陷阱
专注讲解Linux中的常用命令,共计发布100+文章。
本系列将精讲Linux0.11内核中的每一个文件,共计会发布100+文章。
和Linux内核102系列不同,本系列将会从全局描绘Linux内核的各个模块,而非逐行源码分析,适合想对Linux系统有宏观了解的家人阅读。
😉【Linux】Linux概述1-linux对物理内存的使用
关于小希
😉嘿嘿嘿,我是小希,专注Linux内核领域,同时讲解C语言、汇编等知识。
我的微信:C_Linux_Cloud,期待与您学习交流!

加微信请备注哦
小希的座右铭:
别看简单,简单也是难。别看难,难也是简单。我的文章都是讲述简单的知识,如果你喜欢这种风格:
下一期想看什么?在评论区留言吧!我们下期见!

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








