131.分割回文串
给定一个字符串 s,将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是回文串。
返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
示例: 输入: "aab" 输出: [ ["aa","b"], ["a","a","b"] ]
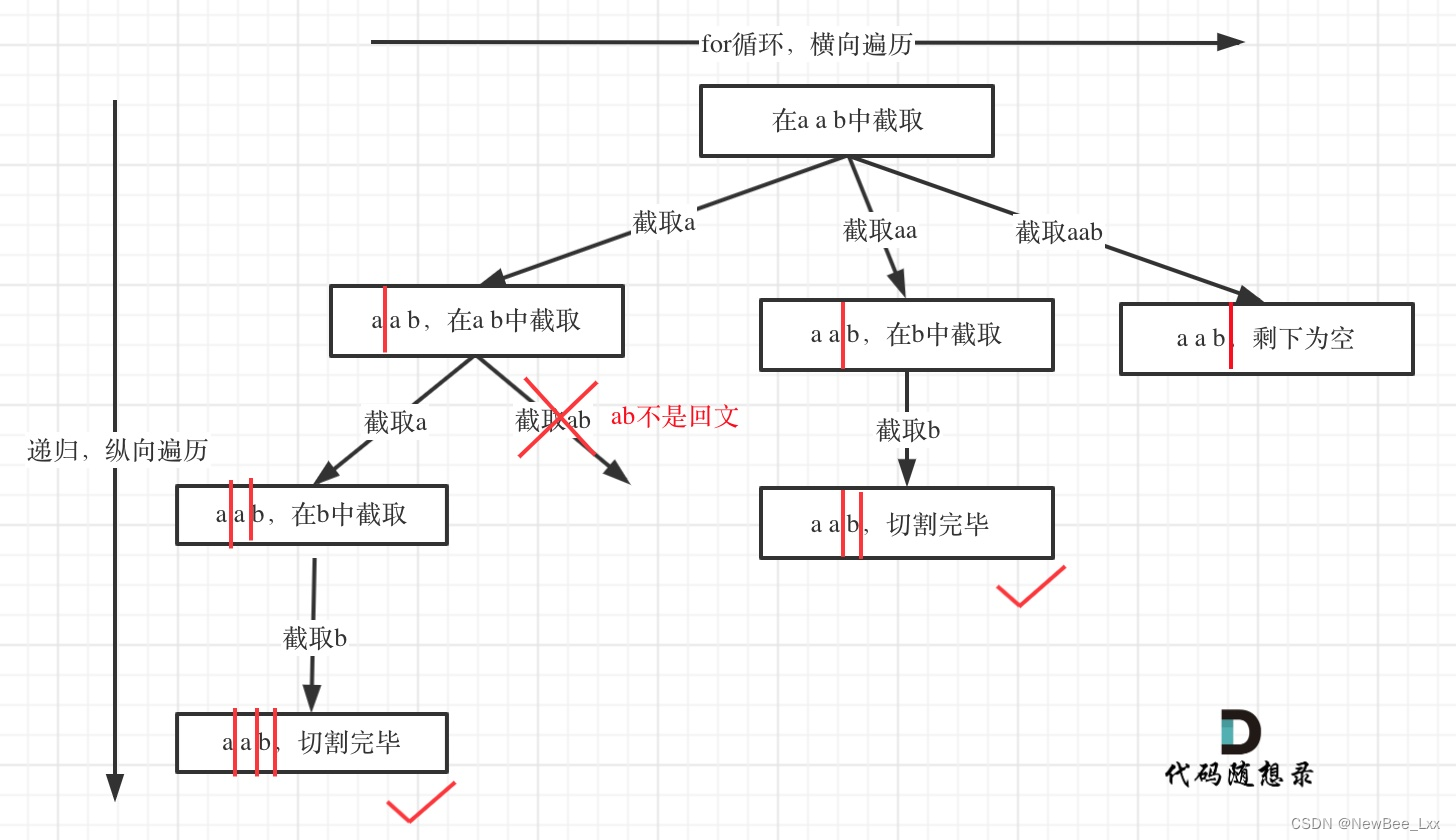
idnex就是分割线,如果分割线大于等于整个字符串的长度了就说明找到一组分割方案了
首先看看分割出来的字符串是不是回文串,不是就跳过本次循环,是就把个回文串塞进path里面
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<string>> result;
vector<string> path; // 放已经回文的子串
void backtracking (const string& s, int startIndex) {
// 如果起始位置已经大于s的大小,说明已经找到了一组分割方案了
if (startIndex >= s.size()) {
result.push_back(path);
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (isPalindrome(s, startIndex, i)) { // 是回文子串
// 获取[startIndex,i]在s中的子串
string str = s.substr(startIndex, i - startIndex + 1);
path.push_back(str);
} else { // 不是回文,跳过
continue;
}
backtracking(s, i + 1); // 寻找i+1为起始位置的子串
path.pop_back(); // 回溯过程,弹出本次已经添加的子串
}
}
bool isPalindrome(const string& s, int start, int end) {
for (int i = start, j = end; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (s[i] != s[j]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public:
vector<vector<string>> partition(string s) {
result.clear();
path.clear();
backtracking(s, 0);
return result;
}
};93.复原IP地址
给定一个只包含数字的字符串,复原它并返回所有可能的 IP 地址格式。
有效的 IP 地址 正好由四个整数(每个整数位于 0 到 255 之间组成,且不能含有前导 0),整数之间用 '.' 分隔。
例如:"0.1.2.201" 和 "192.168.1.1" 是 有效的 IP 地址,但是 "0.011.255.245"、"192.168.1.312" 和 "192.168@1.1" 是 无效的 IP 地址。
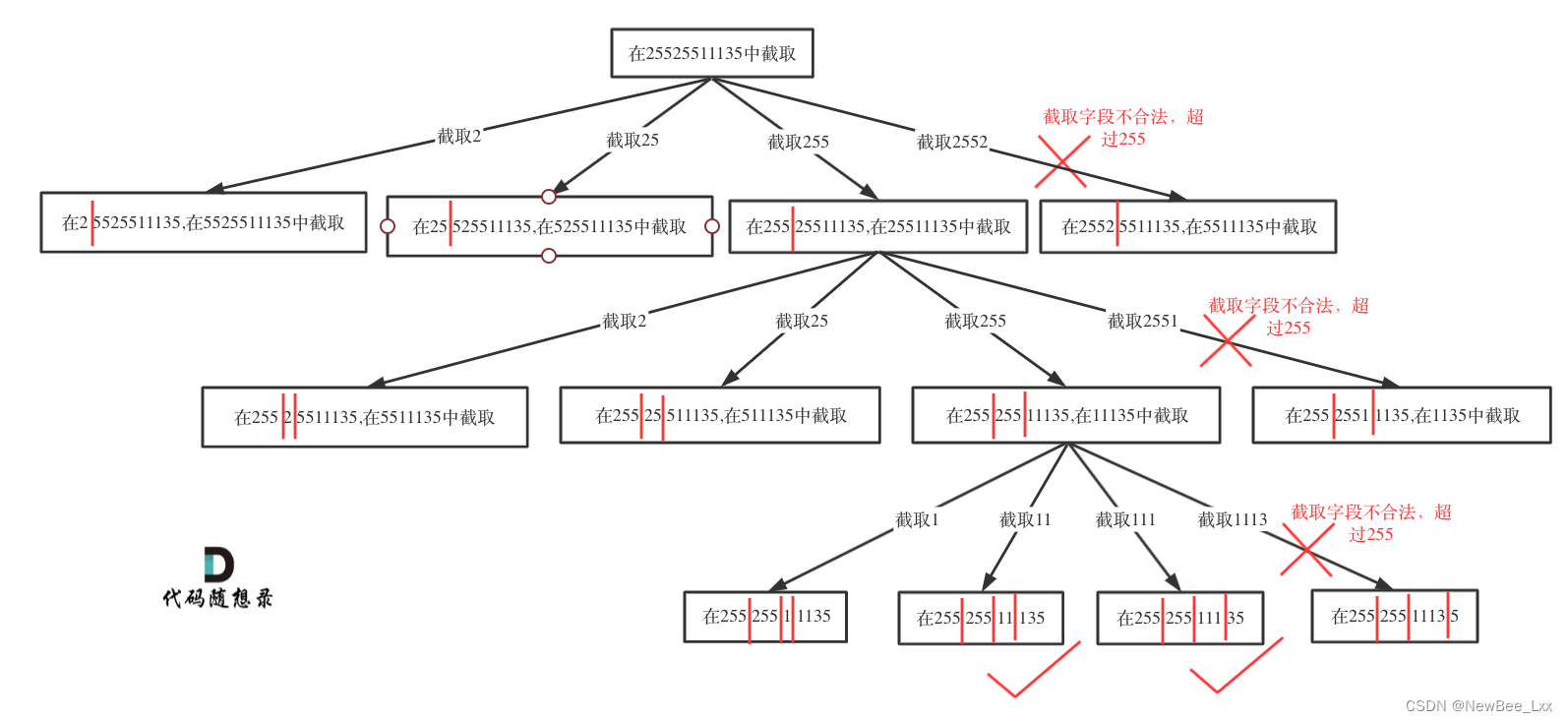
终止条件:
点变成了三个,说明前三段合法,只需检查最后一段是否合法
合法就将整个字符串push进去
依旧是模板循环,判断index这段是否合法,合法就在这段的后面加点,点的数量加一,然后回溯,
回溯中i+2是因为相比正常情况多了一个点,
class Solution {
private:
vector<string> result;// 记录结果
// startIndex: 搜索的起始位置,pointNum:添加逗点的数量
void backtracking(string& s, int startIndex, int pointNum) {
if (pointNum == 3) { // 逗点数量为3时,分隔结束
// 判断第四段子字符串是否合法,如果合法就放进result中
if (isValid(s, startIndex, s.size() - 1)) {
result.push_back(s);
}
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (isValid(s, startIndex, i)) { // 判断 [startIndex,i] 这个区间的子串是否合法
s.insert(s.begin() + i + 1 , '.'); // 在i的后面插入一个逗点
pointNum++;
backtracking(s, i + 2, pointNum); // 插入逗点之后下一个子串的起始位置为i+2
pointNum--; // 回溯
s.erase(s.begin() + i + 1); // 回溯删掉逗点
} else break; // 不合法,直接结束本层循环
}
}
// 判断字符串s在左闭又闭区间[start, end]所组成的数字是否合法
bool isValid(const string& s, int start, int end) {
if (start > end) {
return false;
}
if (s[start] == '0' && start != end) { // 0开头的数字不合法
return false;
}
int num = 0;
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
if (s[i] > '9' || s[i] < '0') { // 遇到非数字字符不合法
return false;
}
num = num * 10 + (s[i] - '0');
if (num > 255) { // 如果大于255了不合法
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public:
vector<string> restoreIpAddresses(string s) {
result.clear();
if (s.size() < 4 || s.size() > 12) return result; // 算是剪枝了
backtracking(s, 0, 0);
return result;
}
};78.子集
给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
示例: 输入: nums = [1,2,3] 输出: [ [3], [1], [2], [1,2,3], [1,3], [2,3], [1,2], [] ]
找树的所有节点
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> path;
void backtracking(vector<int>& nums, int startIndex) {
result.push_back(path); // 收集子集,要放在终止添加的上面,否则会漏掉自己
if (startIndex >= nums.size()) { // 终止条件可以不加
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.size(); i++) {
path.push_back(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums, i + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {
result.clear();
path.clear();
backtracking(nums, 0);
return result;
}
};90.子集II
给定一个可能包含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
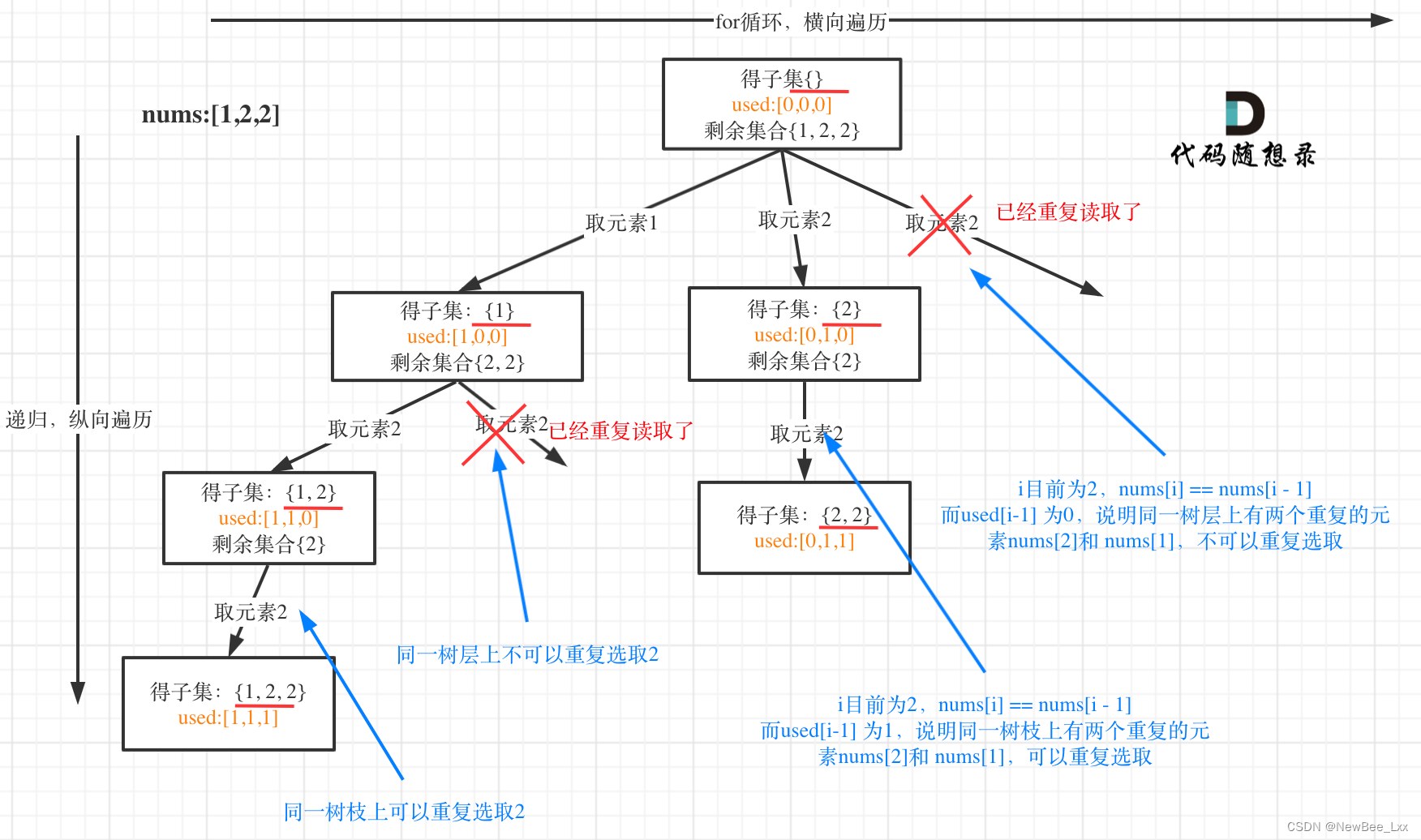
上两道题的组合题
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> path;
void backtracking(vector<int>& nums, int startIndex, vector<bool>& used) {
result.push_back(path);
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.size(); i++) {
// used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树枝candidates[i - 1]使用过
// used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层candidates[i - 1]使用过
// 而我们要对同一树层使用过的元素进行跳过
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {
continue;
}
path.push_back(nums[i]);
used[i] = true;
backtracking(nums, i + 1, used);
used[i] = false;
path.pop_back();
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsetsWithDup(vector<int>& nums) {
result.clear();
path.clear();
vector<bool> used(nums.size(), false);
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // 去重需要排序
backtracking(nums, 0, used);
return result;
}
};491.递增子序列
给定一个整型数组, 你的任务是找到所有该数组的递增子序列,递增子序列的长度至少是2。
示例:
- 输入: [4, 6, 7, 7]
- 输出: [[4, 6], [4, 7], [4, 6, 7], [4, 6, 7, 7], [6, 7], [6, 7, 7], [7,7], [4,7,7]]
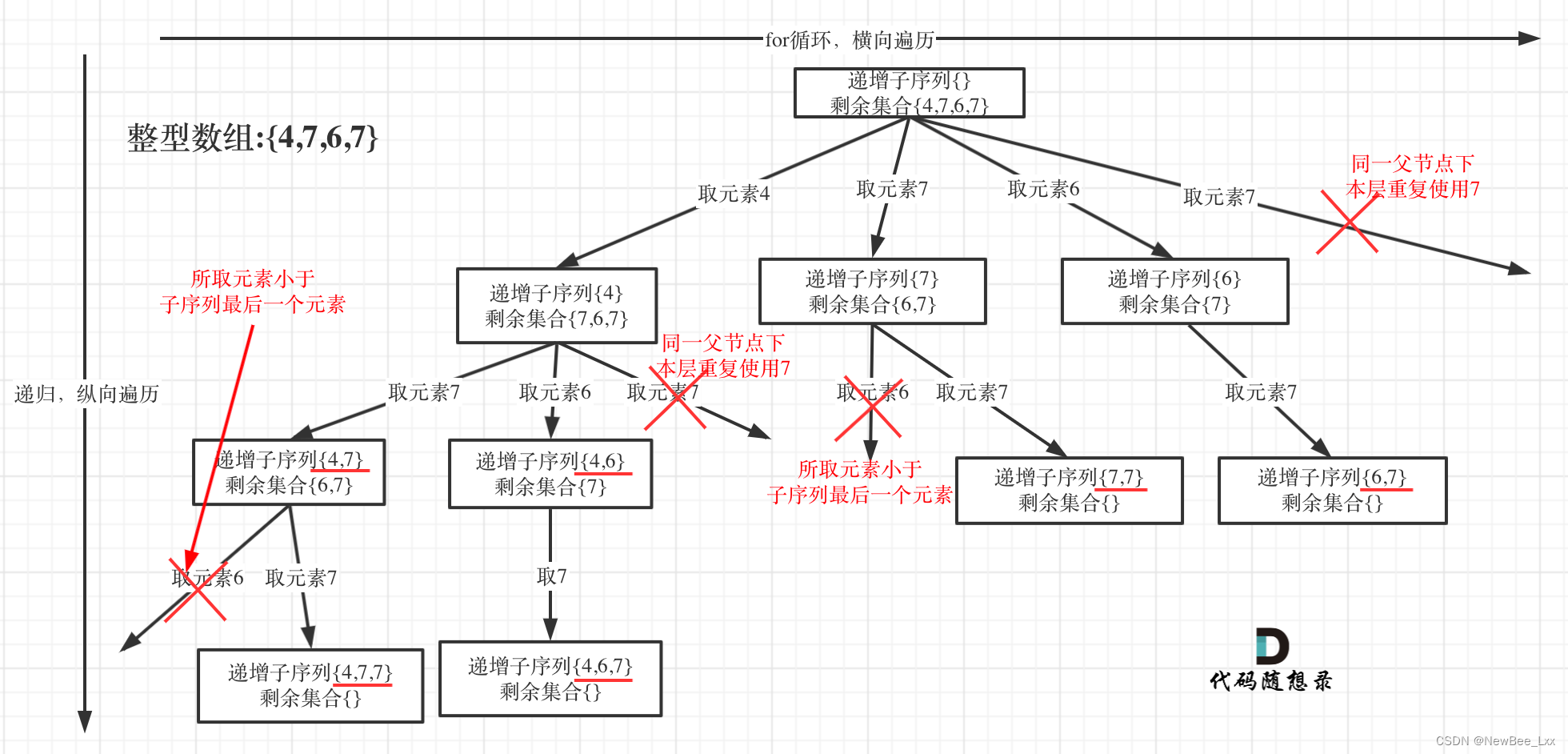
大小大于1就直接塞reseult里,不能进入的条件:下一个元素比path里的最后一个数小,数层重复,直接contnue
// 版本一
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> path;
void backtracking(vector<int>& nums, int startIndex) {
if (path.size() > 1) {
result.push_back(path);
// 注意这里不要加return,要取树上的节点
}
unordered_set<int> uset; // 使用set对本层元素进行去重
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if ((!path.empty() && nums[i] < path.back())
|| uset.find(nums[i]) != uset.end()) {
continue;
}
uset.insert(nums[i]); // 记录这个元素在本层用过了,本层后面不能再用了
path.push_back(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums, i + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> findSubsequences(vector<int>& nums) {
result.clear();
path.clear();
backtracking(nums, 0);
return result;
}
};







 本文介绍了几个编程问题,涉及回文串分割、IP地址复原、整数数组子集查找和递增子序列的查找,涉及回溯算法和字符串处理技巧。
本文介绍了几个编程问题,涉及回文串分割、IP地址复原、整数数组子集查找和递增子序列的查找,涉及回溯算法和字符串处理技巧。














 829
829











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








